Hinweis
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, sich anzumelden oder das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
In diesem Artikel wird veranschaulicht, wie Sie ein Netzwerk von Datenflussblöcken erstellen, die Bildverarbeitung in einer Windows Forms-Anwendung ausführen.
In diesem Beispiel werden Bilddateien aus dem angegebenen Ordner geladen, ein zusammengesetztes Bild erstellt und das Ergebnis angezeigt. Im Beispiel wird das Datenflussmodell verwendet, um Bilder über das Netzwerk weiterzuleiten. Im Datenflussmodell kommunizieren unabhängige Komponenten eines Programms miteinander, indem Nachrichten gesendet werden. Wenn eine Komponente eine Nachricht empfängt, führt sie eine Aktion aus und übergibt das Ergebnis dann an eine andere Komponente. Vergleichen Sie dies mit dem Steuerungsflussmodell, in dem eine Anwendung Kontrollstrukturen verwendet, z. B. bedingte Anweisungen, Schleifen usw., um die Reihenfolge der Vorgänge in einem Programm zu steuern.
Voraussetzungen
Lesen Sie Dataflow, bevor Sie diese Anleitung starten.
Hinweis
Die TPL-Datenflussbibliothek (der System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow Namespace) ist in .NET 6 und höheren Versionen enthalten. Für .NET Framework- und .NET Standard-Projekte müssen Sie das 📦 NuGet-Paket "System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow" installieren.
Abschnitte
Diese exemplarische Vorgehensweise enthält folgende Abschnitte:
Erstellen der Windows Forms-Anwendung
In diesem Abschnitt wird beschrieben, wie Sie die grundlegende Windows Forms-Anwendung erstellen und dem Hauptformular Steuerelemente hinzufügen.
So erstellen Sie die Windows Forms-Anwendung
Erstellen Sie in Visual Studio ein Visual C#- oder Visual Basic-Windows Forms-Anwendungsprojekt . In diesem Dokument wird das Projekt benannt
CompositeImages.Fügen Sie im Formular-Designer für das Hauptformular Form1.cs (Form1.vb für Visual Basic) ein ToolStrip Steuerelement hinzu.
Fügen Sie dem ToolStripButton Steuerelement ein ToolStrip Steuerelement hinzu. Legen Sie die DisplayStyle Eigenschaft auf Text und die Text Eigenschaft auf "Ordner auswählen" fest.
Fügen Sie dem ToolStripButton Steuerelement ein zweites ToolStrip Steuerelement hinzu. Legen Sie die DisplayStyle Eigenschaft auf Text, die Text Eigenschaft auf Cancel und die Enabled Eigenschaft auf
False.Fügen Sie dem Hauptformular ein PictureBox Objekt hinzu. Setzen Sie die Dock-Eigenschaft auf Fill.
Erstellen des Dataflow-Netzwerks
In diesem Abschnitt wird beschrieben, wie Sie das Datenflussnetzwerk erstellen, das die Bildverarbeitung durchführt.
So erstellen Sie das Dataflow-Netzwerk
Fügen Sie ihrem Projekt einen Verweis auf System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow.dll hinzu.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass Form1.cs (Form1.vb für Visual Basic) die folgenden
using(Usingin Visual Basic)-Anweisungen enthält:using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing; using System.Drawing.Imaging; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow; using System.Windows.Forms;Fügen Sie der Klasse
Form1die folgenden Datenmitglieder hinzu:// The head of the dataflow network. ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null; // Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network. CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;Fügen Sie die folgende Methode
CreateImageProcessingNetworkzur KlasseForm1hinzu. Diese Methode erstellt das Bildverarbeitungsnetzwerk.// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the // head node of the network. ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork() { // // Create the dataflow blocks that form the network. // // Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input // and returns a collection of Bitmap objects. var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path => { try { return LoadBitmaps(path); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection // to the next stage of the network. return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>(); } }); // Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects // and returns a single composite bitmap. var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps => { try { return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { // Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage // of the network. return null; } }); // Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form. var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap => { // Display the bitmap. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage; pictureBox1.Image = bitmap; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by // displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and // enables the user to select another folder. var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate { // Display the error image to indicate that the operation // was cancelled. pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage; pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage; // Enable the user to select another folder. toolStripButton1.Enabled = true; toolStripButton2.Enabled = false; Cursor = DefaultCursor; }, // Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context // so that the action runs on the UI thread. new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions { TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext() }); // // Connect the network. // // Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the // collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0); // Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled. // When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap. // The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the // bitmap only if it is non-null. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null); // Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled. // When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap // offers the message to operationCancelled. // operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a // predicate. createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled); // Return the head of the network. return loadBitmaps; }Implementieren Sie die
