Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
When you access file data using the Azure portal, the portal makes requests to Azure Files behind the scenes. These requests can be authorized using either your Microsoft Entra account or the storage account access key. The portal indicates which method you're using, and enables you to switch between the two if you have the appropriate permissions.
Important
Accessing a file share using storage account keys carries inherent security risks, so always authenticate with Microsoft Entra when possible. For information on how to protect and manage your keys, see Manage storage account access keys.
You can also specify how to authorize an individual file share operation in the Azure portal. By default, the portal uses whichever method you're already using to authorize all file shares, but you have the option to change this setting for individual file shares.
Applies to
| Management model | Billing model | Media tier | Redundancy | SMB | NFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Geo (GRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | GeoZone (GZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v1 | SSD (premium) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v1 | SSD (premium) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Geo (GRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | GeoZone (GZRS) |
Permissions needed to access file data
Depending on how you want to authorize access to file data in the Azure portal, you'll need specific permissions. In most cases, these permissions are provided via Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC).
Use your Microsoft Entra account (recommended)
To access file data from the Azure portal using your Microsoft Entra account, both of the following statements must be true:
- You're assigned either a built-in or custom role that provides access to file data.
- You're assigned the Azure Resource Manager Reader role, at a minimum, scoped to the level of the storage account or higher. The Reader role grants the most restricted permissions, but another Azure Resource Manager role that grants access to storage account management resources is also acceptable.
The Azure Resource Manager Reader role permits users to view storage account resources, but not modify them. It doesn't provide read permissions to data in Azure Storage, but only to account management resources. The Reader role is necessary so that users can navigate to file shares in the Azure portal.
There are two new built-in roles that have the required permissions to access file data with OAuth:
For information about the built-in roles that support access to file data, see Access Azure file shares using Microsoft Entra ID with Azure Files OAuth over REST.
Note
The Storage File Data Privileged Contributor role has permissions to read, write, delete, and modify ACLs/NTFS permissions on files/directories in Azure file shares. Modifying ACLs/NTFS permissions isn't supported via the Azure portal.
Custom roles can support different combinations of the same permissions provided by the built-in roles. For more information about creating Azure custom roles, see Azure custom roles and Understand role definitions for Azure resources.
Use the storage account access key (not recommended)
To access file data with the storage account access key, you must have an Azure role assigned to you that includes the Azure RBAC action Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action. This Azure role may be a built-in role or a custom role. Built-in roles that support Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action include the following, listed in order from least to greatest permissions:
- The Reader and Data Access role
- The Storage Account Contributor role
- The Azure Resource Manager Contributor role
- The Azure Resource Manager Owner role
When you attempt to access file data in the Azure portal, the portal first checks whether you've been assigned a role with Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action. If you've been assigned a role with this action, then the portal uses the storage account key for accessing file data. If you haven't been assigned a role with this action, then the portal attempts to access data using your Microsoft Entra account.
Important
When a storage account is locked with an Azure Resource Manager ReadOnly lock, the List Keys operation isn't permitted for that storage account. List Keys is a POST operation, and all POST operations are prevented when a ReadOnly lock is configured for the account. For this reason, when the account is locked with a ReadOnly lock, users must use Microsoft Entra credentials to access file data in the portal. For information about accessing file data in the Azure portal with Microsoft Entra ID, see Use your Microsoft Entra account.
Note
The classic subscription administrator roles Service Administrator and Co-Administrator include the equivalent of the Azure Resource Manager Owner role. The Owner role includes all actions, including the Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listkeys/action, so a user with one of these administrative roles can also access file data with the storage account key. For more information, see Azure roles, Microsoft Entra roles, and classic subscription administrator roles.
Specify how to authorize operations on a specific file share
You can change the authentication method for individual file shares. By default, the portal uses the current authentication method. To determine the current authentication method, follow these steps.
- Navigate to your storage account in the Azure portal.
- In the service menu, under Data storage, select File shares.
- Select a file share.
- Select Browse.
- The Authentication method indicates whether you're currently using the storage account access key or your Microsoft Entra account to authenticate and authorize file share operations. If you're currently authenticating using the storage account access key, you'll see Access Key specified as the authentication method, as in the following image. If you're authenticating using your Microsoft Entra account, you'll see Microsoft Entra user account specified instead.
