Azure HDInsight Interactive Query Cluster (Hive LLAP) sizing guide
This document describes the sizing of the HDInsight Interactive Query Cluster (Hive LLAP cluster) for a typical workload to achieve reasonable performance. Note that the recommendations provided in this document are generic guidelines and specific workloads may need specific tuning.
Azure Default VM Types for HDInsight Interactive Query Cluster(LLAP)
| Node Type | Instance | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Head | D13 v2 | 8 vcpus, 56-GB RAM, 400 GB SSD |
| Worker | D14 v2 | 16 vcpus, 112 GB RAM, 800 GB SSD |
| ZooKeeper | A4 v2 | 4 vcpus, 8-GB RAM, 40 GB SSD |
Note: All recommended configurations values are based on D14 v2 type worker node
Configuration:
| Configuration Key | Recommended value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb | 102400 (MB) | Total memory given, in MB, for all YARN containers on a node |
| yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb | 102400 (MB) | The maximum allocation for every container request at the RM, in MBs. Memory requests higher than this value won't take effect |
| yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-vcores | 12 | The maximum number of CPU cores for every container request at the Resource Manager. Requests higher than this value won't take effect. |
| yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores | 12 | Number of CPU cores per NodeManager that can be allocated for containers. |
| yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.llap.capacity | 85 (%) | YARN capacity allocation for LLAP queue |
| tez.am.resource.memory.mb | 4096 (MB) | The amount of memory in MB to be used by the tez AppMaster |
| hive.server2.tez.sessions.per.default.queue | <number_of_worker_nodes> | The number of sessions for each queue named in the hive.server2.tez.default.queues. This number corresponds to number of query coordinators(Tez AMs) |
| hive.tez.container.size | 4096 (MB) | Specified Tez container size in MB |
| hive.llap.daemon.num.executors | 19 | Number of executors per LLAP daemon |
| hive.llap.io.threadpool.size | 19 | Thread pool size for executors |
| hive.llap.daemon.yarn.container.mb | 81920 (MB) | Total memory in MB used by individual LLAP daemons (Memory per daemon) |
| hive.llap.io.memory.size | 242688 (MB) | Cache size in MB per LLAP daemon provided SSD cache is enabled |
| hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask.size | 2048 (MB) | memory size in MB to do Map Join |
LLAP Architecture/Components:
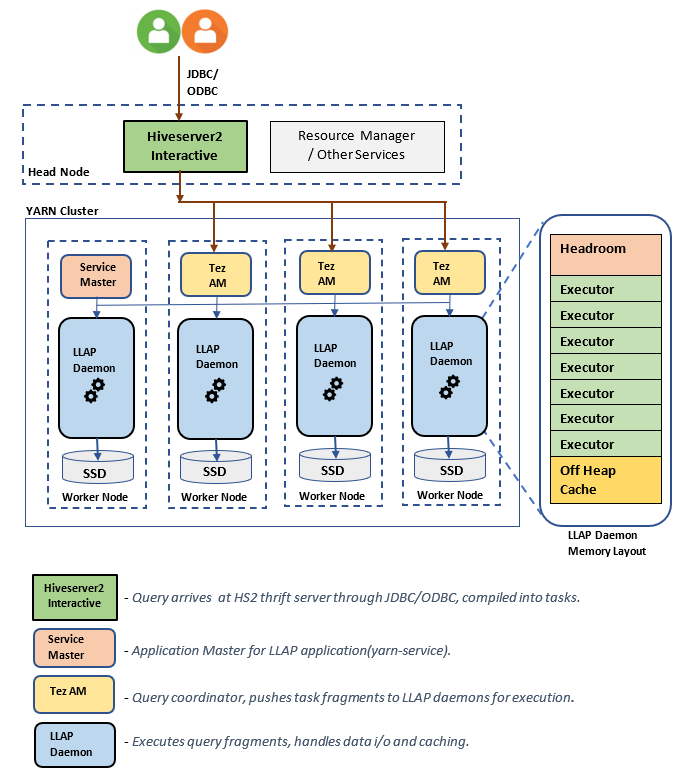
LLAP Daemon size estimations:
1. Determining total YARN memory allocation for all containers on a node
Configuration: yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb
This value indicates a maximum sum of memory in MB that can be used by the YARN containers on each node. The value specified should be lesser than the total amount of physical memory on that node.