LoadBitmaps-Methode.// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path. IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path) { List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>(); // Load a variety of image types. foreach (string bitmapType in new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" }) { // Load each bitmap for the current extension. foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType)) { // Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested. cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); try { // Add the Bitmap object to the collection. bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName)); } catch (Exception) { // TODO: A complete application might handle the error. } } } return bitmaps; }Implementieren Sie die
CreateCompositeBitmap-Methode.// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects. // This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps // to create the composite image. Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps) { Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray(); // Compute the maximum width and height components of all // bitmaps in the collection. Rectangle largest = new Rectangle(); foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray) { if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width) largest.Width = bitmap.Width; if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height) largest.Height = bitmap.Height; } // Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions. Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb); // Lock the result Bitmap. var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, result.PixelFormat); // Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects. var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray select bitmap.LockBits( new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size), ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb)) .ToList(); // Compute each column in parallel. Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions { CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token }, i => { // Compute each row. for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++) { // Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions // contain the current location. int count = 0; // The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components. int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0; // For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components. foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList) { // Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image. if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j) { unsafe { byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); a += *pix; pix++; r += *pix; pix++; g += *pix; pix++; b += *pix; } count++; } } //prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner if (count == 0) break; unsafe { // Compute the average of each color component. a /= count; r /= count; g /= count; b /= count; // Set the result pixel. byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride)); byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i)); *pix = (byte)a; pix++; *pix = (byte)r; pix++; *pix = (byte)g; pix++; *pix = (byte)b; } } }); // Unlock the source bitmaps. for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++) { bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]); } // Unlock the result bitmap. result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData); // Return the result. return result; }Hinweis
Die C#-Version der
CreateCompositeBitmapMethode verwendet Zeiger, um eine effiziente Verarbeitung der System.Drawing.Bitmap Objekte zu ermöglichen. Daher müssen Sie die Option "Unsicheren Code zulassen" in Ihrem Projekt aktivieren, um das unsichere Schlüsselwort zu verwenden. Weitere Informationen zum Aktivieren von unsicherem Code in einem Visual C#-Projekt finden Sie unter Build page, Project Designer (C#).For more information about how to enable unsafe code in a Visual C# project project.
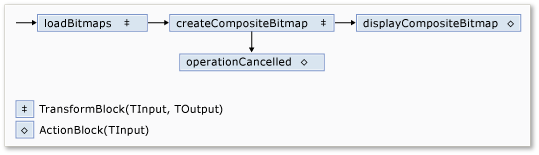
In der folgenden Tabelle werden die Member des Netzwerks beschrieben.
| Mitglied | Typ | Description |
|---|---|---|
loadBitmaps |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Verwendet einen Ordnerpfad als Eingabe und erzeugt eine Sammlung von Bitmap Objekten als Ausgabe. |
createCompositeBitmap |
TransformBlock<TInput,TOutput> | Verwendet eine Auflistung von Bitmap Objekten als Eingabe und erzeugt eine zusammengesetzte Bitmap als Ausgabe. |
displayCompositeBitmap |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Zeigt die zusammengesetzte Bitmap im Formular an. |
operationCancelled |
ActionBlock<TInput> | Zeigt ein Bild an, das angibt, dass der Vorgang abgebrochen wird, und ermöglicht es dem Benutzer, einen anderen Ordner auszuwählen. |
Um die Datenflussblöcke mit einem Netzwerk zu verbinden, verwendet dieses Beispiel die LinkTo Methode. Die LinkTo Methode enthält eine überladene Version, die ein Predicate<T> Objekt verwendet, das bestimmt, ob der Zielblock eine Nachricht akzeptiert oder ablehnt. Mit diesem Filtermechanismus können Nachrichtenblöcke nur bestimmte Werte empfangen. In diesem Beispiel kann das Netzwerk auf zwei Arten verzweigt werden. Die Hauptzweigung lädt die Bilder vom Datenträger, erstellt das zusammengesetzte Bild und zeigt dieses Bild auf dem Formular an. Der Alternativzweig bricht den aktuellen Vorgang ab. Die Predicate<T> Objekte ermöglichen es den Datenflussblöcken entlang der Hauptzweigung, zur alternativen Verzweigung zu wechseln, indem bestimmte Nachrichten abgelehnt werden. Wenn der Benutzer beispielsweise den Vorgang abbricht, erzeugt createCompositeBitmap der Datenflussblock null (Nothingin Visual Basic) als Ausgabe. Der Datenflussblock displayCompositeBitmap lehnt Eingabewerte null ab, und daher wird die Nachricht operationCancelled angeboten. Der Datenflussblock operationCancelled akzeptiert alle Nachrichten und zeigt daher ein Bild an, das angibt, dass der Vorgang abgebrochen wird.
