Anmerkung
Der Zugriff auf diese Seite erfordert eine Genehmigung. Du kannst versuchen, dich anzumelden oder die Verzeichnisse zu wechseln.
Der Zugriff auf diese Seite erfordert eine Genehmigung. Du kannst versuchen , die Verzeichnisse zu wechseln.
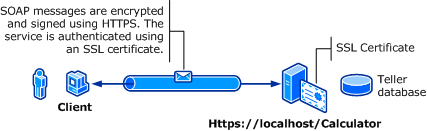
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt einen Wcf-Dienst (Windows Communication Foundation) und einen Client. Der Server benötigt ein gültiges X.509-Zertifikat, das für Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) verwendet werden kann, und die Clients müssen dem Zertifikat des Servers vertrauen. Darüber hinaus verfügt der Webdienst bereits über eine SSL-Implementierung, die verwendet werden kann. Weitere Informationen zum Aktivieren der Standardauthentifizierung für Internetinformationsdienste (INTERNET Information Services, IIS) finden Sie unter "Standardauthentifizierung".
| Charakteristisch | BESCHREIBUNG |
|---|---|
| Sicherheitsmodus | Transport |
| Interoperabilität | Mit vorhandenen Webdienstclients und Diensten |
| Authentifizierung (Server) Authentifizierung (Client) |
Ja (mit HTTPS) Ja (über Benutzername/Kennwort) |
| Integrität | Ja |
| Vertraulichkeit | Ja |
| Transport | HTTPS |
| Verbindlich | WSHttpBinding |
Dienstleistung
Der folgende Code und die folgende Konfiguration sollen unabhängig ausgeführt werden. Führen Sie eine der folgenden Aktionen aus:
Erstellen Sie einen eigenständigen Dienst, der den Code ohne Konfiguration verwendet.
Erstellen Sie einen Dienst mithilfe der bereitgestellten Konfiguration, definieren Sie jedoch keine Endpunkte.
Programmcode
Der folgende Code zeigt, wie Sie einen Dienstendpunkt erstellen, der einen Windows-Domänenbenutzernamen und ein Kennwort für die Übertragungssicherheit verwendet. Beachten Sie, dass für den Dienst ein X.509-Zertifikat erforderlich ist, um sich beim Client zu authentifizieren. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Arbeiten mit Zertifikaten und Vorgehensweise: Konfigurieren eines Ports mit einem SSL-Zertifikat.
// Create the binding.
WSHttpBinding binding = new WSHttpBinding();
binding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport;
binding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
// Create the URI for the endpoint.
Uri httpUri = new Uri("https://localhost/Calculator");
// Create the service host and add an endpoint.
ServiceHost myServiceHost = new ServiceHost(
typeof(ServiceModel.Calculator), httpUri);
myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(
typeof(ServiceModel.ICalculator), binding, "");
// Open the service.
myServiceHost.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Listening...");
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to exit.");
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the service.
myServiceHost.Close();
' Create the binding.
Dim binding As New WSHttpBinding()
binding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport
binding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType = HttpClientCredentialType.Basic
' Create the URI for the endpoint.
Dim httpUri As New Uri("https://localhost/Calculator")
' Create the service host and add an endpoint.
Dim myServiceHost As New ServiceHost(GetType(ServiceModel.Calculator), httpUri)
myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(GetType(ServiceModel.ICalculator), binding, "")
' Open the service.
myServiceHost.Open()
Console.WriteLine("Listening...")
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to exit.")
Console.ReadLine()
' Close the service.
myServiceHost.Close()
Konfiguration
Im Folgenden wird ein Dienst für die Verwendung der Standardauthentifizierung mit Sicherheit auf Transportebene konfiguriert:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="UsernameWithTransport">
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Basic" />
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<services>
<service name="BasicAuthentication.Calculator">
<endpoint address="https://localhost/Calculator"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="UsernameWithTransport"
name="BasicEndpoint"
contract="BasicAuthentication.ICalculator" />
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Kunde
Programmcode
Der folgende Code zeigt den Clientcode, der den Benutzernamen und das Kennwort enthält. Beachten Sie, dass der Benutzer einen gültigen Windows-Benutzernamen und ein gültiges Kennwort angeben muss. Der Code, der den Benutzernamen und das Kennwort zurückgibt, wird hier nicht angezeigt. Verwenden Sie ein Dialogfeld oder eine andere Schnittstelle, um den Benutzer nach den Informationen abzufragen.
Hinweis
Benutzername und Kennwort können nur mit Code festgelegt werden.
// Create the binding.
WSHttpBinding myBinding = new WSHttpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport;
myBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
// Create the endpoint address. Note that the machine name
// must match the subject or DNS field of the X.509 certificate
// used to authenticate the service.
EndpointAddress ea = new
EndpointAddress("https://machineName/Calculator");
// Create the client. The code for the calculator
// client is not shown here. See the sample applications
// for examples of the calculator code.
CalculatorClient cc =
new CalculatorClient(myBinding, ea);
// The client must provide a user name and password. The code
// to return the user name and password is not shown here. Use
// a database to store the user name and passwords, or use the
// ASP.NET Membership provider database.
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = ReturnUsername();
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = ReturnPassword();
try
{
// Begin using the client.
cc.Open();
Console.WriteLine(cc.Add(100, 11));
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the client.
cc.Close();
}
' Create the binding.
Dim myBinding As New WSHttpBinding()
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport
myBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType = HttpClientCredentialType.Basic
' Create the endpoint address. Note that the machine name
' must match the subject or DNS field of the X.509 certificate
' used to authenticate the service.
Dim ea As New EndpointAddress("https://machineName/Calculator")
' Create the client. The code for the calculator
' client is not shown here. See the sample applications
' for examples of the calculator code.
Dim cc As New CalculatorClient(myBinding, ea)
' The client must provide a user name and password. The code
' to return the user name and password is not shown here. Use
' a database to store the user name and passwords, or use the
' ASP.NET Membership provider database.
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = ReturnUsername()
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = ReturnPassword()
' Begin using the client.
Try
cc.Open()
Console.WriteLine(cc.Add(100, 11))
Console.ReadLine()
' Close the client.
cc.Close()
Catch tex As TimeoutException
Console.WriteLine(tex.Message)
cc.Abort()
Catch cex As CommunicationException
Console.WriteLine(cex.Message)
cc.Abort()
Finally
Console.WriteLine("Closed the client")
Console.ReadLine()
End Try
Konfiguration
Der folgende Code zeigt die Clientkonfiguration.
Hinweis
Sie können die Konfiguration nicht verwenden, um den Benutzernamen und das Kennwort festzulegen. Die hier gezeigte Konfiguration muss mithilfe von Code erweitert werden, um den Benutzernamen und das Kennwort festzulegen.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator" >
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Basic" />
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<client>
<endpoint address="https://machineName/Calculator"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator"
contract="ICalculator"
name="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator" />
</client>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>