Azure Virtual Machines high availability for SAP NetWeaver on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
This article describes how to deploy virtual machines (VMs), configure the VMs, install the cluster framework, and install a highly available SAP NetWeaver 7.50 system.
In the example configurations and installation commands, ASCS instance number 00, ERS instance number 02, and SAP System ID NW1 are used. The names of the resources (for example, VMs and virtual networks) in the example assume that you used the ASCS/SCS template with Resource Prefix NW1 to create the resources.
Prerequisites
Read the following SAP Notes and papers first:
- SAP Note 1928533, which has:
- A list of Azure VM sizes that are supported for the deployment of SAP software.
- Important capacity information for Azure VM sizes.
- Supported SAP software and operating system (OS) and database combinations.
- Required SAP kernel version for Windows and Linux on Microsoft Azure.
- SAP Note 2015553 lists prerequisites for SAP-supported SAP software deployments in Azure.
- SAP Note 2002167 has recommended OS settings for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
- SAP Note 2009879 has SAP HANA Guidelines for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- SAP Note 2178632 has detailed information about all monitoring metrics reported for SAP in Azure.
- SAP Note 2191498 has the required SAP Host Agent version for Linux in Azure.
- SAP Note 2243692 has information about SAP licensing on Linux in Azure.
- SAP Note 1999351 has more troubleshooting information for the Azure Enhanced Monitoring Extension for SAP.
- SAP Community WIKI has all required SAP Notes for Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines planning and implementation for SAP on Linux
- Azure Virtual Machines deployment for SAP on Linux
- Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP on Linux
- Product Documentation for Red Hat Gluster Storage
- SAP NetWeaver in Pacemaker cluster
- General RHEL documentation:
- Azure-specific RHEL documentation:
Overview
To achieve high availability, SAP NetWeaver requires shared storage. GlusterFS is configured in a separate cluster and multiple SAP systems can use it.
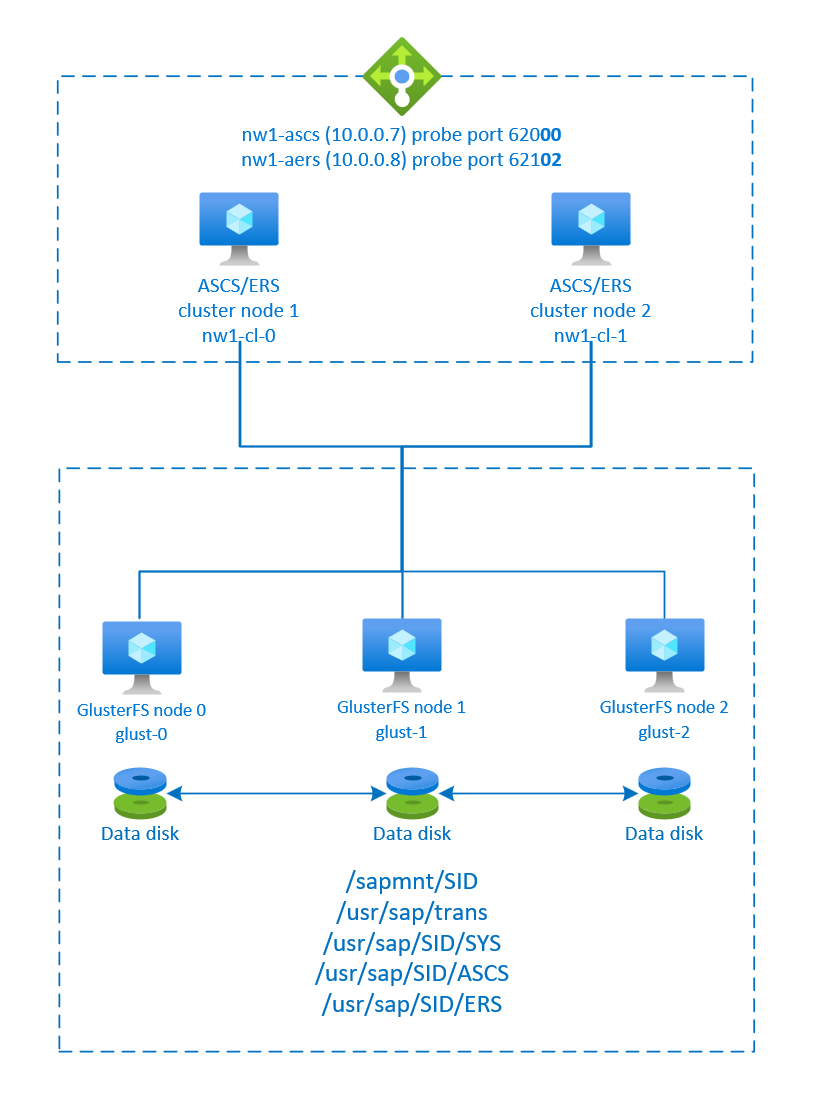
SAP NetWeaver ASCS, SAP NetWeaver SCS, SAP NetWeaver ERS, and the SAP HANA database use virtual hostname and virtual IP addresses. On Azure, a load balancer is required to use a virtual IP address. We recommend using Standard Azure Load Balancer. The configuration here shows a load balancer with:
- Front-end IP address 10.0.0.7 for ASCS
- Front-end IP address 10.0.0.8 for ERS
- Probe port 62000 for ASCS
- Probe port 62101 for ERS
Set up GlusterFS
SAP NetWeaver requires shared storage for the transport and profile directory. To see how to set up GlusterFS for SAP NetWeaver, see GlusterFS on Azure VMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP NetWeaver.
