Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article covers building a solution where you encrypt managed disks with customer-managed keys using Azure Key Vaults stored in a different Microsoft Entra tenant. This configuration can be ideal for several scenarios, one example being Azure support for service providers that want to offer bring-your-own encryption keys to their customers where resources from the service provider's tenant are encrypted with keys from their customer's tenant.
A disk encryption set with federated identity in a cross-tenant CMK workflow spans service provider/ISV tenant resources (disk encryption set, managed identities, and app registrations) and customer tenant resources (enterprise apps, user role assignments, and key vault). In this case, the source Azure resource is the service provider's disk encryption set.
If you have questions about cross-tenant customer-managed keys with managed disks, email crosstenantcmkvteam@service.microsoft.com.
Limitations
- Managed Disks and the customer's Key Vault must be in the same Azure region, but they can be in different subscriptions.
Preview - Ultra Disk and Premium SSD v2
This configuration is also available for Ultra Disks and Premium SSD v2 disks, as a preview configuration, in select regions.
Sign up for the preview using either the PowerShell:
Register-AzProviderFeature -FeatureName UserAssignedIdentityForDirectDriveDisks -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.Compute
Register-AzProviderFeature -FeatureName CrossTenantCMKForDirectDriveDisks -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.Compute
Or the CLI:
az feature register --name UserAssignedIdentityForDirectDriveDisks --namespace Microsoft.Compute
az feature register --name CrossTenantCMKForDirectDriveDisks --namespace Microsoft.Compute
Preview regional availability
The preview for Ultra Disks and Premium SSD v2 disks is currently only available in the following regions:
- Australia East
- Southeast Asia
- Canada Central
- North Europe
- France Central
- Germany West Central
- Korea Central
- Sweden Central
- UK South
- West US
- Central US
About cross-tenant customer-managed keys
Many service providers building Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings on Azure want to offer their customers the option to manage their own encryption keys. Customer-managed keys allow a service provider to encrypt the customer's data using an encryption key that is managed by the service provider's customer and that isn't accessible to the service provider. In Azure, the service provider's customer can use Azure Key Vault to manage their encryption keys in their own Microsoft Entra tenant and subscription.
Azure platform services and resources that are owned by the service provider and that reside in the service provider's tenant require access to the key from the customer's tenant to perform the encryption/decryption operations.
The image below shows a data encryption at rest with federated identity in a cross-tenant CMK workflow spanning a service provider and its customer.
In the example above, there are two Microsoft Entra tenants: an independent service provider's tenant (Tenant 1), and a customer's tenant (Tenant 2). Tenant 1 hosts Azure platform services and Tenant 2 hosts the customer's key vault.
A multitenant application registration is created by the service provider in Tenant 1. A federated identity credential is created on this application using a user-assigned managed identity. Then, the name and application ID of the app is shared with the customer.
A user with the appropriate permissions installs the service provider's application in the customer tenant, Tenant 2. A user then grants the service principal associated with the installed application access to the customer's key vault. The customer also stores the encryption key, or customer-managed key, in the key vault. The customer shares the key location (the URL of the key) with the service provider.
The service provider now has:
- An application ID for a multitenant application installed in the customer's tenant, which has been granted access to the customer-managed key.
- A managed identity configured as the credential on the multitenant application.
- The location of the key in the customer's key vault.
With these three parameters, the service provider provisions Azure resources in Tenant 1 that can be encrypted with the customer-managed key in Tenant 2.
Let's divide the above end-to-end solution into three phases:
- The service provider configures identities.
- The customer grants the service provider's multitenant app access to an encryption key in Azure Key Vault.
- The service provider encrypts data in an Azure resource using the CMK.
Operations in Phase 1 would be a one-time setup for most service provider applications. Operations in Phases 2 and 3 would repeat for each customer.
Phase 1 - The service provider configures a Microsoft Entra application
| Step | Description | Minimum role in Azure RBAC | Minimum role in Microsoft Entra RBAC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Create a new multitenant Microsoft Entra application registration or start with an existing application registration. Note the application ID (client ID) of the application registration using Azure portal, Microsoft Graph API, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI | None | Application Developer |
| 2. | Create a user-assigned managed identity (to be used as a Federated Identity Credential). Azure portal / Azure CLI / Azure PowerShell/ Azure Resource Manager Templates |
Managed identity contributor | None |
| 3. | Configure user-assigned managed identity as a federated identity credential on the application, so that it can impersonate the identity of the application. Graph API reference/ Azure portal/ Azure CLI/ Azure PowerShell |
None | Owner of the application |
| 4. | Share the application name and application ID with the customer, so that they can install and authorize the application. | None | None |
Considerations for service providers
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates aren't recommended for creating Microsoft Entra applications.