Total memory for all YARN containers on a node = (Total physical memory – memory for OS + Other services)
Set this value to ~90% of the available RAM size.
For D14 v2, the recommended value is 102400 MB.
2. Determining maximum amount of memory per YARN container request
Configuration: yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb
This value indicates the maximum allocation for every container request at the Resource Manager, in MB. Memory requests higher than the specified value won't take effect. The Resource Manager can give memory to containers in increments of yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb and can't exceed the size specified by yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb. The value specified shouldn't be more than the total given memory for all containers on the node specified by yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb.
For D14 v2 worker nodes, the recommended value is 102400 MB
3. Determining maximum amount of vcores per YARN container request
Configuration: yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-vcores
This value indicates the maximum number of virtual CPU cores for every container request at the Resource Manager. Requesting a higher number of vcores then this value won't take effect. It's a global property of the YARN scheduler. For LLAP daemon container, this value can be set to 75% of total available vcores. The remaining 25% should be reserved for NodeManager, DataNode, and other services running on the worker nodes.
There are 16 vcores on D14 v2 VMs and 75% of total 16 vcores can be used by LLAP daemon container.
For D14 v2, the recommended value is 12.
4. Number of concurrent queries
Configuration: hive.server2.tez.sessions.per.default.queue
This configuration value determines the number of Tez sessions that can be launched in parallel. These Tez sessions are launched for each of the queues specified by "hive.server2.tez.default.queues." It corresponds to the number of Tez AMs (Query Coordinators). It's recommended to be the same as the number of worker nodes. The number of Tez AMs can be higher than the number of LLAP daemon nodes. The Tez AM's primary responsibility is to coordinate the query execution and assign query plan fragments to corresponding LLAP daemons for execution. Keep this value as multiple of many LLAP daemon nodes to achieve higher throughput.
Default HDInsight cluster has four LLAP daemons running on four worker nodes, so the recommended value is 4.
Ambari UI slider for Hive config variable hive.server2.tez.sessions.per.default.queue:
5. Tez Container and Tez Application Master size
Configuration: tez.am.resource.memory.mb, hive.tez.container.size
tez.am.resource.memory.mb - defines the Tez Application Master size.
The recommended value is 4096 MB.
hive.tez.container.size - defines the amount of memory given for Tez container. This value must be set between the YARN minimum container size(yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb) and the YARN maximum container size(yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb). The LLAP daemon executors use this value for limiting memory usage per executor.
The recommended value is 4096 MB.
6. LLAP Queue capacity allocation
Configuration: yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.llap.capacity
This value indicates a percentage of capacity given to LLAP queue. The capacity allocations may have different values for different workloads depending on how the YARN queues are configured. If your workload is read-only operations, then setting it as high as 90% of the capacity should work. However, if your workload is mix of update/delete/merge operations using managed tables, it's recommended to give 85% of the capacity for LLAP queue. The remaining 15% capacity can be used by other tasks such as compaction etc. to allocate containers from default queue. That way tasks in default queue won't deprive of YARN resources.
For D14v2 worker nodes, the recommended value for LLAP queue is 85.
(For readonly workloads, it can be increased up to 90 as suitable.)
7. LLAP daemon container size
Configuration: hive.llap.daemon.yarn.container.mb
LLAP daemon is run as a YARN container on each worker node. The total memory size for LLAP daemon container depends on following factors,
- Configurations of YARN container size (yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb, yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb, yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb)
- Number of Tez AMs on a node
- Total memory configured for all containers on a node and LLAP queue capacity
Memory needed by Tez Application Masters(Tez AM) can be calculated as follows.
Tez AM acts as a query coordinator and the number of Tez AMs should be configured based on many concurrent queries to be served. Theoretically, we can consider one Tez AM per worker node. However, it's possible that you may see more than one Tez AM on a worker node. For calculation purpose, we assume uniform distribution of Tez AMs across all LLAP daemon nodes/worker nodes.
It's recommended to have 4 GB of memory per Tez AM.
Number of Tez Ams = value specified by Hive config hive.server2.tez.sessions.per.default.queue.
Number of LLAP daemon nodes = specified by env variable num_llap_nodes_for_llap_daemons in Ambari UI.
Tez AM container size = value specified by Tez config tez.am.resource.memory.mb.
Tez AM memory per node = (ceil(Number of Tez AMs / Number of LLAP daemon nodes) x Tez AM container size**)**
For D14 v2, the default configuration has four Tez AMs and four LLAP daemon nodes.
Tez AM memory per node = (ceil(4/4) x 4 GB) = 4 GB
Total Memory available for LLAP queue per worker node can be calculated as follows:
This value depends on the total amount of memory available for all YARN containers on a node(yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb) and the percentage of capacity configured for LLAP queue(yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.llap.capacity).
Total memory for LLAP queue on worker node = Total memory available for all YARN containers on a node x Percentage of capacity for LLAP queue.
For D14 v2, this value is (100 GB x 0.85) = 85 GB.
The LLAP daemon container size is calculated as follows;
LLAP daemon container size = (Total memory for LLAP queue on a worker node) – (Tez AM memory per node) - (Service Master container size)
There is only one Service Master (Application Master for LLAP service) on the cluster spawned on one of the worker nodes. For calculation purpose, we consider one service master per worker node.
For D14 v2 worker node, HDI 4.0 - the recommended value is (85 GB - 4 GB - 1 GB)) = 80 GB
8. Determining number of executors per LLAP daemon
Configuration: hive.llap.daemon.num.executors, hive.llap.io.threadpool.size
hive.llap.daemon.num.executors:
This configuration controls the number of executors that can execute tasks in parallel per LLAP daemon. This value depends on the number of vcores, the amount of memory used per executor, and the amount of total memory available for LLAP daemon container. The number of executors can be oversubscribed to 120% of available vcores per worker node. However, it should be adjusted if it doesn't meet the memory requirements based on memory needed per executor and the LLAP daemon container size.
Each executor is equivalent to a Tez container and can consume 4 GB(Tez container size) of memory. All executors in LLAP daemon share the same heap memory. With the assumption that not all executors run memory intensive operations at the same time, you can consider 75% of Tez container size(4 GB) per executor. This way you can increase the number of executors by giving each executor less memory (for example, 3 GB) for increased parallelism. However, it is recommended to tune this setting for your target workload.
There are 16 vcores on D14 v2 VMs. For D14 v2, the recommended value for num of executors is (16 vcores x 120%) ~= 19 on each worker node considering 3 GB per executor.
hive.llap.io.threadpool.size:
This value specifies the thread pool size for executors. Since executors are fixed as specified, it is same as number of executors per LLAP daemon.
For D14 v2, the recommended value is 19.
9. Determining LLAP daemon cache size
Configuration: hive.llap.io.memory.size
LLAP daemon container memory consists of following components;
- Head room
- Heap memory used by executors (Xmx)
- In-memory cache per daemon (its off-heap memory size, not applicable when SSD cache is enabled)
- In-memory cache metadata size (applicable only when SSD cache is enabled)
Headroom size:
This size indicates a portion of off-heap memory used for Java VM overhead (metaspace, threads stack, gc data structures, etc.). Generally, this overhead is about 6% of the heap size (Xmx). To be on the safer side, this value can be calculated as 6% of total LLAP daemon memory size.
For D14 v2, the recommended value is ceil(80 GB x 0.06) ~= 4 GB.
Heap size(Xmx):
It is amount of heap memory available for all executors.
Total Heap size = Number of executors x 3 GB
For D14 v2, this value is 19 x 3 GB = 57 GB
Ambari environment variable for LLAP heap size:

When SSD cache is disabled, the in-memory cache is amount of memory that is left after taking out Headroom size and Heap size from the LLAP daemon container size.
Cache size calculation differs when SSD cache is enabled.
Setting hive.llap.io.allocator.mmap = true enables SSD caching.
When SSD cache is enabled, some portion of the memory will be used to store metadata for the SSD cache. The metadata is stored in memory and it's expected to be ~8% of SSD cache size.
SSD Cache in-memory metadata size = LLAP daemon container size - (Head room + Heap size)
For D14 v2, with HDI 4.0, SSD cache in-memory metadata size = 80 GB - (4 GB + 57 GB) = 19 GB
Given the size of available memory for storing SSD cache metadata, we can calculate the size of SSD cache that can be supported.
Size of in-memory metadata for SSD cache = LLAP daemon container size - (Head room + Heap size)
= 19 GB
Size of SSD cache = size of in-memory metadata for SSD cache(19 GB) / 0.08 (8 percent)
For D14 v2 and HDI 4.0, the recommended SSD cache size = 19 GB / 0.08 ~= 237 GB
10. Adjusting Map Join memory
Configuration: hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask.size
Make sure you have hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask enabled for this parameter to take effect.
This configuration determines the threshold for MapJoin selection by Hive optimizer that considers oversubscription of memory from other executors to have more room for in-memory hash tables to allow more map join conversions. Considering 3 GB per executor, this size can be oversubscribed to 3 GB, but some heap memory may also be used for sort buffers, shuffle buffers, etc. by the other operations.
So for D14 v2, with 3-GB memory per executor, it's recommended to set this value to 2048 MB.
(Note: This value may need adjustments that are suitable for your workload. Setting this value too low may not use autoconvert feature. And setting it too high may result into out of memory exceptions or GC pauses that can result into adverse performance.)
11. Number of LLAP daemons
Ambari environment variables: num_llap_nodes, num_llap_nodes_for_llap_daemons
num_llap_nodes - specifies number of nodes used by Hive LLAP service, this includes nodes running LLAP daemon, LLAP Service Master, and Tez Application Master(Tez AM).

num_llap_nodes_for_llap_daemons - specified number of nodes used only for LLAP daemons. LLAP daemon container sizes are set to max fit node, so it results in one llap daemon on each node.

It's recommended to keep both values same as number of worker nodes in Interactive Query cluster.
Considerations for Workload Management
If you want to enable workload management for LLAP, make sure you reserve enough capacity for workload management to function as expected. The workload management requires configuration of a custom YARN queue, which is in addition to llap queue. Make sure you divide total cluster resource capacity between llap queue and workload management queue in accordance to your workload requirements.
Workload management spawns Tez Application Masters(Tez AMs) when a resource plan is activated.
Note:
- Tez AMs spawned by activating a resource plan consume resources from the workload management queue as specified by
hive.server2.tez.interactive.queue. - The number of Tez AMs would depend on the value of
QUERY_PARALLELISMspecified in the resource plan. - Once the workload management is active, Tez AMs in LLAP queue will not be used. Only Tez AMs from workload management queue are used for query coordination. Tez AMs in the
llapqueue are used when workload management is disabled.
For example: Total cluster capacity = 100-GB memory, divided between LLAP, Workload Management, and Default queues as follows:
- LLAP queue capacity = 70 GB
- Workload management queue capacity = 20 GB
- Default queue capacity = 10 GB
With 20 GB in workload management queue capacity, a resource plan can specify QUERY_PARALLELISM value as five, which means workload management can launch five Tez AMs with 4-GB container size each. If QUERY_PARALLELISM is higher than the capacity, you may see some Tez AMs stop responding in ACCEPTED state. The Hive server 2 Interactive cannot submit query fragments to the Tez AMs that are not in RUNNING state.
Next Steps
If setting these values didn't resolve your issue, visit one of the following...
Get answers from Azure experts through Azure Community Support.
Connect with @AzureSupport - the official Microsoft Azure account for improving customer experience by connecting the Azure community to the right resources: answers, support, and experts.
If you need more help, you can submit a support request from the Azure portal. Select Support from the menu bar or open the Help + support hub. For more detailed information, review How to create an Azure support request. Access to Subscription Management and billing support is included with your Microsoft Azure subscription, and Technical Support is provided through one of the Azure Support Plans.
Other References: