Administer DNS and create conditional forwarders in a Microsoft Entra Domain Services managed domain
Microsoft Entra Domain Services includes a Domain Name System (DNS) server that provides name resolution for the managed domain. This DNS server includes built-in DNS records and updates for the key components that allow the service to run.
As you run your own applications and services, you may need to create DNS records for machines that aren't joined to the domain, configure virtual IP addresses for load balancers, or set up external DNS forwarders. Users who belong to the AAD DC Administrators group are granted DNS administration privileges on the Domain Services managed domain and can create and edit custom DNS records.
In a hybrid environment, DNS zones and records configured in other DNS namespaces, such as an on-premises AD DS environment, aren't synchronized to the managed domain. To resolve named resources in other DNS namespaces, create and use conditional forwarders that point to existing DNS servers in your environment.
Domain Services communicates with multiple Azure endpoints during normal operations. Redirecting zones such as file.core.windows.net or blob.core.windows.net puts Domain Services in an unsupportable state.
Refrain from redirecting DNS zones related to windowsazure.com or core.windows.net. If DNS redirection is required, limit the redirection to individual host names instead of zones. For example, use server1.file.core.windows.net instead of file.core.windows.net.
Note
Creating or changing root hints or server-level DNS forwarders isn't supported and causes issues for the Domain Services managed domain.
This article shows you how to install the DNS Server tools then use the DNS console to manage records and create conditional forwarders in Domain Services.
Before you begin
To complete this article, you need the following resources and privileges:
- An active Azure subscription.
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an account.
- A Microsoft Entra tenant associated with your subscription, either synchronized with an on-premises directory or a cloud-only directory.
- A Microsoft Entra Domain Services managed domain enabled and configured in your Microsoft Entra tenant.
- If needed, complete the tutorial to create and configure a Microsoft Entra Domain Services managed domain.
- Connectivity from your Domain Services virtual network to where your other DNS namespaces are hosted.
- This connectivity can be provided with an Azure ExpressRoute or Azure VPN Gateway connection.
- A Windows Server management VM that is joined to the managed domain.
- If needed, complete the tutorial to create a Windows Server VM and join it to a managed domain.
- A user account that's a member of the Microsoft Entra DC administrators group in your Microsoft Entra tenant.
Install DNS Server tools
To create and modify DNS records in a managed domain, you need to install the DNS Server tools. These tools can be installed as a feature in Windows Server. For more information on how to install the administrative tools on a Windows client, see install Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
Sign in to your management VM. For steps on how to connect using the Microsoft Entra admin center, see Connect to a Windows Server VM.
If Server Manager doesn't open by default when you sign in to the VM, select the Start menu, then choose Server Manager.
In the Dashboard pane of the Server Manager window, select Add Roles and Features.
On the Before You Begin page of the Add Roles and Features Wizard, select Next.
For the Installation Type, leave the Role-based or feature-based installation option checked and select Next.
On the Server Selection page, choose the current VM from the server pool, such as myvm.aaddscontoso.com, then select Next.
On the Server Roles page, click Next.
On the Features page, expand the Remote Server Administration Tools node, then expand the Role Administration Tools node. Select DNS Server Tools feature from the list of role administration tools.
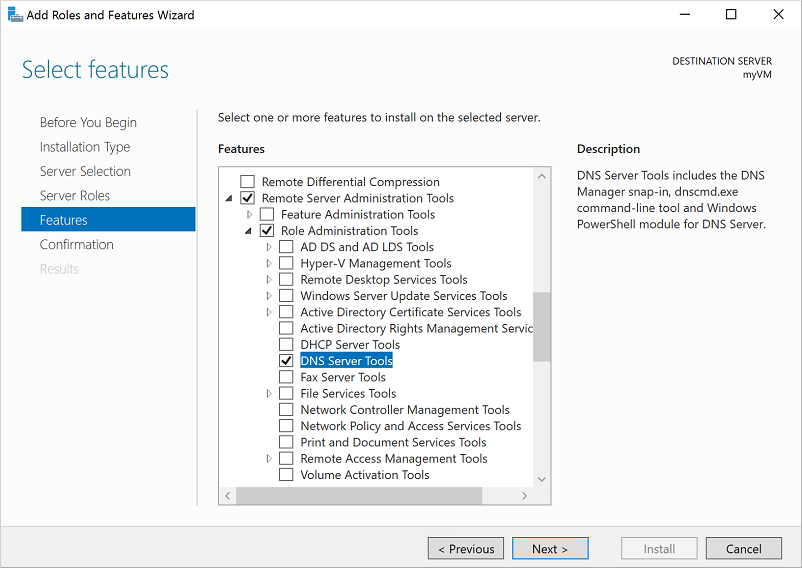
On the Confirmation page, select Install. It may take a minute or two to install the DNS Server Tools.