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt das Bildverarbeitungsnetzwerk:
Da die Datenflussblöcke displayCompositeBitmap und operationCancelled auf der Benutzeroberfläche eingesetzt werden, ist es wichtig, dass diese Aktionen auf dem Benutzeroberflächenthread ausgeführt werden. Dazu stellen diese Objekte während der Konstruktion ein ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions Objekt bereit, bei dem die TaskScheduler Eigenschaft auf TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext festgelegt ist. Die TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext Methode erstellt ein TaskScheduler Objekt, das arbeit am aktuellen Synchronisierungskontext ausführt. Da die CreateImageProcessingNetwork Methode vom Handler der Schaltfläche " Ordner auswählen " aufgerufen wird, die im Benutzeroberflächenthread ausgeführt wird, werden die Aktionen für die displayCompositeBitmap und operationCancelled die Datenflussblöcke auch im Benutzeroberflächenthread ausgeführt.
In diesem Beispiel wird ein freigegebenes Abbruchtoken verwendet, anstatt die CancellationToken Eigenschaft festzulegen, da die CancellationToken Eigenschaft die Ausführung des Datenflussblocks dauerhaft abbricht. Ein Abbruchtoken ermöglicht es diesem Beispiel, dasselbe Datenflussnetzwerk mehrmals wiederzuverwenden, auch wenn der Benutzer einen oder mehrere Vorgänge abbricht. Ein Beispiel zum CancellationToken dauerhaften Abbrechen der Ausführung eines Datenflussblocks finden Sie unter How to: Cancel a Dataflow Block.
Verbinden des Dataflow-Netzwerks mit der Benutzeroberfläche
In diesem Abschnitt wird beschrieben, wie Sie das Datenflussnetzwerk mit der Benutzeroberfläche verbinden. Die Erstellung des zusammengesetzten Bilds und der Abbruch des Vorgangs werden über die Schaltflächen " Ordner auswählen " und "Abbrechen " initiiert. Wenn der Benutzer eine dieser Schaltflächen auswäht, wird die entsprechende Aktion asynchron initiiert.
So verbinden Sie das Dataflow-Netzwerk mit der Benutzeroberfläche
Erstellen Sie im Formular-Designer für das Hauptformular einen Ereignishandler für das Click Ereignis für die Schaltfläche " Ordner auswählen ".
Implementieren Sie das Click Ereignis für die Schaltfläche " Ordner auswählen ".
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button. private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to // select a folder. FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog { ShowNewFolderButton = false }; // Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder // if it exists. string initialDirectory = Path.Combine( Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures), "Sample Pictures"); if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory)) { dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory; } // Show the dialog and process the dataflow network. if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { // Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable // cancellation. cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource(); // Create the image processing network if needed. headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork(); // Post the selected path to the network. headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath); // Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button. toolStripButton1.Enabled = false; toolStripButton2.Enabled = true; // Show a wait cursor. Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor; } }Erstellen Sie im Formular-Designer für das Hauptformular einen Ereignishandler für das Click Ereignis für die Schaltfläche "Abbrechen ".
Implementieren Sie das Click Ereignis für die Schaltfläche "Abbrechen ".
// Event handler for the Cancel button. private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of // the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request. cancellationTokenSource.Cancel(); }
Vollständiges Beispiel
Das folgende Beispiel zeigt den vollständigen Code für diese exemplarische Vorgehensweise.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading.Tasks.Dataflow;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CompositeImages
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
// The head of the dataflow network.