Prepare the infrastructure
Azure Marketplace contains images qualified for SAP with the High Availability add-on, which you can use to deploy new VMs by using various versions of Red Hat.
Deploy Linux VMs manually via the Azure portal
This document assumes that you already deployed an Azure virtual network, subnet, and resource group.
Deploy VMs for SAP ASCS, ERS and Application servers. Choose a suitable RHEL image that's supported for the SAP system. You can deploy a VM in any one of the availability options: virtual machine scale set, availability zone, or availability set.
Configure Azure load balancer
During VM configuration, you have an option to create or select exiting load balancer in networking section. Follow the steps below to configure a standard load balancer for the high-availability setup of SAP ASCS and SAP ERS.
Follow create load balancer guide to set up a standard load balancer for a high availability SAP system using the Azure portal. During the setup of load balancer, consider following points.
- Frontend IP Configuration: Create two frontend IP, one for ASCS and another for ERS. Select the same virtual network and subnet as your ASCS/ERS virtual machines.
- Backend Pool: Create backend pool and add ASCS and ERS VMs.
- Inbound rules: Create two load balancing rule, one for ASCS and another for ERS. Follow the same steps for both load balancing rules.
- Frontend IP address: Select frontend IP
- Backend pool: Select backend pool
- Check "High availability ports"
- Protocol: TCP
- Health Probe: Create health probe with below details (applies for both ASCS or ERS)
- Protocol: TCP
- Port: [for example: 620<Instance-no.> for ASCS, 621<Instance-no.> for ERS]
- Interval: 5
- Probe Threshold: 2
- Idle timeout (minutes): 30
- Check "Enable Floating IP"
Note
Health probe configuration property numberOfProbes, otherwise known as "Unhealthy threshold" in Portal, isn't respected. So to control the number of successful or failed consecutive probes, set the property "probeThreshold" to 2. It is currently not possible to set this property using Azure portal, so use either the Azure CLI or PowerShell command.
Note
When VMs without public IP addresses are placed in the back-end pool of an internal (no public IP address) Standard Azure load balancer, there's no outbound internet connectivity unless more configuration is performed to allow routing to public endpoints. For more information on how to achieve outbound connectivity, see Public endpoint connectivity for VMs using Azure Standard Load Balancer in SAP high-availability scenarios.
Important
Don't enable TCP timestamps on Azure VMs placed behind Azure Load Balancer. Enabling TCP timestamps causes the health probes to fail. Set the parameter net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps to 0. For more information, see Load Balancer health probes.
Set up (A)SCS
Next, you'll prepare and install the SAP ASCS and ERS instances.
Create a Pacemaker cluster
Follow the steps in Set up Pacemaker on Red Hat Enterprise Linux in Azure to create a basic Pacemaker cluster for this (A)SCS server.
Prepare for the SAP NetWeaver installation
The following items are prefixed with:
- [A]: Applicable to all nodes
- [1]: Only applicable to node 1
- [2]: Only applicable to node 2
[A] Set up hostname resolution.
