Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: ![]() Databricks SQL
Databricks SQL ![]() Databricks Runtime 10.4 LTS and above
Databricks Runtime 10.4 LTS and above ![]() Unity Catalog only
Unity Catalog only
In the SYSTEM catalog, the INFORMATION_SCHEMA is a SQL standard schema that provides metadata about objects across all catalogs in the metastore. It does not contain metadata about hive_metastore objects.
Separately, each catalog created in Unity Catalog also automatically includes an information_schema that describes metadata about objects in that catalog only.
Both types of information schemas automatically filter results to include only the objects you have Unity Catalog privileges to access. This behavior differs from other Azure Databricks system tables. See How information schema system tables handle permissions.
The purpose of the information schema is to provide a SQL-based, privilege-aware, and self-describing API for accessing catalog metadata.
How information schema system tables handle permissions
system.information_schema differs from other system tables in that it implements automatic filtering. This means you see only the objects (catalogs, schemas, tables, columns, etc.) that you have privileges to access in Unity Catalog. If your privileges change, what you see in the information schema changes accordingly. For example, when you query information_schema.tables, only rows for tables you have permission to see are returned.
Like all other system tables, you need explicit USE and SELECT permissions to access and query from the information schema.
Entity relationship diagram of the information schema
The following entity relationship (ER) diagram provides an overview of a subset of information schema views and how they relate to each other.
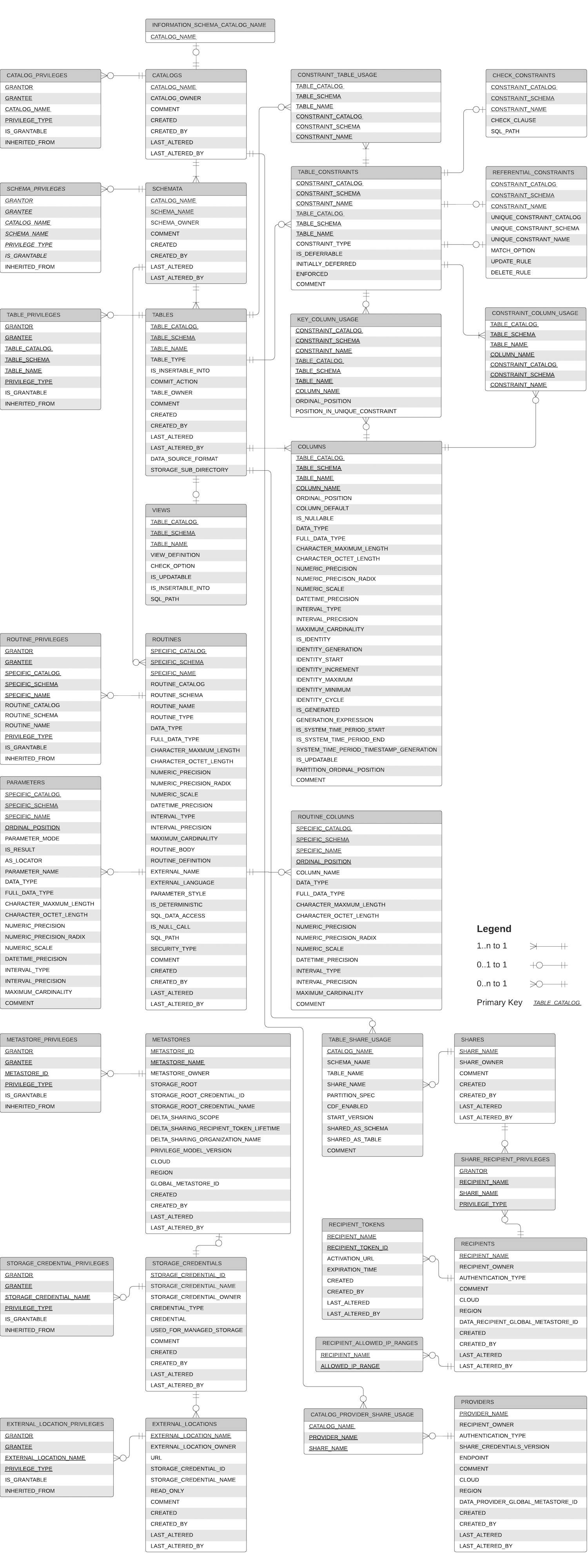
Information schema views
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CATALOG_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the catalogs. |
| CATALOG_PROVIDER_SHARE_USAGE | Describes provider share mounted onto catalogs. |
| CATALOG_TAGS | Contains tags that have been applied to the catalogs. |
| CATALOGS | Describes catalogs. |
| CHECK_CONSTRAINTS | Reserved for future use. |
| COLUMN_MASKS | Describes column masks on table columns in the catalog. |
| COLUMN_TAGS | Contains column tagging metadata within a table. |
| COLUMNS | Describes columns of tables and views in the catalog. |
| CONNECTION_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the foreign connections. |
| CONNECTIONS | Describes foreign connections. |
| CONSTRAINT_COLUMN_USAGE | Describes the constraints referencing columns in the catalog. |
| CONSTRAINT_TABLE_USAGE | Describes the constraints referencing tables in the catalog. |
| CREDENTIAL_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the credentials. |
| CREDENTIALS | Describes credentials. |
| EXTERNAL_LOCATION_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the external locations. |
| EXTERNAL_LOCATIONS | Describes external locations. |
| INFORMATION_SCHEMA_CATALOG_NAME | Returns the name of this information schema's catalog. |
| KEY_COLUMN_USAGE | Lists the columns of the primary or foreign key constraints within the catalog. |
| METASTORE_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the current metastore. |
| METASTORES | Describes the current metastore. |
| PARAMETERS | Describes parameters of routines (functions) in the catalog. |
| PROVIDERS | Describes providers. |
| RECIPIENT_ALLOWED_IP_RANGES | Lists allowed IP ranges for recipients. |
| RECIPIENT_TOKENS | Lists tokens for recipients. |
