Hinweis
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, sich anzumelden oder das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
Quantifizierervorgänge geben einen Boolean Wert zurück, der angibt, ob einige oder alle Elemente in einer Sequenz eine Bedingung erfüllen.
Die folgende Abbildung zeigt zwei verschiedene Quantifizierervorgänge für zwei verschiedene Quellsequenzen. Bei dem ersten Vorgang wird gefragt, ob eines der Elemente das Zeichen "A" ist. Der zweite Vorgang fragt, ob alle Elemente das Zeichen "A" sind. Beide Methoden geben in diesem Beispiel zurück true .
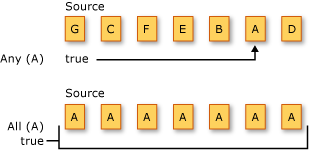
Die Standardabfrageoperatormethoden, die Quantifizierervorgänge ausführen, sind im folgenden Abschnitt aufgeführt.
Methodik
| Methodenname | BESCHREIBUNG | Syntax des Visual Basic-Abfrageausdrucks | Mehr Informationen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alle | Bestimmt, ob alle Elemente in einer Sequenz eine Bedingung erfüllen. | Aggregate … In … Into All(…) |
Enumerable.All Queryable.All |
| Beliebig | Bestimmt, ob elemente in einer Sequenz eine Bedingung erfüllen. | Aggregate … In … Into Any() |
Enumerable.Any Queryable.Any |
| Enthält | Bestimmt, ob eine Sequenz ein angegebenes Element enthält. | Nicht zutreffend. | Enumerable.Contains Queryable.Contains |
Beispiele für die Abfrageausdruckssyntax
In diesen Beispielen wird die Aggregate Klausel in Visual Basic als Teil der Filterbedingung in einer LINQ-Abfrage verwendet.
Im folgenden Beispiel werden die Aggregate-Klausel und die All-Erweiterungsmethode verwendet, um aus einer Sammlung die Personen zurückzugeben, deren Haustiere alle älter als ein bestimmtes Alter sind.
Class Person
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Pets As Pet()
End Class
Class Pet
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Age As Integer
End Class
Sub All()
Dim barley As New Pet With {.Name = "Barley", .Age = 4}
Dim boots As New Pet With {.Name = "Boots", .Age = 1}
Dim whiskers As New Pet With {.Name = "Whiskers", .Age = 6}
Dim bluemoon As New Pet With {.Name = "Blue Moon", .Age = 9}
Dim daisy As New Pet With {.Name = "Daisy", .Age = 3}
Dim charlotte As New Person With {.Name = "Charlotte", .Pets = New Pet() {barley, boots}}
Dim arlene As New Person With {.Name = "Arlene", .Pets = New Pet() {whiskers}}
Dim rui As New Person With {.Name = "Rui", .Pets = New Pet() {bluemoon, daisy}}
' Create the list of Person objects that will be queried.
Dim people As New System.Collections.Generic.List(Of Person)(New Person() {charlotte, arlene, rui})
Dim query = From pers In people
Where (Aggregate pt In pers.Pets Into All(pt.Age > 2))
Select pers.Name
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each name As String In query
sb.AppendLine(name)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' Arlene
' Rui
End Sub
Im nächsten Beispiel wird die Aggregate Klausel und die Any Erweiterungsmethode verwendet, um aus einer Auflistung die Personen zurückzugeben, die mindestens ein Haustier haben, das älter als ein angegebenes Alter ist.
Class Person
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Pets As Pet()
End Class
Class Pet
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Age As Integer
End Class
Sub Any()
Dim barley As New Pet With {.Name = "Barley", .Age = 4}
Dim boots As New Pet With {.Name = "Boots", .Age = 1}
Dim whiskers As New Pet With {.Name = "Whiskers", .Age = 6}
Dim bluemoon As New Pet With {.Name = "Blue Moon", .Age = 9}
Dim daisy As New Pet With {.Name = "Daisy", .Age = 3}
Dim charlotte As New Person With {.Name = "Charlotte", .Pets = New Pet() {barley, boots}}
Dim arlene As New Person With {.Name = "Arlene", .Pets = New Pet() {whiskers}}
Dim rui As New Person With {.Name = "Rui", .Pets = New Pet() {bluemoon, daisy}}
' Create the list of Person objects that will be queried.
Dim people As New System.Collections.Generic.List(Of Person)(New Person() {charlotte, arlene, rui})
Dim query = From pers In people
Where (Aggregate pt In pers.Pets Into Any(pt.Age > 7))
Select pers.Name
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each name As String In query
sb.AppendLine(name)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' Rui
End Sub