You can either use a DNS server or modify the
/etc/hostsfile on all nodes. This example shows how to use the/etc/hostsfile. Replace the IP address and the hostname in the following commands:sudo vi /etc/hostsInsert the following lines to the
/etc/hostsfile. Change the IP address and hostname to match your environment.# IP addresses of the GlusterFS nodes 10.0.0.40 glust-0 10.0.0.41 glust-1 10.0.0.42 glust-2 # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for SAP NetWeaver ASCS 10.0.0.7 nw1-ascs # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for SAP NetWeaver ASCS ERS 10.0.0.8 nw1-aers[A] Create the shared directories.
sudo mkdir -p /sapmnt/NW1 sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/trans sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW1/SYS sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00 sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/NW1/ERS02 sudo chattr +i /sapmnt/NW1 sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/trans sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW1/SYS sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00 sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/NW1/ERS02[A] Install the GlusterFS client and other required packages.
sudo yum -y install glusterfs-fuse resource-agents resource-agents-sap[A] Check the version of
resource-agents-sap.Make sure that the version of the installed
resource-agents-sappackage is at least 3.9.5-124.el7.sudo yum info resource-agents-sap # Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos # Repodata is over 2 weeks old. Install yum-cron? Or run: yum makecache fast # Installed Packages # Name : resource-agents-sap # Arch : x86_64 # Version : 3.9.5 # Release : 124.el7 # Size : 100 k # Repo : installed # From repo : rhel-sap-for-rhel-7-server-rpms # Summary : SAP cluster resource agents and connector script # URL : https://github.com/ClusterLabs/resource-agents # License : GPLv2+ # Description : The SAP resource agents and connector script interface with # : Pacemaker to allow SAP instances to be managed in a cluster # : environment.[A] Add mount entries.
sudo vi /etc/fstab # Add the following lines to fstab, save and exit glust-0:/NW1-sapmnt /sapmnt/NW1 glusterfs backup-volfile-servers=glust-1:glust-2 0 0 glust-0:/NW1-trans /usr/sap/trans glusterfs backup-volfile-servers=glust-1:glust-2 0 0 glust-0:/NW1-sys /usr/sap/NW1/SYS glusterfs backup-volfile-servers=glust-1:glust-2 0 0Mount the new shares.
sudo mount -a[A] Configure the SWAP file.
sudo vi /etc/waagent.conf # Set the property ResourceDisk.EnableSwap to y # Create and use swapfile on resource disk. ResourceDisk.EnableSwap=y # Set the size of the SWAP file with property ResourceDisk.SwapSizeMB # The free space of resource disk varies by virtual machine size. Make sure that you do not set a value that is too big. You can check the SWAP space with command swapon # Size of the swapfile. ResourceDisk.SwapSizeMB=2000Restart the agent to activate the change.
sudo service waagent restart[A] Configure RHEL.
Based on the RHEL version, perform the configuration mentioned in SAP Note 2002167, SAP Note 2772999, or SAP Note 3108316.
Install SAP NetWeaver ASCS/ERS
[1] Configure the cluster default properties.
pcs resource defaults resource-stickiness=1 pcs resource defaults migration-threshold=3[1] Create a virtual IP resource and health probe for the ASCS instance.
sudo pcs node standby nw1-cl-1 sudo pcs resource create fs_NW1_ASCS Filesystem device='glust-0:/NW1-ascs' \ directory='/usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00' fstype='glusterfs' \ options='backup-volfile-servers=glust-1:glust-2' \ --group g-NW1_ASCS sudo pcs resource create vip_NW1_ASCS IPaddr2 \ ip=10.0.0.7 \ --group g-NW1_ASCS sudo pcs resource create nc_NW1_ASCS azure-lb port=62000 \ --group g-NW1_ASCSMake sure that the cluster status is okay and that all resources are started. Which node the resources are running on isn't important.
sudo pcs status # Node nw1-cl-1: standby # Online: [ nw1-cl-0 ] # # Full list of resources: # # rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 # Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS # fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 # nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 # vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0[1] Install SAP NetWeaver ASCS.
Install SAP NetWeaver ASCS as the root on the first node by using a virtual hostname that maps to the IP address of the load balancer front-end configuration for the ASCS, for example, nw1-ascs and 10.0.0.7, and the instance number that you used for the probe of the load balancer, for example, 00.