| RECIPIENTS | Describes recipients. |
| REFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTS | Describes referential (foreign key) constraints defined in the catalog. |
| ROUTINE_COLUMNS | Describes result columns of table valued functions. |
| ROUTINE_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the routines in the catalog. |
| ROUTINES | Describes routines (functions) in the catalog. |
| ROW_FILTERS | Describes row filters on tables in the catalog. |
| SCHEMA_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the schemas in the catalog. |
| SCHEMA_TAGS | Contains schema tagging metadata within the schema. |
| SCHEMA_SHARE_USAGE | Describes the schemas referenced in shares. |
| SCHEMATA | Describes schemas within the catalog. |
| SHARE_RECIPIENT_PRIVILEGES | Describes the recipients granted access to shares. |
| SHARES | Describes shares. |
| STORAGE_CREDENTIAL_PRIVILEGES | [Deprecated] Lists principals that have privileges on the storage credentials. |
| STORAGE_CREDENTIALS | [Deprecated] Describes storage credentials. |
| TABLE_CONSTRAINTS | Describes metadata for all primary and foreign key constraints within the catalog. |
| TABLE_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the tables and views in the catalog. |
| TABLE_SHARE_USAGE | Describes the tables referenced in shares. |
| TABLE_TAGS | Contains table tagging metadata within a table. |
| TABLES | Describes tables and views defined within the catalog. |
| VIEWS | Describes view specific information about the views in the catalog. |
| VOLUMES | Describes volumes defined in the catalog. |
| VOLUME_PRIVILEGES | Lists principals that have privileges on the volumes in the catalog. |
| VOLUME_TAGS | Contains volume tagging metadata applied to a volume. |
Notes
- The information schema implements privilege-aware filtering. You automatically see only the objects you have Unity Catalog permissions to access. See How information schema system tables handle permissions.
- A manual sync using
REPAIR TABLEmay be required for some catalog metadata changes to be reflected in the information schema. For more information, see REPAIR TABLE. - All identifiers except column and tag names are stored in the information schema as lowercase
STRING. For query performance, avoid using functions likeLOWER()orUPPER()on the identifier column. Instead, compare identifiers directly using lowercase values. - To prevent query timeouts, apply selective filters when querying the information schema (e.g.
WHERE table_catalog = 'main' AND table_schema = 'default'). Refer to the documentation above for a full list of columns that can be used as filters for each Information Schema table.- Note that
LIMITpushdown is not currently supported, so although it can truncate the results it will not improve performance.
- Note that
Examples
> SELECT table_name, column_name
FROM information_schema.columns
WHERE data_type = 'DOUBLE'
AND table_schema = 'information_schema';
The following are examples of workflows that use the system level information schema tables.
If you want to view all tables that have been created in the last 24 hours, your query could look like the following.
> SELECT table_name, table_owner, created_by, last_altered, last_altered_by, table_catalog
FROM system.information_schema.tables
WHERE datediff(now(), last_altered) < 1;
If you want to view how many tables you have in each schema, consider the following example.
> SELECT table_schema, count(table_name)
FROM system.information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = 'tpch'
GROUP BY table_schema
ORDER BY 2 DESC