Managing VM updates with Maintenance Configurations
Applies to: ✔️ Linux VMs ✔️ Windows VMs ✔️ Flexible scale sets ✔️ Uniform scale sets
Azure frequently updates its infrastructure to improve reliability, performance, and security, or to launch new features. Most updates are transparent to users, but some sensitive workloads can't tolerate even few seconds of a virtual machine (VM) freezing or disconnecting for maintenance. Sensitive workloads might include gaming, media streaming, and financial transactions.
You can use the Maintenance Configurations feature to control and manage updates for many Azure VM resources. Maintenance Configurations is integrated with Azure Resource Graph for a low-latency and high-scale customer experience.
Important
To use Maintenance Configurations, you must have a role of at least contributor and ensure that your subscription is registered with a maintenance resource provider.
Scopes
Maintenance Configurations currently supports three scopes: host, OS image, and guest. Although each scope allows scheduling and managing updates, the major difference lies in the resources that they support:
| Scope | Supported resources |
|---|---|
| Host | Isolated VMs, isolated virtual machine scale sets, dedicated hosts |
| OS image | Virtual machine scale sets |
| Guest | VMs, Azure Arc-enabled servers |
Host
With the host scope, you can manage platform updates that don't require a restart on your isolated VMs, isolated virtual machine scale sets, and dedicated hosts.
Features and limitations unique to this scope include:
- You can set schedules anytime within 35 days. After 35 days, updates are automatically applied.
- A minimum of a two-hour maintenance window is required.
- Rack-level maintenance isn't currently supported.
Learn more about Azure dedicated hosts.
OS image
Using the OS image scope with Maintenance Configurations lets you decide when to apply upgrades to OS disks in your virtual machine scale sets through an easier and more predictable experience. An upgrade works by replacing the OS disk of a VM with a new disk created from the latest image version. Any configured extensions and custom data scripts are run on the OS disk, while data disks are retained.
Features and limitations unique to this scope include:
- For scale sets to use Maintenance Configurations, they need to have automatic OS upgrades enabled.
- You can schedule recurrence up to a week (7 days).
- A minimum of 5 hours is required for the maintenance window.
Guest
The guest scope integrates with Azure Update Manager. You can use it to save recurring deployment schedules to install updates for your Windows Server and Linux machines in Azure, in on-premises environments, and in other cloud environments connected through Azure Arc-enabled servers.
Features and limitations unique to this scope include:
- Patch orchestration for virtual machines needs to be set to
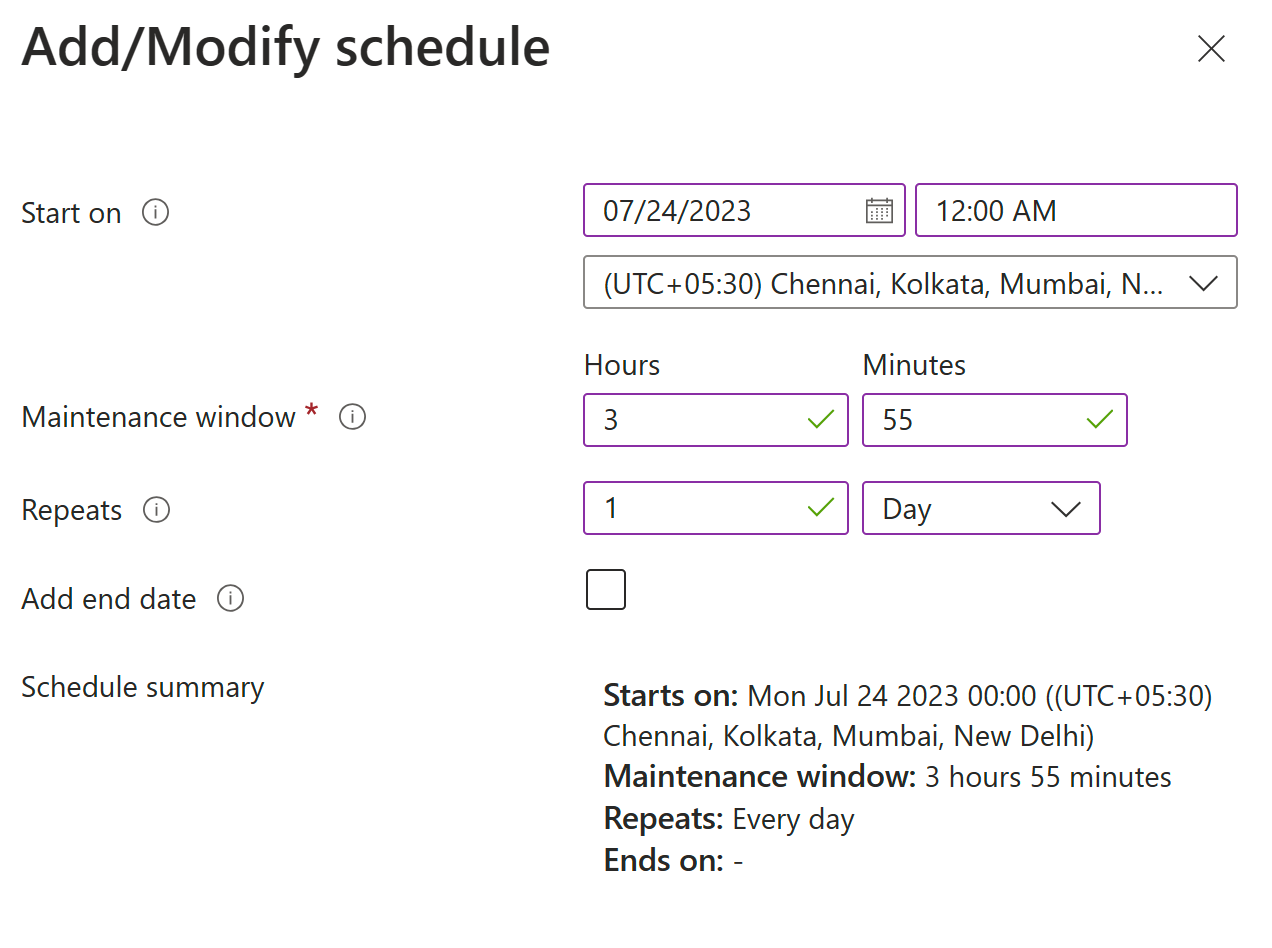
AutomaticByPlatform. - The upper maintenance window is 3 hours and 55 minutes.
- A minimum of 1 hour and 30 minutes is required for the maintenance window.
- The value of Repeats should be at least 6 hours.