You can use the
sapinstparameterSAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USERto allow a nonroot user to connect tosapinst.# Allow access to SWPM. This rule is not permanent. If you reboot the machine, you have to run the command again. sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4237/tcp sudo <swpm>/sapinst SAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USER=sapadminIf the installation fails to create a subfolder in /usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00, try setting the owner and group of the ASCS00 folder and retry.
sudo chown nw1adm /usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00 sudo chgrp sapsys /usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00[1] Create a virtual IP resource and health probe for the ERS instance.
sudo pcs node unstandby nw1-cl-1 sudo pcs node standby nw1-cl-0 sudo pcs resource create fs_NW1_AERS Filesystem device='glust-0:/NW1-aers' \ directory='/usr/sap/NW1/ERS02' fstype='glusterfs' \ options='backup-volfile-servers=glust-1:glust-2' \ --group g-NW1_AERS sudo pcs resource create vip_NW1_AERS IPaddr2 \ ip=10.0.0.8 \ --group g-NW1_AERS sudo pcs resource create nc_NW1_AERS azure-lb port=62102 \ --group g-NW1_AERSMake sure that the cluster status is okay and that all resources are started. Which node the resources are running on isn't important.
sudo pcs status # Node nw1-cl-0: standby # Online: [ nw1-cl-1 ] # # Full list of resources: # # rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-1 # Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS # fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 # nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 # vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 # Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS # fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 # nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 # vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1[2] Install SAP NetWeaver ERS.
Install SAP NetWeaver ERS as the root on the second node by using a virtual hostname that maps to the IP address of the load balancer front-end configuration for the ERS, for example, nw1-aers and 10.0.0.8, and the instance number that you used for the probe of the load balancer, for example, 02.
You can use the
sapinstparameterSAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USERto allow a nonroot user to connect tosapinst.# Allow access to SWPM. This rule is not permanent. If you reboot the machine, you have to run the command again. sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4237/tcp sudo <swpm>/sapinst SAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USER=sapadminIf the installation fails to create a subfolder in /usr/sap/NW1/ERS02, try setting the owner and group of the ERS02 folder and retry.
sudo chown nw1adm /usr/sap/NW1/ERS02 sudo chgrp sapsys /usr/sap/NW1/ERS02[1] Adapt the ASCS/SCS and ERS instance profiles.
ASCS/SCS profile:
sudo vi /sapmnt/NW1/profile/NW1_ASCS00_nw1-ascs # Change the restart command to a start command #Restart_Program_01 = local $(_EN) pf=$(_PF) Start_Program_01 = local $(_EN) pf=$(_PF) # Add the keep alive parameter, if using ENSA1 enque/encni/set_so_keepalive = TRUEFor both ENSA1 and ENSA2, make sure that the
keepaliveOS parameters are set as described in SAP Note 1410736.ERS profile:
sudo vi /sapmnt/NW1/profile/NW1_ERS02_nw1-aers # Change the restart command to a start command #Restart_Program_00 = local $(_ER) pf=$(_PFL) NR=$(SCSID) Start_Program_00 = local $(_ER) pf=$(_PFL) NR=$(SCSID) # remove Autostart from ERS profile # Autostart = 1
[A] Configure Keep Alive.
The communication between the SAP NetWeaver application server and the ASCS/SCS is routed through a software load balancer. The load balancer disconnects inactive connections after a configurable timeout. To prevent this action, set a parameter in the SAP NetWeaver ASCS/SCS profile, if you're using ENSA1. Change the Linux system
keepalivesettings on all SAP servers for both ENSA1 and ENSA2. For more information, see SAP Note 1410736.# Change the Linux system configuration sudo sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time=300[A] Update the
/usr/sap/sapservicesfile.To prevent the start of the instances by the
sapinitstartup script, all instances managed by Pacemaker must be commented out from the/usr/sap/sapservicesfile.sudo vi /usr/sap/sapservices # On the node where you installed the ASCS, comment out the following line # LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00/exe:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH; /usr/sap/NW1/ASCS00/exe/sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW1/SYS/profile/NW1_ASCS00_nw1-ascs -D -u nw1adm # On the node where you installed the ERS, comment out the following line # LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/sap/NW1/ERS02/exe:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH; /usr/sap/NW1/ERS02/exe/sapstartsrv pf=/usr/sap/NW1/ERS02/profile/NW1_ERS02_nw1-aers -D -u nw1adm[1] Create the SAP cluster resources.
