Copy data from and to ODBC data stores using Azure Data Factory or Synapse Analytics
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article outlines how to use the Copy Activity in Azure Data Factory to copy data from and to an ODBC data store. It builds on the copy activity overview article that presents a general overview of copy activity.
Supported capabilities
This ODBC connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR |
|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/sink) | ② |
| Lookup activity | ② |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For a list of data stores that are supported as sources/sinks, see the Supported data stores table.
Specifically, this ODBC connector supports copying data from/to any ODBC-compatible data stores using Basic or Anonymous authentication. A 64-bit ODBC driver is required. For ODBC sink, the service support ODBC version 2.0 standard.
Prerequisites
To use this ODBC connector, you need to:
- Set up a Self-hosted Integration Runtime. See Self-hosted Integration Runtime article for details.
- Install the 64-bit ODBC driver for the data store on the Integration Runtime machine.
Getting started
To perform the Copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- The Copy Data tool
- The Azure portal
- The .NET SDK
- The Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- The REST API
- The Azure Resource Manager template
Create a linked service to an ODBC data store using UI
Use the following steps to create a linked service to an ODBC data store in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
Search for ODBC and select the ODBC connector.
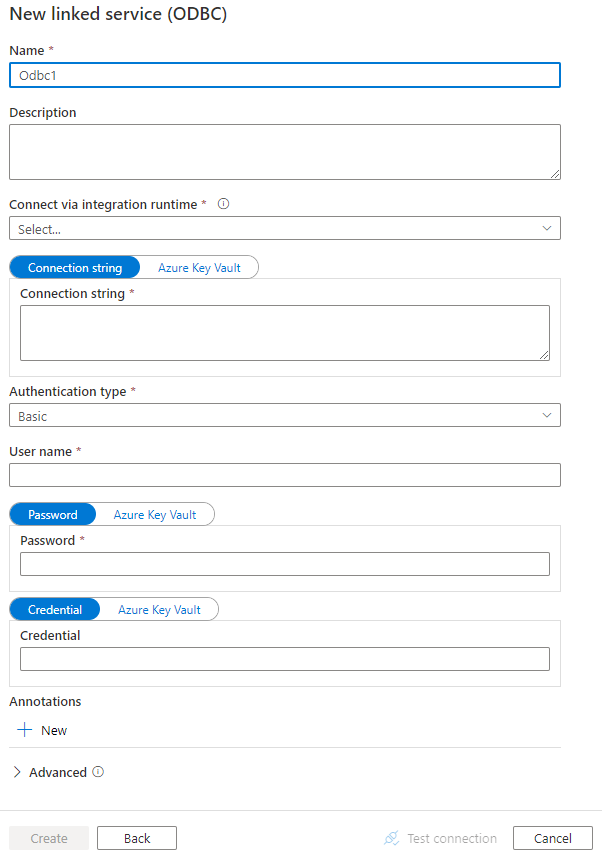
Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that are used to define Data Factory entities specific to ODBC connector.
Linked service properties
The following properties are supported for ODBC linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to: Odbc | Yes |
| connectionString | The connection string excluding the credential portion. You can specify the connection string with pattern like Driver={SQL Server};Server=Server.database.windows.net; Database=TestDatabase;, or use the system DSN (Data Source Name) you set up on the Integration Runtime machine with DSN=<name of the DSN on IR machine>; (you need still specify the credential portion in linked service accordingly).You can also put a password in Azure Key Vault and pull the password configuration out of the connection string. Refer to Store credentials in Azure Key Vault with more details. |
Yes |
| authenticationType | Type of authentication used to connect to the ODBC data store. Allowed values are: Basic and Anonymous. |
Yes |
| userName | Specify user name if you are using Basic authentication. | No |
| password | Specify password for the user account you specified for the userName. Mark this field as a SecureString to store it securely, or reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. | No |
| credential | The access credential portion of the connection string specified in driver-specific property-value format. Example: "RefreshToken=<secret refresh token>;". Mark this field as a SecureString. |
No |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to be used to connect to the data store. A Self-hosted Integration Runtime is required as mentioned in Prerequisites. | Yes |
Example 1: using Basic authentication
{
"name": "ODBCLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "Odbc",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "<connection string>",
"authenticationType": "Basic",
"userName": "<username>",
"password": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<password>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example 2: using Anonymous authentication
{
"name": "ODBCLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "Odbc",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "<connection string>",
"authenticationType": "Anonymous",
"credential": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "RefreshToken=<secret refresh token>;"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see the datasets article. This section provides a list of properties supported by ODBC dataset.
To copy data from/to ODBC-compatible data store, the following properties are supported:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to: OdbcTable | Yes |
| tableName | Name of the table in the ODBC data store. | No for source (if "query" in activity source is specified); Yes for sink |
Example
{
"name": "ODBCDataset",
"properties": {
"type": "OdbcTable",
"schema": [],
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<ODBC linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"typeProperties": {
"tableName": "<table name>"
}
}
}
If you were using RelationalTable typed dataset, it is still supported as-is, while you are suggested to use the new one going forward.
Copy activity properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties supported by ODBC source.
ODBC as source
To copy data from ODBC-compatible data store, the following properties are supported in the copy activity source section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to: OdbcSource | Yes |
| query | Use the custom SQL query to read data. For example: "SELECT * FROM MyTable". |
No (if "tableName" in dataset is specified) |
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromODBC",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<ODBC input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "OdbcSource",
"query": "SELECT * FROM MyTable"
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
If you were using RelationalSource typed source, it is still supported as-is, while you are suggested to use the new one going forward.
ODBC as sink
To copy data to ODBC-compatible data store, set the sink type in the copy activity to OdbcSink. The following properties are supported in the copy activity sink section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity sink must be set to: OdbcSink | Yes |
| writeBatchTimeout | Wait time for the batch insert operation to complete before it times out. Allowed values are: timespan. Example: "00:30:00" (30 minutes). |
No |
| writeBatchSize | Inserts data into the SQL table when the buffer size reaches writeBatchSize. Allowed values are: integer (number of rows). |
No (default is 0 - auto detected) |
| preCopyScript | Specify a SQL query for Copy Activity to execute before writing data into data store in each run. You can use this property to clean up the pre-loaded data. | No |
Note
For "writeBatchSize", if it's not set (auto-detected), copy activity first detects whether the driver supports batch operations, and set it to 10000 if it does, or set it to 1 if it doesn't. If you explicitly set the value other than 0, copy activity honors the value and fails at runtime if the driver doesn't support batch operations.
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyToODBC",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<ODBC output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "<source type>"
},
"sink": {
"type": "OdbcSink",
"writeBatchSize": 100000
}
}
}
]
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
Troubleshoot connectivity issues
To troubleshoot connection issues, use the Diagnostics tab of Integration Runtime Configuration Manager.
- Launch Integration Runtime Configuration Manager.
- Switch to the Diagnostics tab.
- Under the "Test Connection" section, select the type of data store (linked service).
- Specify the connection string that is used to connect to the data store, choose the authentication and enter user name, password, and/or credentials.
- Click Test connection to test the connection to the data store.
Related content
For a list of data stores supported as sources and sinks by the copy activity, see supported data stores.