Walkthrough: Debug a multithreaded app using the Threads window (C#, Visual Basic, C++)
Several Visual Studio user interface elements help you debug multithreaded apps. This article introduces multithreaded debugging features in the code editor window, Debug Location toolbar, and Threads window. For information about other tools for debugging multithreaded apps, see Get started debugging multithreaded apps.
Completing this tutorial takes only a few minutes, and familiarizes you with the basics of debugging multithreaded apps.
Create a multithreaded app project
Create the following multithreaded app project to use in this tutorial:
Open Visual Studio and create a new project.
If the start window is not open, choose File > Start Window.
On the start window, choose New project.
On the start window, choose Create a new project.
On the Create a new project window, enter or type console in the search box. Next, choose C# or C++ from the Language list, and then choose Windows from the Platform list.
After you apply the language and platform filters, choose the Console App for .NET Core, .NET 5+, or C++, and then choose Next.
Note
If you don't see the correct template, go to Tools > Get Tools and Features..., which opens the Visual Studio Installer. Choose the .NET desktop development or Desktop development with C++ workload, then choose Modify.
In the Configure your new project window, type a name or use the default name in the Project name box. Then, choose Next or Create, whichever option is available.
For .NET Core or .NET 5+, choose either the recommended target framework or .NET 8, and then choose Create.
A new console project appears. After the project has been created, a source file appears. Depending on the language you have chosen, the source file might be called Program.cs or MyThreadWalkthroughApp.cpp.
Replace the code in the source file with the C# or C++ example code from Get started debugging multithreaded apps.
Select File > Save All.
Start debugging
Find the following lines in the source code:
Set a breakpoint on the
Console.WriteLine();line by clicking in the left gutter, or selecting the line and pressing F9.The breakpoint appears as a red circle in the left gutter next to the code line.
Select Debug > Start Debugging, or press F5.
The app starts in debug mode, and pauses at the breakpoint.
While in break mode, open the Threads window by selecting Debug > Windows > Threads. You must be in a debugging session to open or see the Threads and other debugging windows.
Examine thread markers
In the source code, locate the
Console.WriteLine();line.- Right-click in the Threads window, and select Show Threads in Source
 from the menu.
from the menu.
The gutter next to the source code line now displays a thread marker icon
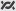 . The thread marker indicates that a thread is stopped at this location. If there is more than one stopped thread at the location, the
. The thread marker indicates that a thread is stopped at this location. If there is more than one stopped thread at the location, the 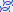 icon appears.
icon appears.- Right-click in the Threads window, and select Show Threads in Source
Hover the pointer over the thread marker. A DataTip appears, showing the name and thread ID number for the stopped thread or threads. The thread names may be
<No Name>.Tip
To help identify nameless threads, you can rename them in the Threads window. Right-click the thread and select Rename.
Right-click the thread marker in the source code to see the available options on the shortcut menu.
Flag and unflag threads
You can flag threads to keep track of threads you want to pay special attention to.
Flag and unflag threads from the source code editor or from the Threads window. Choose whether to display only flagged threads, or all threads, from the Debug Location or Threads window toolbars. Selections made from any location affect all locations.
Flag and unflag threads in source code
Open the Debug Location toolbar by selecting View > Toolbars > Debug Location. You can also right-click in the toolbar area and select Debug Location.
The Debug Location toolbar has three fields: Process, Thread, and Stack Frame. Drop down the Thread list, and note how many threads there are. In the Thread list, the currently executing thread is marked by a > symbol.
In the source code window, hover over a thread marker icon in the gutter and select the flag icon (or one of the empty flag icons) in the DataTip. The flag icon turns red.
You can also right-click a thread marker icon, point to Flag, and then select a thread to flag from the shortcut menu.
On the Debug Location toolbar, select the Show Only Flagged Threads icon
 , to the right of the Thread field. The icon is grayed out unless one or more threads are flagged.
, to the right of the Thread field. The icon is grayed out unless one or more threads are flagged.Only the flagged thread now appears in the Thread dropdown in the toolbar. To show all threads again, select the Show Only Flagged Threads icon again.