When feature installation is complete, select Close to exit the Add Roles and Features wizard.
Open the DNS management console to administer DNS
With the DNS Server tools installed, you can administer DNS records on the managed domain.
Note
To administer DNS in a managed domain, you must be signed in to a user account that's a member of the AAD DC Administrators group.
From the Start screen, select Administrative Tools. A list of available management tools is shown, including DNS installed in the previous section. Select DNS to launch the DNS Management console.
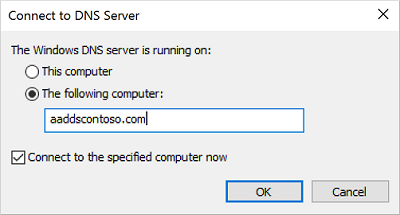
In the Connect to DNS Server dialog, select The following computer, then enter the DNS domain name of the managed domain, such as aaddscontoso.com:
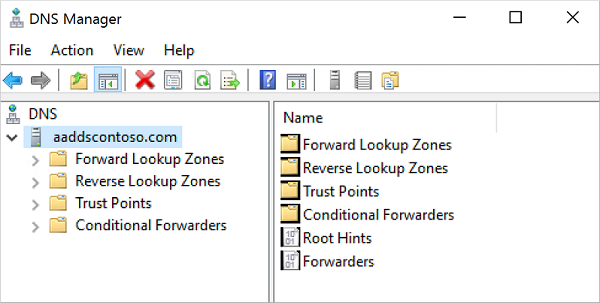
The DNS Console connects to the specified managed domain. Expand the Forward Lookup Zones or Reverse Lookup Zones to create your required DNS entries or edit existing records as needed.
Warning
When you manage records using the DNS Server tools, make sure that you don't delete or modify the built-in DNS records that are used by Domain Services. Built-in DNS records include domain DNS records, name server records, and other records used for DC location. If you modify these records, domain services are disrupted on the virtual network.
Create conditional forwarders
A Domain Services DNS zone should only contain the zone and records for the managed domain itself. Don't create additional zones in the managed domain to resolve named resources in other DNS namespaces. Instead, use conditional forwarders in the managed domain to tell the DNS server where to go in order to resolve addresses for those resources.
A conditional forwarder is a configuration option in a DNS server that lets you define a DNS domain, such as contoso.com, to forward queries to. Instead of the local DNS server trying to resolve queries for records in that domain, DNS queries are forwarded to the configured DNS for that domain. This configuration makes sure that the correct DNS records are returned, as you don't create a local a DNS zone with duplicate records in the managed domain to reflect those resources.
To create a conditional forwarder in your managed domain, complete the following steps:
Select your DNS zone, such as aaddscontoso.com.
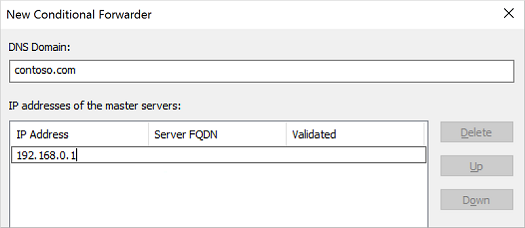
Select Conditional Forwarders, then right-select and choose New Conditional Forwarder...
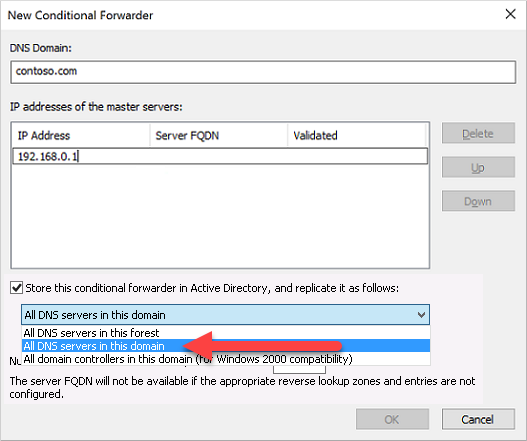
Enter your other DNS Domain, such as contoso.com, then enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers for that namespace, as shown in the following example:
Check the box for Store this conditional forwarder in Active Directory, and replicate it as follows, then select the option for All DNS servers in this domain, as shown in the following example:
Important
If the conditional forwarder is stored in the forest instead of the domain, the conditional forwarder fails.
To create the conditional forwarder, select OK.
Name resolution of the resources in other namespaces from VMs connected to the managed domain should now resolve correctly. Queries for the DNS domain configured in the conditional forwarder are passed to the relevant DNS servers.
Next steps
For more information about managing DNS, see the DNS tools article on Technet.