ITargetBlock<string> headBlock = null;
// Enables the user interface to signal cancellation to the network.
CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// Creates the image processing dataflow network and returns the
// head node of the network.
ITargetBlock<string> CreateImageProcessingNetwork()
{
//
// Create the dataflow blocks that form the network.
//
// Create a dataflow block that takes a folder path as input
// and returns a collection of Bitmap objects.
var loadBitmaps = new TransformBlock<string, IEnumerable<Bitmap>>(path =>
{
try
{
return LoadBitmaps(path);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing the empty collection
// to the next stage of the network.
return Enumerable.Empty<Bitmap>();
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that takes a collection of Bitmap objects
// and returns a single composite bitmap.
var createCompositeBitmap = new TransformBlock<IEnumerable<Bitmap>, Bitmap>(bitmaps =>
{
try
{
return CreateCompositeBitmap(bitmaps);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Handle cancellation by passing null to the next stage
// of the network.
return null;
}
});
// Create a dataflow block that displays the provided bitmap on the form.
var displayCompositeBitmap = new ActionBlock<Bitmap>(bitmap =>
{
// Display the bitmap.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage;
pictureBox1.Image = bitmap;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
// Create a dataflow block that responds to a cancellation request by
// displaying an image to indicate that the operation is cancelled and
// enables the user to select another folder.
var operationCancelled = new ActionBlock<object>(delegate
{
// Display the error image to indicate that the operation
// was cancelled.
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.CenterImage;
pictureBox1.Image = pictureBox1.ErrorImage;
// Enable the user to select another folder.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = true;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = false;
Cursor = DefaultCursor;
},
// Specify a task scheduler from the current synchronization context
// so that the action runs on the UI thread.
new ExecutionDataflowBlockOptions
{
TaskScheduler = TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()
});
//
// Connect the network.
//
// Link loadBitmaps to createCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that createCompositeBitmap accepts the
// collection of bitmaps only if that collection has at least one member.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(createCompositeBitmap, bitmaps => bitmaps.Count() > 0);
// Also link loadBitmaps to operationCancelled.
// When createCompositeBitmap rejects the message, loadBitmaps
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
loadBitmaps.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Link createCompositeBitmap to displayCompositeBitmap.
// The provided predicate ensures that displayCompositeBitmap accepts the
// bitmap only if it is non-null.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(displayCompositeBitmap, bitmap => bitmap != null);
// Also link createCompositeBitmap to operationCancelled.
// When displayCompositeBitmap rejects the message, createCompositeBitmap
// offers the message to operationCancelled.
// operationCancelled accepts all messages because we do not provide a
// predicate.
createCompositeBitmap.LinkTo(operationCancelled);
// Return the head of the network.
return loadBitmaps;
}
// Loads all bitmap files that exist at the provided path.
IEnumerable<Bitmap> LoadBitmaps(string path)
{
List<Bitmap> bitmaps = new List<Bitmap>();
// Load a variety of image types.
foreach (string bitmapType in
new string[] { "*.bmp", "*.gif", "*.jpg", "*.png", "*.tif" })
{
// Load each bitmap for the current extension.
foreach (string fileName in Directory.GetFiles(path, bitmapType))
{
// Throw OperationCanceledException if cancellation is requested.
cancellationTokenSource.Token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
try
{
// Add the Bitmap object to the collection.
bitmaps.Add(new Bitmap(fileName));
}
catch (Exception)
{
// TODO: A complete application might handle the error.
}
}
}
return bitmaps;
}
// Creates a composite bitmap from the provided collection of Bitmap objects.
// This method computes the average color of each pixel among all bitmaps
// to create the composite image.
Bitmap CreateCompositeBitmap(IEnumerable<Bitmap> bitmaps)
{
Bitmap[] bitmapArray = bitmaps.ToArray();
// Compute the maximum width and height components of all
// bitmaps in the collection.
Rectangle largest = new Rectangle();
foreach (var bitmap in bitmapArray)
{
if (bitmap.Width > largest.Width)
largest.Width = bitmap.Width;
if (bitmap.Height > largest.Height)
largest.Height = bitmap.Height;
}
// Create a 32-bit Bitmap object with the greatest dimensions.