Depending on whether you are running an ENSA1 or ENSA2 system, select respective tab to define the resources. SAP introduced support for ENSA2, including replication, in SAP NetWeaver 7.52. Starting with ABAP Platform 1809, ENSA2 is installed by default. For ENSA2 support, see SAP Note 2630416 for enqueue server 2 support.
If you use enqueue server 2 architecture (ENSA2), install resource agent resource-agents-sap-4.1.1-12.el7.x86_64 or newer and define the resources as shown here:
sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=true sudo pcs resource create rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 SAPInstance \ InstanceName=NW1_ASCS00_nw1-ascs START_PROFILE="/sapmnt/NW1/profile/NW1_ASCS00_nw1-ascs" \ AUTOMATIC_RECOVER=false \ meta resource-stickiness=5000 migration-threshold=1 failure-timeout=60 \ op monitor interval=20 on-fail=restart timeout=60 \ op start interval=0 timeout=600 op stop interval=0 timeout=600 \ --group g-NW1_ASCS sudo pcs resource meta g-NW1_ASCS resource-stickiness=3000 sudo pcs resource create rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 SAPInstance \ InstanceName=NW1_ERS02_nw1-aers START_PROFILE="/sapmnt/NW1/profile/NW1_ERS02_nw1-aers" \ AUTOMATIC_RECOVER=false IS_ERS=true \ op monitor interval=20 on-fail=restart timeout=60 op start interval=0 timeout=600 op stop interval=0 timeout=600 \ --group g-NW1_AERS sudo pcs constraint colocation add g-NW1_AERS with g-NW1_ASCS -5000 sudo pcs constraint location rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 rule score=2000 runs_ers_NW1 eq 1 sudo pcs constraint order start g-NW1_ASCS then stop g-NW1_AERS kind=Optional symmetrical=false sudo pcs node unstandby nw1-cl-0 sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=falseNote
If you're upgrading from an older version and switching to enqueue server 2, see SAP Note 2641322.
Note
The timeouts in the preceding configuration are only examples and might need to be adapted to the specific SAP setup.
Make sure that the cluster status is okay and that all resources are started. Which node the resources are running on isn't important.
sudo pcs status # Online: [ nw1-cl-0 nw1-cl-1 ] # # Full list of resources: # # rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 # Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS # fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 # nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 # vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 # rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1 # Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS # fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 # nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 # vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 # rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0[A] Add firewall rules for ASCS and ERS on both nodes.
# Probe Port of ASCS sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62000,3200,3600,3900,8100,50013,50014,50016}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62000,3200,3600,3900,8100,50013,50014,50016}/tcp # Probe Port of ERS sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62102,3202,3302,50213,50214,50216}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={62102,3202,3302,50213,50214,50216}/tcp
SAP NetWeaver application server preparation
Some databases require that the database instance installation runs on an application server. Prepare the application server VMs to be able to use them in these cases.
The following steps assume that you install the application server on a server different from the ASCS/SCS and HANA servers. Otherwise, some of the steps (like configuring hostname resolution) aren't needed.
Set up hostname resolution.
You can either use a DNS server or modify the
/etc/hostsfile on all nodes. This example shows how to use the/etc/hostsfile. Replace the IP address and the hostname in the following commands:sudo vi /etc/hostsInsert the following lines to
/etc/hosts. Change the IP address and hostname to match your environment.# IP addresses of the GlusterFS nodes 10.0.0.40 glust-0 10.0.0.41 glust-1 10.0.0.42 glust-2 # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for SAP NetWeaver ASCS 10.0.0.7 nw1-ascs # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for SAP NetWeaver ASCS ERS 10.0.0.8 nw1-aers # IP address of the load balancer frontend configuration for database 10.0.0.13 nw1-dbCreate the
sapmntdirectory.sudo mkdir -p /sapmnt/NW1 sudo mkdir -p /usr/sap/trans sudo chattr +i /sapmnt/NW1 sudo chattr +i /usr/sap/transInstall the GlusterFS client and other requirements.
sudo yum -y install glusterfs-fuse uuiddAdd mount entries.