Tip
After you have flagged some threads, you can place your cursor in the code editor, right-click, and select Run Flagged Threads to Cursor. Make sure to choose code that all flagged threads will reach. Run Flagged Threads to Cursor will pause threads on the selected line of code, making it easier to control the order of execution by freezing and thawing threads.
To toggle the flagged or unflagged status of the currently executing thread, select the single flag Toggle Current Thread Flagged State toolbar button, to the left of the Show Only Flagged Threads button. Flagging the current thread is useful for locating the current thread when only flagged threads are showing.
To unflag a thread, hover over the thread marker in the source code and select the red flag icon to clear it, or right-click the thread marker and select Unflag.
Flag and unflag threads in the Threads window
In the Threads window, flagged threads have red flag icons next to them, while unflagged threads, if shown, have empty outline icons.

Select a flag icon to change the thread state to flagged or unflagged, depending on its current state.
You can also right-click a line and select Flag, Unflag, or Unflag All Threads from the shortcut menu.
The Threads window toolbar also has a Show Flagged Threads Only button, which is the right-hand one of the two flag icons. It works the same as the button on the Debug Location toolbar, and either button controls the display in both locations.
Other Threads window features
In the Threads window, select the header of any column to sort the threads by that column. Select again to reverse the sort order. If all threads are showing, selecting the flag icon column sorts the threads by flagged or unflagged status.
The second column of the Threads window (with no header) is the Current Thread column. A yellow arrow in this column marks the current execution point.
The Location column shows where each thread appears in the source code. Select the expand arrow next to the Location entry, or hover over the entry, to show a partial call stack for that thread.
Tip
For a graphical view of the call stacks for threads, use the Parallel Stacks window. To open the window, while debugging, select Debug> Windows > Parallel Stacks.
In addition to Flag, Unflag, and Unflag All Threads, the right-click context menu for Thread window items has:
- The Show Threads in Source button.
- Hexadecimal display, which changes the Thread IDs in the Threads window from decimal to hexadecimal format.
- Switch To Thread, which immediately switches execution to that thread.
- Rename, which lets you change the thread name.
- Freeze and Thaw commands.
Freeze and thaw thread execution
You can freeze and thaw, or suspend and resume, threads to control the order in which the threads perform work. Freezing and thawing threads can help you resolve concurrency issues, such as deadlocks and race conditions.
Tip
To follow a single thread without freezing other threads, which is also a common debugging scenario, see Get started debugging multithreaded applications.
To freeze and unfreeze threads:
In the Threads window, right-click any thread and then select Freeze. A Pause icon in the Current Thread column indicates that the thread is frozen.
Select Columns in the Threads window toolbar, and then select Suspended Count to display the Suspended Count column. The suspended count value for the frozen thread is 1.
Right-click the frozen thread and select Thaw.
The Pause icon disappears, and the Suspended Count value changes to 0.
Switch to another thread
You may see a The application is in break mode window when you try to switch to another thread. This window tells you that the thread does not have any code that the current debugger can display. For example, you may be debugging managed code, but the thread is native code. The window offers suggestions for resolving the issue.
To switch to another thread:
In the Threads window, make a note of the current thread ID, which is the thread with a yellow arrow in the Current Thread column. You'll want to switch back to this thread to continue your app.
Right-click a different thread and select Switch To Thread from the context menu.
Observe that the yellow arrow location has changed in the Threads window. The original current thread marker also remains, as an outline.
Look at the tooltip on the thread marker in the code source editor, and the list in the Thread dropdown on the Debug Location toolbar. Observe that the current thread has also changed there.
On the Debug Location toolbar, select a different thread from the Thread list. Note that the current thread changes in the other two locations also.
In the source code editor, right-click a thread marker, point to Switch To Thread, and select another thread from the list. Observe that the current thread changes in all three locations.
With the thread marker in source code, you can switch only to threads that are stopped at that location. By using the Threads window and Debug Location toolbar, you can switch to any thread.
You've now learned the basics of debugging multithreaded apps. You can observe, flag and unflag, and freeze and thaw threads by using the Threads window, the Thread list in the Debug Location toolbar, or thread markers in the source code editor.