Investigate apps discovered by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
The Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps integration with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint provides a seamless Shadow IT visibility and control solution. Our integration enables Defender for Cloud Apps administrators to investigate discovered devices, network events, and app usage.
Prerequisites
Before performing the procedures in this article, make sure that you've integrated Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps.
Investigate discovered devices in Defender for Cloud Apps
After you integrate Defender for Endpoint with Defender for Cloud Apps, investigate discovered device data in the cloud discovery dashboard.
In the Microsoft Defender portal, under Cloud Apps, select Cloud Discovery > Dashboard.
At the top of the page, select Defender-managed endpoints. This stream contains data from any operating systems mentioned in Defender for Cloud Apps prerequisites.
Across the top, you'll see the number of discovered devices added after the integration.
Select the Devices tab.
Drill down into each device that's listed, and use the tabs to view the investigation data. Find correlations between the devices, the users, IP addresses, and apps that were involved in incidents:
Overview:
- Device risk level: Shows how risky the device's profile is relative to other devices in your organization, as indicated by the severity (high, medium, low, informational). Defender for Cloud Apps uses device profiles from Defender for Endpoint for each device based on advanced analytics. Activity that is anomalous to a device's baseline is evaluated and determines the device's risk level. Use the device risk level to determine which devices to investigate first.
- Transactions: Information about the number of transactions that took place on the device over the selected period of time.
- Total traffic: Information about the total amount of traffic (in MB) over the selected period of time.
- Uploads: Information about the total amount of traffic (in MB) uploaded by the device over the selected period of time.
- Downloads: Information about the total amount of traffic (in MB) downloaded by the device over the selected period of time.
Discovered apps: Lists all the discovered apps that were accessed by the device.
User history: Lists all the users who signed in to the device.
IP address history: Lists all the IP addresses that were assigned to the device.
As with any other cloud discovery source, you can export the data from the Defender-managed endpoints report for further investigation.
Note
- Defender for Endpoint forwards data to Defender for Cloud Apps in chunks of ~4 MB (~4000 endpoint transactions)
- If the 4 MB limit isn't reached within 1 hour, Defender for Endpoint reports all the transactions performed over the last hour.
Discover apps via Defender for Endpoint when the endpoint is behind a network proxy
Defender for Cloud Apps can discover Shadow IT network events detected from Defender for Endpoint devices that are working in the same environment as a network proxy. For example, if your Windows 10 endpoint device is in the same environment as ZScalar, Defender for Cloud Apps can discover Shadow IT applications via the Win10 Endpoint Users stream.
Investigate device network events in Microsoft Defender XDR
Note
Network events should be used to investigate discovered apps and not used to debug missing data.
Use the following steps to gain more granular visibility on device's network activity in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint:
- In the Microsoft Defender Portal, under Cloud Apps, select Cloud Discovery. Then select the Devices tab.
- Select the machine you want to investigate and then in the top-left select View in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
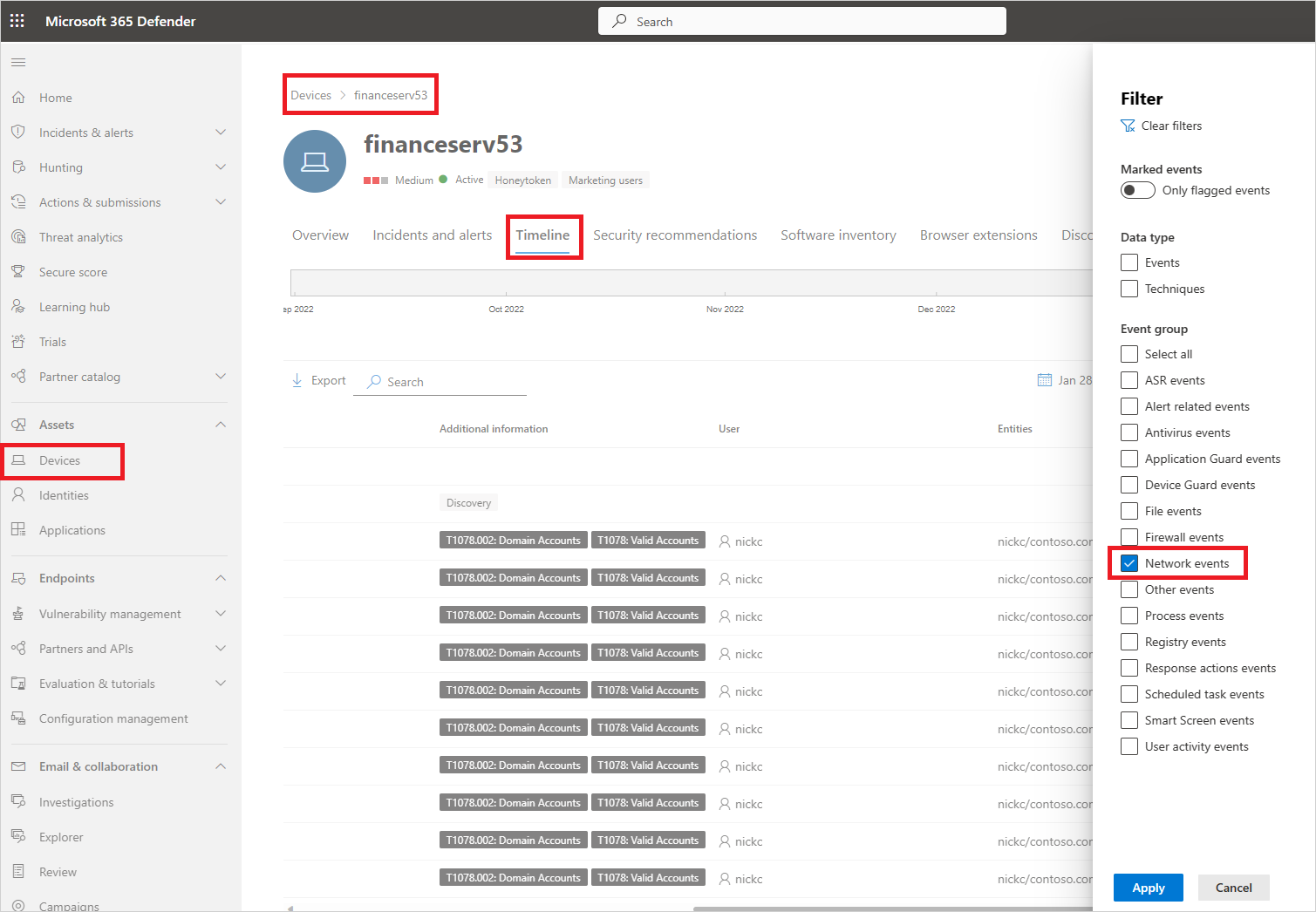
- In Microsoft Defender XDR, under Assets -> Devices > {selected device}, select Timeline.
- Under Filters, select Network events.
- Investigate the device's network events as required.
Investigate app usage in Microsoft Defender XDR with advanced hunting
Use the following steps to gain more granular visibility on app-related network events in Defender for Endpoint:
In the Microsoft Defender Portal, under Cloud Apps, select Cloud Discovery. Then select the Discovered apps tab.
Select the app you want to investigate to open its drawer.
Select the app's Domain list and then copy the list of domains.
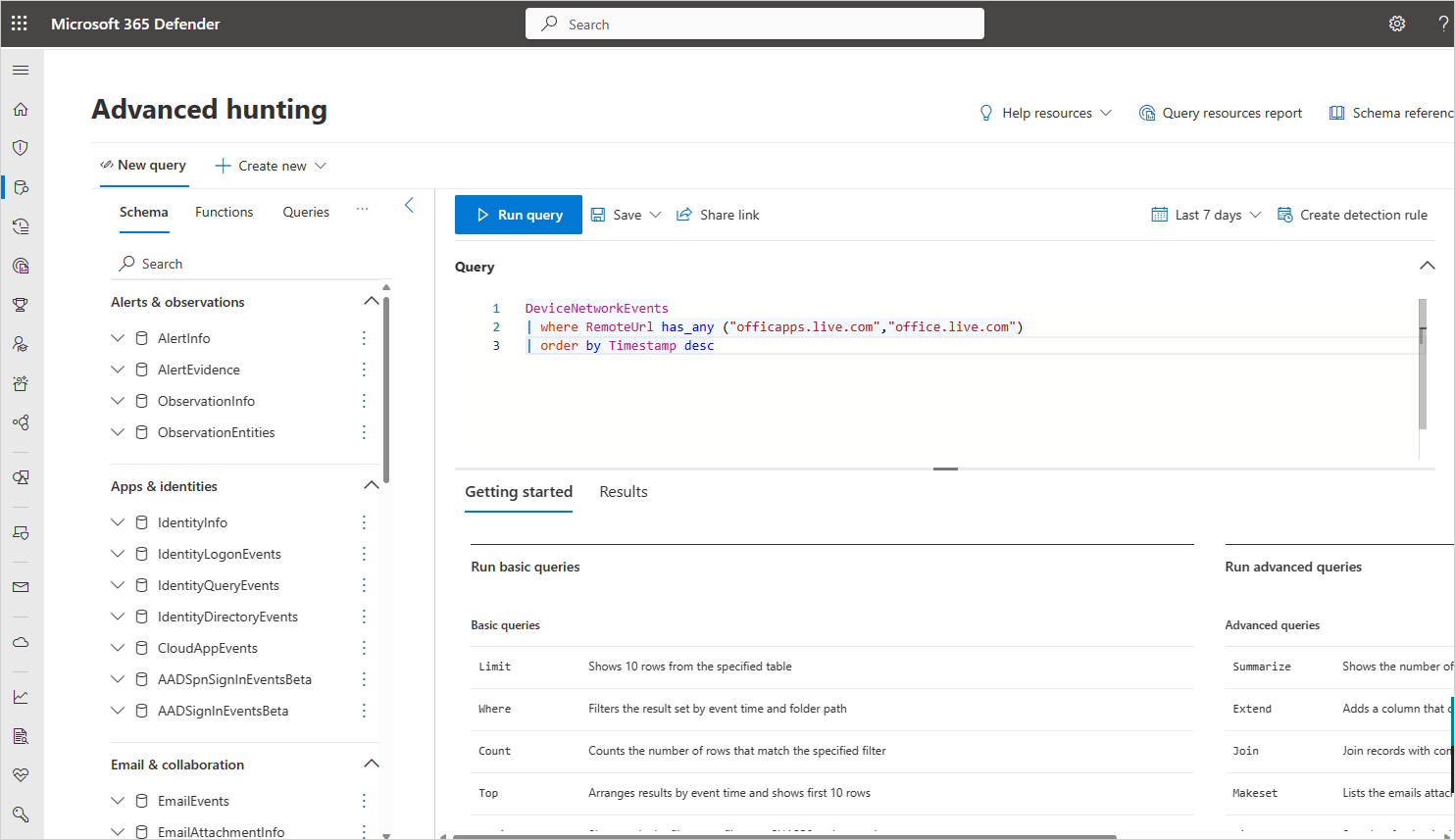
In Microsoft Defender XDR, under Hunting, select Advanced hunting.
Paste the following query and replace
<DOMAIN_LIST>with the list of domains you copied earlier.DeviceNetworkEvents | where RemoteUrl has_any ("<DOMAIN_LIST>") | order by Timestamp descRun the query and investigate network events for this app.
Investigate unsanctioned apps in Microsoft Defender XDR
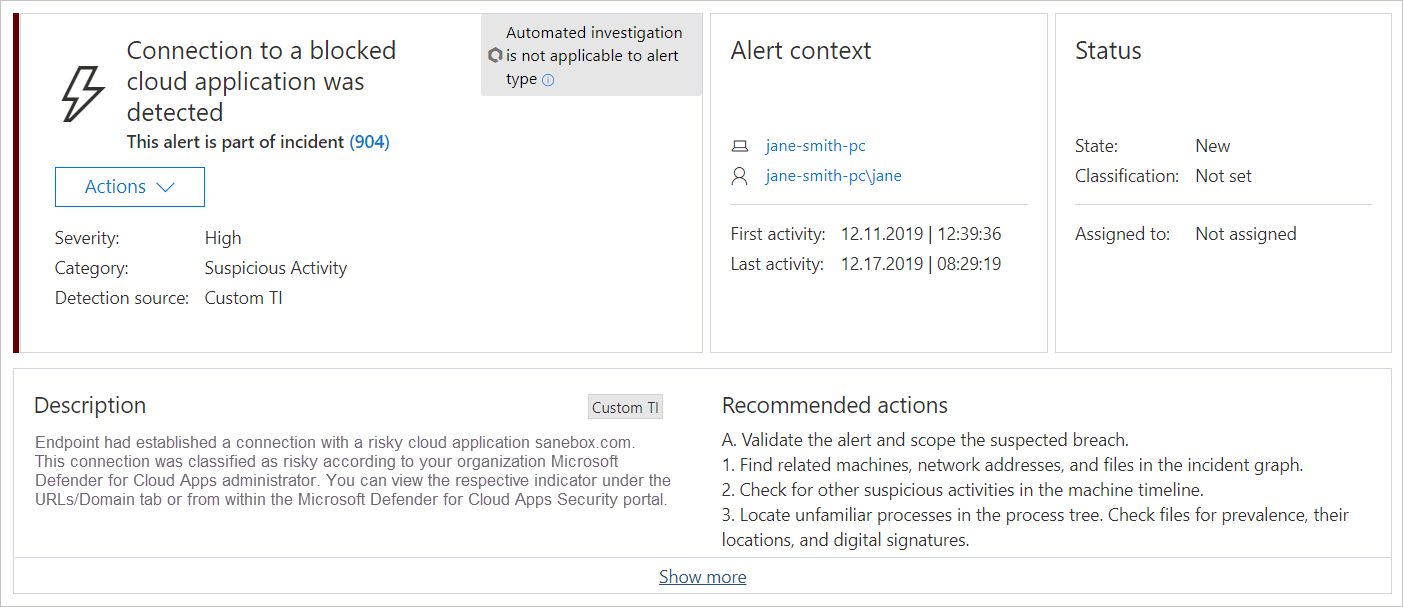
Every attempt to access an unsanctioned app triggers an alert in Microsoft Defender XDR with in-depth details about the entire session. This enables you to perform deeper investigations into attempts to access unsanctioned apps, as well as providing additional relevant information for use in endpoint device investigation.
Sometimes, access to an unsanctioned app isn't blocked, either because the endpoint device isn't configured correctly or if the enforcement policy hasn't yet propagated to the endpoint. In this instance, Defender for Endpoint administrators will receive an alert in Microsoft Defender XDR that the unsanctioned app wasn't blocked.
Note
- It takes up to two hours after you tag an app as Unsanctioned for app domains to propagate to endpoint devices.
- By default, apps and domains marked as Unsanctioned in Defender for Cloud Apps, will be blocked for all endpoint devices in the organization.
- Currently, full URLs are not supported for unsanctioned apps. Therefore, when unsanctioning apps configured with full URLs, they are not propagated to Defender for Endpoint and will not be blocked. For example,
google.com/driveis not supported, whiledrive.google.comis supported. - In-browser notifications may vary between different browsers.
Next steps
Related videos
If you run into any problems, we're here to help. To get assistance or support for your product issue, please open a support ticket.