- The same multitenant application can be used to access keys in any number of tenants, like Tenant 2, Tenant 3, Tenant 4, and so on. In each tenant, an independent instance of the application is created that has the same application ID but a different object ID. Each instance of this application is thus authorized independently. Consider how the application object used for this feature is used to partition your application across all customers.
- Application can have a maximum of 20 federated identity credentials, which requires a service provider to share federated identities among its customers. For more information about federated identities design considerations and restrictions, see Configure an app to trust an external identity provider
- In rare scenarios, a service provider might use a single Application object per its customer, but that requires significant maintenance costs to manage applications at scale across all customers.
- In the service provider tenant, it isn't possible to automate the Publisher Verification.
Phase 2 - The customer authorizes access to the key vault
| Step | Description | Least privileged Azure RBAC roles | Least privileged Microsoft Entra roles |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | None | Users with permissions to install applications | |
| 2. | Create an Azure Key Vault and a key used as the customer-managed key. | A user must be assigned the Key Vault Contributor role to create the key vault A user must be assigned the Key Vault Crypto Officer role to add a key to the key vault |
None |
| 3. | Grant the consented application identity access to the Azure key vault by assigning the role Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User | To assign the Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User role to the application, you must have been assigned the User Access Administrator role. | None |
| 4. | Copy the key vault URL and key name into the customer-managed keys configuration of the SaaS offering. | None | None |
Note
To authorize access to the Managed HSM for encryption using CMK, see example for Storage Account here. For more information about managing keys with Managed HSM, see Manage a Managed HSM using the Azure CLI
Considerations for customers of service providers
- In the customer tenant, Tenant 2, an admin can set policies to block non-admin users from installing applications. These policies can prevent non-admin users from creating service principals. If such a policy is configured, then users with permissions to create service principals need to be involved.
- Access to Azure Key Vault can be authorized using Azure RBAC or access policies. When granting access to a key vault, make sure to use the active mechanism for your key vault.
- A Microsoft Entra application registration has an application ID (client ID). When the application is installed in your tenant, a service principal is created. The service principal shares the same application ID as the app registration, but generates its own object ID. When you authorize the application to have access to resources, you might need to use the service principal
NameorObjectIDproperty.
Phase 3 - The service provider encrypts data in an Azure resource using the customer-managed key
After phases 1 and 2 are complete, the service provider can configure encryption on the Azure resource with the key and key vault in the customer's tenant and the Azure resource in the ISV's tenant. The service provider can configure cross-tenant customer-managed keys with the client tools supported by that Azure resource, with an ARM template, or with the REST API.
Configure cross-tenant customer-managed keys
This section describes how to configure a cross-tenant customer-managed key (CMK) and encrypt customer data. You learn how to encrypt customer data in a resource in Tenant1 using a CMK stored in a key vault in Tenant2. You can use the Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
Sign in to the Azure portal and follow these steps.
The service provider configures identities
The following steps are performed by the service provider in the service provider's tenant Tenant1.
The service provider creates a new multi-tenant app registration
You can either create a new multi-tenant Microsoft Entra application registration or start with an existing multi-tenant application registration. If starting with an existing application registration, note the application ID (client ID) of the application.
To create a new registration:
Search for Microsoft Entra ID in the search box. Locate and select the Microsoft Entra ID extension.
Select Manage > App registrations from the left pane.
Select + New registration.
Provide the name for the application registration and select Account in any organizational directory (Any Microsoft Entra directory – Multitenant).
Select Register.
Note the ApplicationId/ClientId of the application.
The service provider creates a user-assigned managed identity
Create a user-assigned managed identity to be used as a federated identity credential.
Search for Managed Identities in the search box. Locate and select the Managed Identities extension.
Select + Create.
Provide the resource group, region, and name for the managed identity.
Select Review + create.