- The start time for a schedule should be at least 15 minutes after the schedule's creation time.
Note
The minimum maintenance window increased from 1 hour and 10 minutes to 1 hour and 30 minutes, while the minimum repeat value is set to 6 hours for new schedules. Your existing schedules aren't affected. However, we strongly recommend that you update existing schedules to include these changes.
The character count for the resource group name and the maintenance configuration name should be less than 128.
Maintenance Configurations provides two scheduled patching modes for VMs in the guest scope: Static Mode and Dynamic Scope Mode. By default, the system operates in Static Mode if you don't configure a Dynamic Scope Mode.
To schedule or modify the maintenance configuration in either mode, a buffer of 15 minutes before the scheduled patch time is required. For instance, if you schedule the patch for 3:00 PM, all modifications (including adding VMs, removing VMs, or altering the dynamic scope) should finish before 2:45 PM.
To learn more about this topic, see Schedule recurring updates for machines by using the Azure portal and Azure Policy.
Important
If you move a resource to a different resource group or subscription, scheduled patching for the resource stops working, because the system currently doesn't support this scenario. As a workaround, follow the steps in the troubleshooting article.
Shut-down machines
You can't apply maintenance updates to any shut-down machines. Ensure that your machine is turned on at least 15 minutes before a scheduled update, or the update might not be applied.
If your machine is shut down at the time of your scheduled update, the maintenance configuration might appear to be disassociated in the Azure portal. This is only a display issue. The maintenance configuration isn't disassociated, and you can check it via the Azure CLI.
Management options
You can create and manage maintenance configurations by using any of the following options:
Important
The API shows a pre/post tasks property, but that property isn't supported at this time.
For an Azure Functions sample, see Scheduling maintenance updates with maintenance configurations and Azure Functions.
Service limits
We recommend the following limits for indicators:
| Indicator | Public Cloud Limit | Mooncake/Fairfax Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Number of schedules per subscription per region | 250 | 250 |
| Total number of resource associations to a schedule | 3,000 | 3,000 |
| Resource associations on each dynamic scope | 1,000 | 1,000 |
| Number of dynamic scopes per resource group or subscription per region | 250 | 250 |
| Number of dynamic scopes per schedule | 200 | 30 |
| Total number of subscriptions attached to all dynamic scopes per schedule | 200 | 30 |
We recommend the following limits for each dynamic scope in the guest scope only:
| Resource | Limit |
|---|---|
| Resource associations | 1,000 |
| Number of tag filters | 50 |
| Number of resource group filters | 50 |
Next steps
- For troubleshooting, see Troubleshoot issues with Maintenance Configurations.
- To learn more, see Maintenance for virtual machines in Azure.