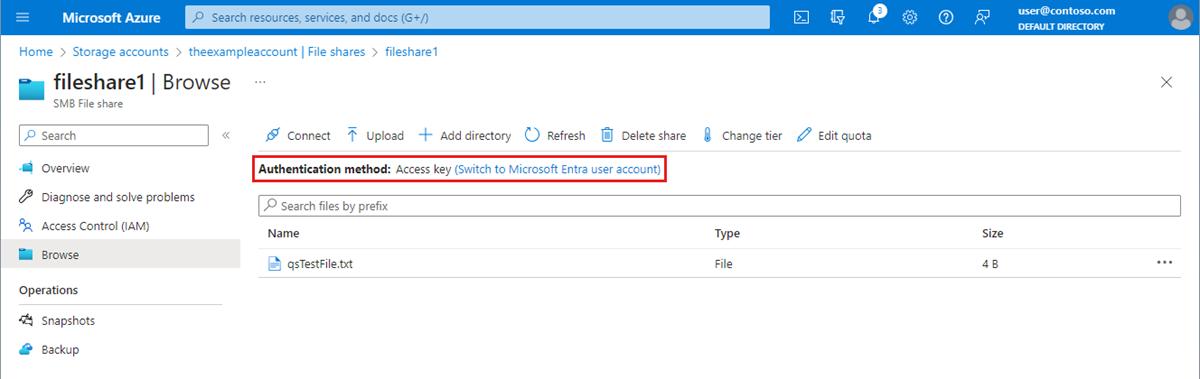
Authenticate with your Microsoft Entra account (recommended)
To switch to using your Microsoft Entra account, select the link highlighted in the image that says Switch to Microsoft Entra user account. If you have the appropriate permissions via the Azure roles that are assigned to you, you'll be able to proceed. However, if you lack the necessary permissions, you'll see an error message that you don't have permissions to list the data using your user account with Microsoft Entra ID.
Two additional RBAC permissions are required to use your Microsoft Entra account:
Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/fileServices/readFileBackupSemantics/actionMicrosoft.Storage/storageAccounts/fileServices/writeFileBackupSemantics/action
No file shares will appear in the list if your Microsoft Entra account lacks permissions to view them.
Authenticate with the storage account access key (not recommended)
To switch to using the account access key, select the link that says Switch to access key. If you have access to the storage account key, then you'll be able to proceed. However, if you lack access to the account key, you'll see an error message that you don't have permissions to use the access key to list data.
No file shares appear in the list if you don't have access to the storage account access key.
Default to Microsoft Entra authorization in the Azure portal
When you create a new storage account, you can specify that the Azure portal will default to authorization with Microsoft Entra ID when a user navigates to file data. You can also configure this setting for an existing storage account. This setting specifies the default authorization method only. Keep in mind that a user can override this setting and choose to authorize data access with the storage account key.
To specify that the portal will use Microsoft Entra authorization by default for data access when you create a storage account, follow these steps:
Create a new storage account, following the instructions in Create a storage account.
On the Advanced tab, in the Security section, check the box next to Default to Microsoft Entra authorization in the Azure portal.
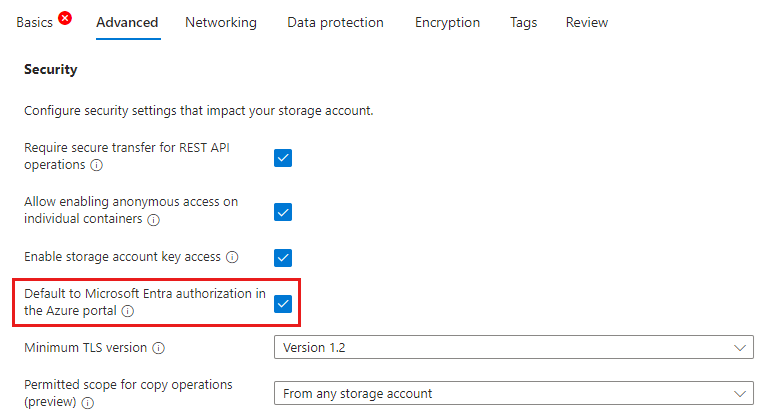
Select Review + create to run validation and create the storage account.
To update this setting for an existing storage account, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the storage account overview in the Azure portal.
- Under Settings, select Configuration.
- Set Default to Microsoft Entra authorization in the Azure portal to Enabled.