On successful deployment, note the Azure ResourceId of the user-assigned managed identity, which is available under Properties. For example:
/subscriptions/tttttttt-0000-tttt-0000-tttt0000tttt/resourcegroups/XTCMKDemo/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/ConsotoCMKDemoUA
The service provider configures the user-assigned managed identity as a federated credential on the application
Configure a user-assigned managed identity as a federated identity credential on the application, so that it can impersonate the identity of the application.
Navigate to Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations > your application.
Select Certificates & secrets.
Select Federated credentials.
Select + Add credential.
Under Federated credential scenario, select Managed Identity.
Click Select a managed identity. From the pane, select the subscription. Under Managed identity, select User-assigned managed identity. In the Select box, search for the managed identity you created earlier, then click Select at the bottom of the pane.
Under Credential details, provide a name and optional description for the credential and select Add.
The service provider shares the application ID with the customer
Find the application ID (client ID) of the multi-tenant application and share it with the customer.
The customer grants the service provider's app access to the key in the key vault
The following steps are performed by the customer in the customer's tenant Tenant2. The customer can use the Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
The user executing the steps must be an administrator with a privileged role such as Application Administrator, Cloud Application Administrator, or Global Administrator.
Sign in to the Azure portal and follow these steps.
The customer installs the service provider application in the customer tenant
To install the service provider's registered application in the customer's tenant, you create a service principal with the application ID from the registered app. You can create the service principal in either of the following ways:
- Use Microsoft Graph, Microsoft Graph PowerShell, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI to manually create the service principal.
- Construct an admin-consent URL and grant tenant-wide consent to create the service principal. You'll need to provide them with your AppId.
The customer creates a key vault
To create the key vault, the user's account must be assigned the Key Vault Contributor role or another role that permits creation of a key vault.
From the Azure portal menu, or from the Home page, select + Create a resource. In the Search box, enter Key vaults. From the results list, select Key vaults. On the Key vaults page, select Create.
On the Basics tab, choose a subscription. Under Resource group, select Create new and enter a resource group name.
Enter a unique name for the key vault.
Select a region and pricing tier.
Enable purge protection for the new key vault.
On the Access policy tab, select Azure role-based access control for Permission model.
Select Review + create and then Create.
Take note of the key vault name and URI Applications that access your key vault must use this URI.
For more information, see Quickstart - Create an Azure Key Vault with the Azure portal.
The customer assigns Key Vault Crypto Officer role to a user account
This step ensures that you can create encryption keys.
- Navigate to your key vault and select Access Control (IAM) from the left pane.
- Under Grant access to this resource, select Add role assignment.
- Search for and select Key Vault Crypto Officer.
- Under Members, select User, group, or service principal.
- Select Members and search for your user account.
- Select Review + Assign.
The customer creates an encryption key
To create the encryption key, the user's account must be assigned the Key Vault Crypto Officer role or another role that permits creation of a key.
- On the Key Vault properties page, select Keys.
- Select Generate/Import.
- On the Create a key screen, specify a name for the key. Leave the other values to their defaults.
- Select Create.
- Copy the key URI.
The customer grants the service provider application access to the key vault
Assign the Azure RBAC role Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User to the service provider's registered application so that it can access the key vault.
- Navigate to your key vault and select Access Control (IAM) from the left pane.
- Under Grant access to this resource, select Add role assignment.
- Search for and select Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User.
- Under Members, select User, group, or service principal.
- Select Members and search for the application name of the application you installed from the service provider.
- Select Review + Assign.
Now you can configure customer-managed keys with the key vault URI and key.
Create a disk encryption set
Now that you've created your Azure Key Vault and performed the required Microsoft Entra configurations, deploy a disk encryption set configured to work across tenants and associate it with a key in the key vault. You can do this using the Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI. You can also use an ARM template or REST API.
To use the Azure portal, sign in to the portal and follow these steps.
Select + Create a resource, search for Disk encryption set, and select Create > Disk encryption set.
Under Project details, select the subscription and resource group in which to create the disk encryption set.
Under Instance details, provide a name for the disk encryption set.