Bitmap result = new Bitmap(largest.Width, largest.Height,
PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb);
// Lock the result Bitmap.
var resultBitmapData = result.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), result.Size), ImageLockMode.WriteOnly,
result.PixelFormat);
// Lock each source bitmap to create a parallel list of BitmapData objects.
var bitmapDataList = (from bitmap in bitmapArray
select bitmap.LockBits(
new Rectangle(new Point(), bitmap.Size),
ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format32bppArgb))
.ToList();
// Compute each column in parallel.
Parallel.For(0, largest.Width, new ParallelOptions
{
CancellationToken = cancellationTokenSource.Token
},
i =>
{
// Compute each row.
for (int j = 0; j < largest.Height; j++)
{
// Counts the number of bitmaps whose dimensions
// contain the current location.
int count = 0;
// The sum of all alpha, red, green, and blue components.
int a = 0, r = 0, g = 0, b = 0;
// For each bitmap, compute the sum of all color components.
foreach (var bitmapData in bitmapDataList)
{
// Ensure that we stay within the bounds of the image.
if (bitmapData.Width > i && bitmapData.Height > j)
{
unsafe
{
byte* row = (byte*)(bitmapData.Scan0 + (j * bitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
a += *pix; pix++;
r += *pix; pix++;
g += *pix; pix++;
b += *pix;
}
count++;
}
}
//prevent divide by zero in bottom right pixelless corner
if (count == 0)
break;
unsafe
{
// Compute the average of each color component.
a /= count;
r /= count;
g /= count;
b /= count;
// Set the result pixel.
byte* row = (byte*)(resultBitmapData.Scan0 + (j * resultBitmapData.Stride));
byte* pix = (byte*)(row + (4 * i));
*pix = (byte)a; pix++;
*pix = (byte)r; pix++;
*pix = (byte)g; pix++;
*pix = (byte)b;
}
}
});
// Unlock the source bitmaps.
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapArray.Length; i++)
{
bitmapArray[i].UnlockBits(bitmapDataList[i]);
}
// Unlock the result bitmap.
result.UnlockBits(resultBitmapData);
// Return the result.
return result;
}
// Event handler for the Choose Folder button.
private void toolStripButton1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a FolderBrowserDialog object to enable the user to
// select a folder.
FolderBrowserDialog dlg = new FolderBrowserDialog
{
ShowNewFolderButton = false
};
// Set the selected path to the common Sample Pictures folder
// if it exists.
string initialDirectory = Path.Combine(
Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.CommonPictures),
"Sample Pictures");
if (Directory.Exists(initialDirectory))
{
dlg.SelectedPath = initialDirectory;
}
// Show the dialog and process the dataflow network.
if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
// Create a new CancellationTokenSource object to enable
// cancellation.
cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
// Create the image processing network if needed.
headBlock ??= CreateImageProcessingNetwork();
// Post the selected path to the network.
headBlock.Post(dlg.SelectedPath);
// Enable the Cancel button and disable the Choose Folder button.
toolStripButton1.Enabled = false;
toolStripButton2.Enabled = true;
// Show a wait cursor.
Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor;
}
}
// Event handler for the Cancel button.
private void toolStripButton2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Signal the request for cancellation. The current component of
// the dataflow network will respond to the cancellation request.
cancellationTokenSource.Cancel();
}
~Form1()
{
cancellationTokenSource.Dispose();
}
}
}
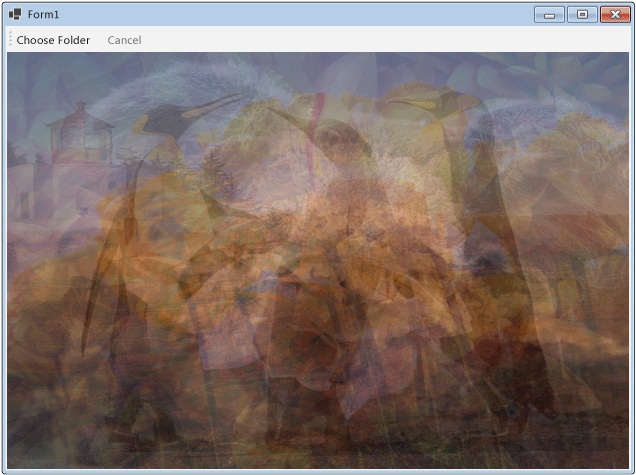
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt eine typische Ausgabe für den allgemeinen Ordner \Sample Pictures\.