sudo vi /etc/fstab # Add the following lines to fstab, save and exit glust-0:/NW1-sapmnt /sapmnt/NW1 glusterfs backup-volfile-servers=glust-1:glust-2 0 0 glust-0:/NW1-trans /usr/sap/trans glusterfs backup-volfile-servers=glust-1:glust-2 0 0Mount the new shares.
sudo mount -aConfigure the SWAP file.
sudo vi /etc/waagent.conf # Set the property ResourceDisk.EnableSwap to y # Create and use swapfile on resource disk. ResourceDisk.EnableSwap=y # Set the size of the SWAP file with property ResourceDisk.SwapSizeMB # The free space of resource disk varies by virtual machine size. Make sure that you do not set a value that is too big. You can check the SWAP space with command swapon # Size of the swapfile. ResourceDisk.SwapSizeMB=2000Restart the agent to activate the change.
sudo service waagent restart
Install the database
In this example, SAP NetWeaver is installed on SAP HANA. You can use every supported database for this installation. For more information on how to install SAP HANA in Azure, see High availability of SAP HANA on Azure VMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. For a list of supported databases, see SAP Note 1928533.
Run the SAP database instance installation.
Install the SAP NetWeaver database instance as the root by using a virtual hostname that maps to the IP address of the load balancer front-end configuration for the database, for example, nw1-db and 10.0.0.13.
You can use the
sapinstparameterSAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USERto allow a nonroot user to connect tosapinst.sudo <swpm>/sapinst SAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USER=sapadmin
SAP NetWeaver application server installation
Follow these steps to install an SAP application server.
Prepare the application server.
Follow the steps in the previous section SAP NetWeaver application server preparation to prepare the application server.
Install the SAP NetWeaver application server.
Install a primary or additional SAP NetWeaver applications server.
You can use the
sapinstparameterSAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USERto allow a nonroot user to connect tosapinst.sudo <swpm>/sapinst SAPINST_REMOTE_ACCESS_USER=sapadminUpdate the SAP HANA secure store.
Update the SAP HANA secure store to point to the virtual name of the SAP HANA System Replication setup.
Run the following command to list the entries as <sapsid>adm:
hdbuserstore ListAll entries should be listed and look similar to:
DATA FILE : /home/nw1adm/.hdb/nw1-di-0/SSFS_HDB.DAT KEY FILE : /home/nw1adm/.hdb/nw1-di-0/SSFS_HDB.KEY KEY DEFAULT ENV : 10.0.0.14:30313 USER: SAPABAP1 DATABASE: NW1The output shows that the IP address of the default entry is pointing to the VM and not to the load balancer's IP address. This entry needs to be changed to point to the virtual hostname of the load balancer. Make sure to use the same port (30313 in the preceding output) and database name (HN1 in the preceding output).
su - nw1adm hdbuserstore SET DEFAULT nw1-db:30313@NW1 SAPABAP1 <password of ABAP schema>
Test the cluster setup
Manually migrate the ASCS instance.
Resource state before starting the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Run the following commands as root to migrate the ASCS instance.
[root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource move rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 [root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource clear rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 # Remove failed actions for the ERS that occurred as part of the migration [root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02Resource state after the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0Simulate a node crash.
Resource state before starting the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0Run the following command as root on the node where the ASCS instance is running.
[root@nw1-cl-1 ~]# echo b > /proc/sysrq-triggerThe status after the node is started again should look like:
Online: [ nw1-cl-0 nw1-cl-1 ] Full list of resources: rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1 Failed Actions: * rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02_monitor_11000 on nw1-cl-0 'not running' (7): call=45, status=complete, exitreason='', last-rc-change='Tue Aug 21 13:52:39 2018', queued=0ms, exec=0msNote
If you're using SBD as a STONITH mechanism, it could happen that after a reboot, when the node attempts to rejoin the cluster, it receives the message "we were allegendly just fenced" message in /var/log/messages and shut down the Pacemaker and Corosync services. To address the issue, you can follow the workaround described in RedHat KB A node shuts down pacemaker after getting fenced and restarting corosync and pacemaker. However, in Azure, set a delay of 150 seconds for Corosync service to startup. Ensure that these steps are applied to all cluster nodes.
Use the following command to clean the failed resources.
[root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02Resource state after the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Block network communication.
Resource state before starting the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Run a firewall rule to block the communication on one of the nodes.
# Execute iptable rule on nw1-cl-0 (10.0.0.7) to block the incoming and outgoing traffic to nw1-cl-1 (10.0.0.8) iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.8 -j DROP; iptables -A OUTPUT -d 10.0.0.8 -j DROPWhen cluster nodes can't communicate with each other, there's a risk of a split-brain scenario. In such situations, cluster nodes try to simultaneously fence each other, which results in a fence race. To avoid this situation, we recommend that you set a priority-fencing-delay property in a cluster configuration (applicable only for pacemaker-2.0.4-6.el8 or higher).
By enabling the
priority-fencing-delayproperty, the cluster introduces a delay in the fencing action, specifically on the node hosting ASCS resource, allowing the node to win the fence race.Run the following command to delete the firewall rule.
# If the iptables rule set on the server gets reset after a reboot, the rules will be cleared out. In case they have not been reset, please proceed to remove the iptables rule using the following command. iptables -D INPUT -s 10.0.0.8 -j DROP; iptables -D OUTPUT -d 10.0.0.8 -j DROPKill the message server process.
Resource state before starting the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Run the following commands as root to identify the process of the message server and kill it.
[root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pgrep -f ms.sapNW1 | xargs kill -9If you kill the message server only once,
sapstartrestarts it. If you kill it often enough, Pacemaker eventually moves the ASCS instance to the other node. Run the following commands as root to clean up the resource state of the ASCS and ERS instance after the test.[root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 [root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02Resource state after the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0Kill the enqueue server process.
Resource state before starting the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0Run the following commands as root on the node where the ASCS instance is running to kill the enqueue server.
#If using ENSA1 [root@nw1-cl-1 ~]# pgrep -f en.sapNW1 | xargs kill -9 #If using ENSA2 [root@nw1-cl-1 ~]# pgrep -f enq.sapNW1 | xargs kill -9The ASCS instance should immediately fail over to the other node, in the case of ENSA1. The ERS instance should also fail over after the ASCS instance is started. Run the following commands as root to clean up the resource state of the ASCS and ERS instance after the test.
[root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 [root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02Resource state after the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Kill the enqueue replication server process.
Resource state before starting the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Run the following command as root on the node where the ERS instance is running to kill the enqueue replication server process.
#If using ENSA1 [root@nw1-cl-1 ~]# pgrep -f er.sapNW1 | xargs kill -9 #If using ENSA2 [root@nw1-cl-1 ~]# pgrep -f enqr.sapNW1 | xargs kill -9If you run the command only once,
sapstartrestarts the process. If you run it often enough,sapstartwon't restart the process and the resource is in a stopped state. Run the following commands as root to clean up the resource state of the ERS instance after the test.[root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pcs resource cleanup rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02Resource state after the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Kill the enqueue
sapstartsrvprocess.Resource state before starting the test:
rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1Run the following commands as root on the node where the ASCS is running.
[root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# pgrep -fl ASCS00.*sapstartsrv # 59545 sapstartsrv [root@nw1-cl-0 ~]# kill -9 59545The
sapstartsrvprocess should always be restarted by the Pacemaker resource agent as part of the monitoring. Resource state after the test:rsc_st_azure (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_ASCS fs_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-0 nc_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-0 vip_NW1_ASCS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-0 rsc_sap_NW1_ASCS00 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-0 Resource Group: g-NW1_AERS fs_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:Filesystem): Started nw1-cl-1 nc_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started nw1-cl-1 vip_NW1_AERS (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started nw1-cl-1 rsc_sap_NW1_ERS02 (ocf::heartbeat:SAPInstance): Started nw1-cl-1
Next steps
- To deploy a cost-optimization scenario where the PAS and AAS instance is deployed with SAP NetWeaver HA cluster on RHEL, see Install SAP dialog instance with SAP ASCS/SCS high availability VMs on RHEL.
- See HA for SAP NW on Azure VMs on RHEL for SAP applications multi-SID guide.
- See Azure Virtual Machines planning and implementation for SAP.
- See Azure Virtual Machines deployment for SAP.
- See Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP.
- To learn how to establish HA and plan for disaster recovery of SAP HANA on Azure (large instances), see SAP HANA (large instances) high availability and disaster recovery on Azure.
- To learn how to establish HA and plan for disaster recovery of SAP HANA on Azure VMs, see High availability of SAP HANA on Azure Virtual Machines.