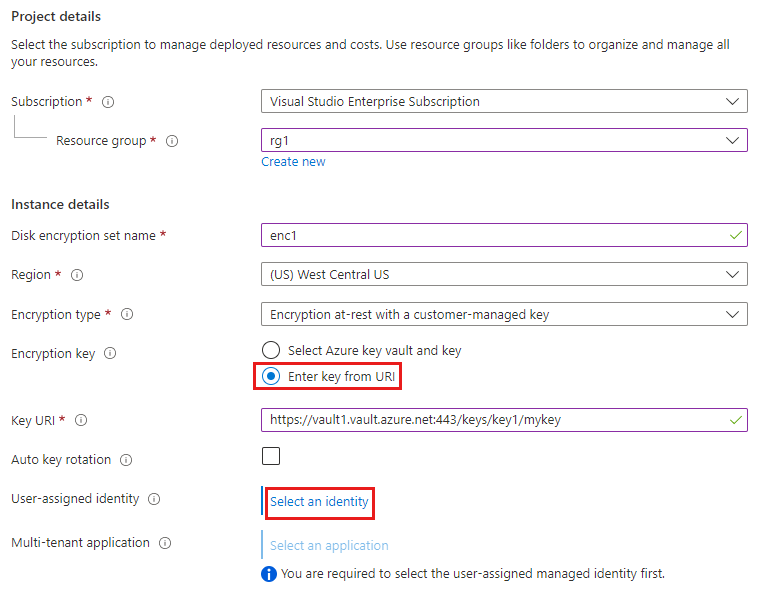
Select the Region in which to create the disk encryption set.
For Encryption type, select Encryption at-rest with a customer-managed key.
Under Encryption key, select the Enter key from URI radio button, and then enter the Key URI of the key created in the customer's tenant.
Under User-assigned identity, select Select an identity.
Select the user-assigned managed identity that you created previously in the ISV's tenant, and then select Add.
Under Multi-tenant application, select Select an application.
Select the multi-tenant registered application that you created previously in the ISV's tenant, and click Select.
Select Review + create.
Use an ARM template
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"desname": {
"defaultValue": "<Enter ISV disk encryption set name>",
"type": "String"
},
"region": {
"defaultValue": "WestCentralUS",
"type": "String"
},
"userassignedmicmk": {
"defaultValue": "/subscriptions/<Enter ISV Subscription Id>/resourceGroups/<Enter ISV resource group name>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<Enter ISV User Assigned Identity Name>",
"type": "String"
},
"cmkfederatedclientId": {
"defaultValue": "<Enter ISV Multi-Tenant App Id>",
"type": "String"
},
"keyVaultURL": {
"defaultValue": "<Enter Client Key URL>",
"type": "String"
},
"encryptionType": {
"defaultValue": "EncryptionAtRestWithCustomerKey",
"type": "String"
}
},
"variables": {},
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets",
"apiVersion": "2021-12-01",
"name": "[parameters('desname')]",
"location": "[parameters('region')]",
"identity": {
"type": "UserAssigned",
"userAssignedIdentities": {
"[parameters('userassignedmicmk')]": {}
}
},
"properties": {
"activeKey": {
"keyUrl": "[parameters('keyVaultURL')]"
},
"federatedClientId": "[parameters('cmkfederatedclientId')]",
"encryptionType": "[parameters('encryptionType')]"
}
}
]
}
Use REST API
Use bearer token as authorization header and application/JSON as content type in BODY. (Network tab, filter to management.azure while performing any ARM request on portal.)
PUT https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<Enter ISV Subscription Id>/resourceGroups/<Enter ISV Resource Group Name>/providers/Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/<Enter ISV Disk Encryption Set Name>?api-version=2021-12-01
Authorization: Bearer ...
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "<Enter ISV disk encryption set name>",
"id": "/subscriptions/<Enter ISV Subscription Id>/resourceGroups/<Enter ISV resource group name>/providers/Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets/<Enter ISV disk encryption set name>/",
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/diskEncryptionSets",
"location": "westcentralus",
"identity": {
"type": "UserAssigned",
"userAssignedIdentities": {
"/subscriptions/<Enter ISV Subscription Id>/resourceGroups/<Enter ISV resource group name>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<Enter ISV User Assigned Identity Name>
": {}
}
},
"properties": {
"activeKey": {
"keyUrl": "<Enter Client Key URL>"
},
"encryptionType": "EncryptionAtRestWithCustomerKey",
"federatedClientId": "<Enter ISV Multi-Tenant App Id>"
}
}
Next steps
See also:







