Hinweis
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, sich anzumelden oder das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
Für den Zugriff auf diese Seite ist eine Autorisierung erforderlich. Sie können versuchen, das Verzeichnis zu wechseln.
Von Mark Russinovich
Veröffentlicht: 16. Dezember 2025
Einführung
Coreinfo ist ein Hilfsprogramm, das Ihnen die Zuordnung zwischen logischen Prozessoren und dem physischen Prozessor, NUMA-Knoten und Socket zeigt, auf dem sie sich befinden, sowie die dem jeweiligen logischen Prozessor zugewiesenen Caches. Es verwendet Windows-APIs (Benutzermodus und Kernelmodus) auf niedriger Ebene, um detaillierte CPU-Topologieinformationen direkt vom Betriebssystem abzurufen. Die Befehlszeilenversion gibt die Darstellung der Zuordnung zu einem logischen Prozessor mit einem Sternchen z.B. "*" aus. Die Benutzeroberfläche bietet mehrere spezialisierte Ansichten, um verschiedene Aspekte der CPU-Topologie Ihres Systems zu untersuchen, einschließlich logischer und physischer Kerne, NUMA-Knoten, Sockets, Cachehierarchien und Echtzeitleistungsmetriken. Coreinfo ist nützlich, um Einblicke in die Prozessor- und Cachetopologie des Systems zu erhalten.
Installation
Extrahieren Sie das Archiv in ein Verzeichnis und führen Sie dann Coreinfo aus, indem Sie diesen Befehl aus diesem Verzeichnis Coreinfo / Coreinfo64 oder Coreinfo64a, abhängig von der Architektur, eingeben. Starten Sie CoreInfoEx / CoreInfoEx64 / CoreInfoEx64a für die UI-Version.
Hinweis: Einige Features erfordern möglicherweise Administratorrechte für den vollständigen Abruf von Informationen.
Übersicht über die Benutzeroberfläche
Die Coreinfo-Benutzeroberfläche besteht aus mehreren wichtigen Komponenten:
Hauptfensterlayout
- Oberes Panel: Zeigt Systeminformationen einschließlich CPU-Name, Architektur und Kernanzahl an.
- Navigationsbereich (links): Bietet schnellen Zugriff auf verschiedene Ansichten
- Inhaltsbereich (Zentriert): Zeigt die Daten und Visualisierungen der ausgewählten Ansicht an.
- Detailbereich (unten): Zeigt detaillierte Informationen an, wenn Kerne oder Zellen ausgewählt werden
- Einstellungen: Access-Darstellungsoptionen und Anwendungseinstellungen
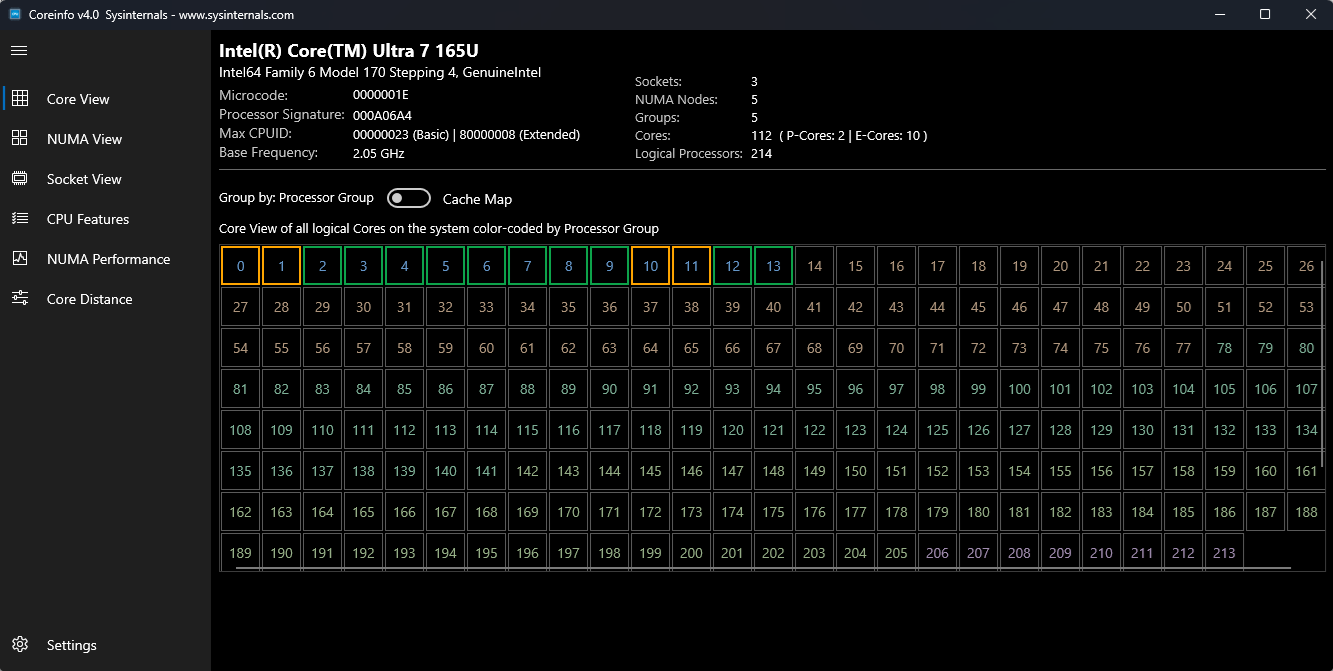 Hauptfenster mit dem vollständigen UI-Layout, dunklem Modus
Hauptfenster mit dem vollständigen UI-Layout, dunklem Modus
Navigationsansichten
Der linke Navigationsbereich bietet Zugriff auf sechs spezialisierte Ansichten:
1. Kernansicht
In der Kernansicht werden alle logischen Prozessoren in Ihrem System in einem Rasterlayout angezeigt, die die Beziehung zwischen logischen Kernen und ihren physischen Ressourcen anzeigen.
Features:
- Rasterlayout: Jede Zelle stellt einen logischen Prozessor dar.
-
Kerntypindikatoren:
- P-Kerne (Performance-Kerne) – auffällig farbig
- E-Cores (Effizienzkerne) - anders gefärbt
- Standardkerne – Standardfarbe
- Umschaltfläche für die Cachezuordnung: Wechseln zwischen Standardansicht und Cachehierarchieansicht
- Interaktive Auswahl: Klicken Sie auf einen beliebigen Kern, um detaillierte Informationen im unteren Bereich anzuzeigen.
Angezeigte Informationen:
- Logische Prozessornummer
- Kerntyp (P-Core/E-Core, falls zutreffend)
- Zugeordnete Cacheebenen (L1, L2, L3)
- NUMA-Knotenzuweisung
- Socketzuweisung
- Gruppenzuweisung
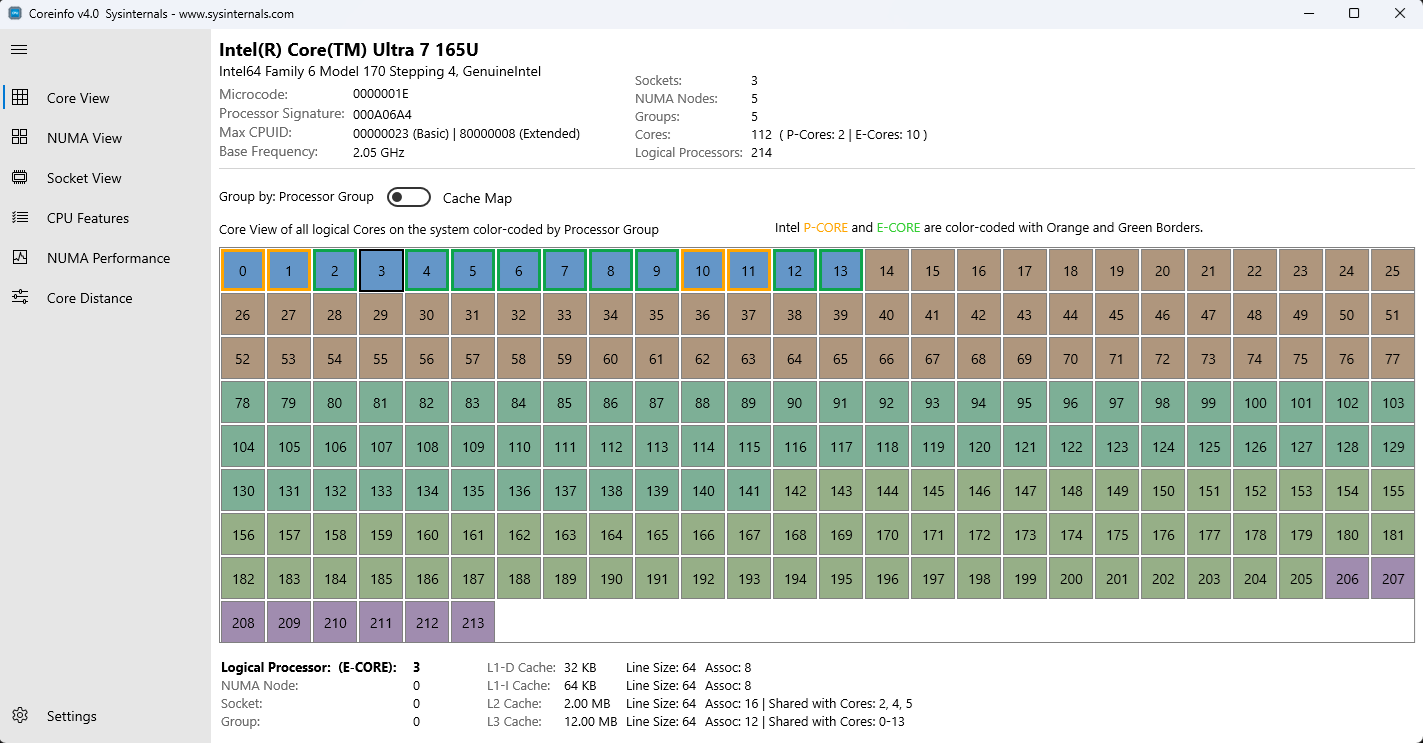 Anzeige logischer Prozessoren im Rasterlayout
Anzeige logischer Prozessoren im Rasterlayout
Detailbereichsinformationen (wenn ein Kern ausgewählt ist):
- Prozessormaske und Affinität
- Cachehierarchie (Datencache, Anweisungscache, Einheitlicher Cache)
- Cachegrößen und -assoziivität
- Größen der Cachezeilen
2. NUMA-Ansicht
Die NUMA-Ansicht (nicht einheitlicher Speicherzugriff) organisiert Kerne nach ihren NUMA-Knotenzuweisungen, wodurch die Speicherlokalität und Zugriffsmuster leicht zu verstehen sind.
Features:
- Node-Based Organisation: Kerne gruppiert nach NUMA-Knoten
- Physische und logische Kerne: Zeigt beide Anzahlen für jeden Knoten an.
- Speicherinformationen: Zeigt den verfügbaren Arbeitsspeicher pro NUMA-Knoten an.
-
Interaktive Navigation:
- Klicken Sie mit einem Klick auf einen NUMA-Knoten, um die Details im unteren Detailbereich anzuzeigen.
- Doppelklicken Sie auf einen NUMA-Knoten, um zur Kernansicht zu navigieren, die alle Kerne aus diesem ausgewählten NUMA-Knoten anzeigt.
- Hierarchische Anzeige: Zeigt die Beziehung zwischen NUMA-Knoten und Kernen an.
Angezeigte Informationen:
- Anzahl der NUMA-Knoten
- Kerne pro NUMA-Knoten (physisch und logisch)
- Arbeitsspeicherkapazität pro Knoten
- Kernverteilung über Knoten hinweg
- Effizienzkernanzahl (falls zutreffend)
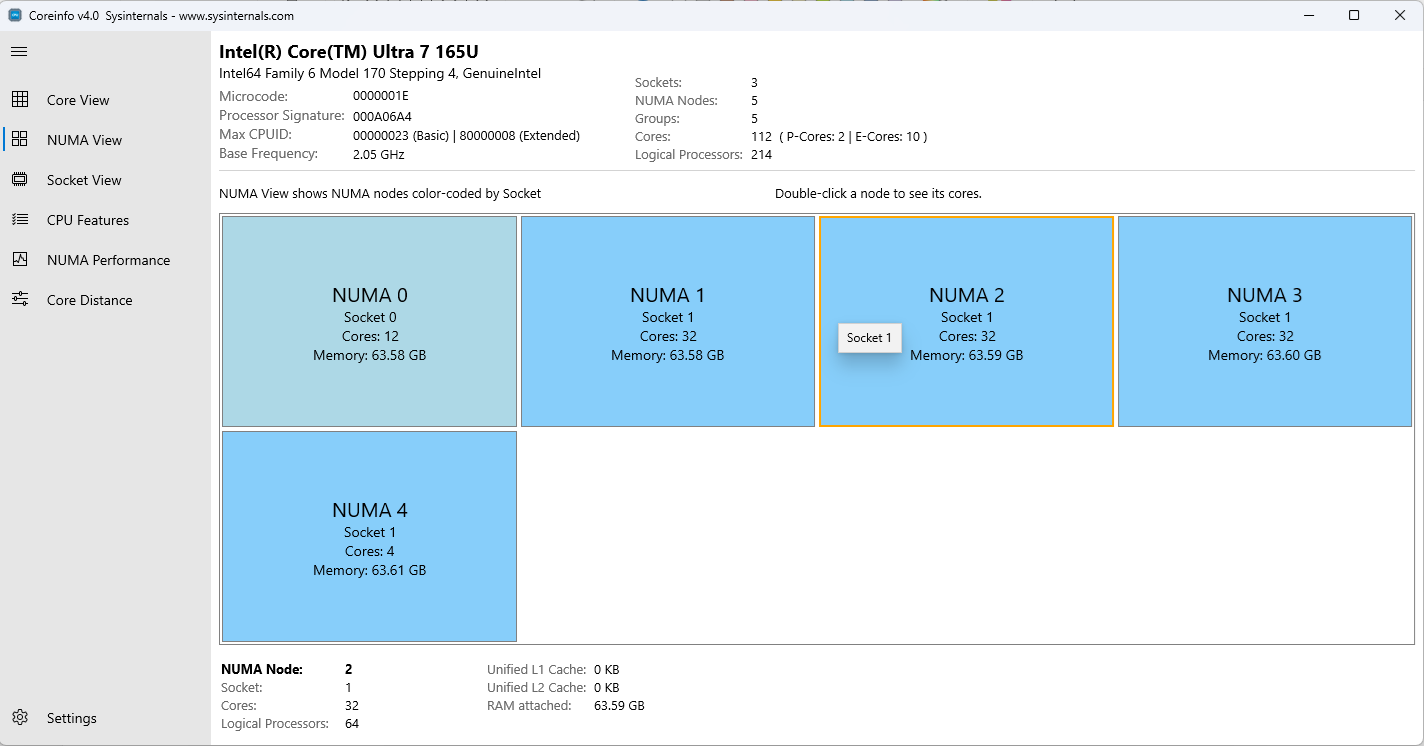 NUMA-Ansicht zeigt Kerne, die nach NUMA-Knoten organisiert sind
NUMA-Ansicht zeigt Kerne, die nach NUMA-Knoten organisiert sind
Anwendungsfälle:
- Optimieren von Speicherzugriffsmustern
- Grundlegendes zur Leistungsbewertung von NUMA-fähigen Anwendungen
- Planen der Thread-/Prozessplatzierung für optimale Leistung
3. Socket-Ansicht
Die Socketansicht zeigt Kerne an, die nach ihrem physischen CPU-Socket organisiert sind, nützlich für das Verständnis von Multi-Socket-Systemen und der Ressourcenverteilung auf Socketebene.
Features:
- Socket-Based Gruppierung: Kerne, die nach physischem Sockel organisiert sind
- Socketinformationen: Socketanzahl und Kernverteilung
-
Interaktive Navigation:
- Einzelklick auf einen Socket, um seine Details im unteren Detailbereich anzuzeigen
- Doppelklicken Sie auf einen Socket, um zur Core-Ansicht zu navigieren, die alle Kerne aus diesem ausgewählten Socket anzeigt.
- Cache-Sharing: Zeigen, welche Kerne auf Sockelebene Caches teilen
Angezeigte Informationen:
- Anzahl der physischen Sockets
- Kerne pro Socket (physisch und logisch)
- Cacheinformationen auf Socketebene
- NUMA-Knoten pro Socket
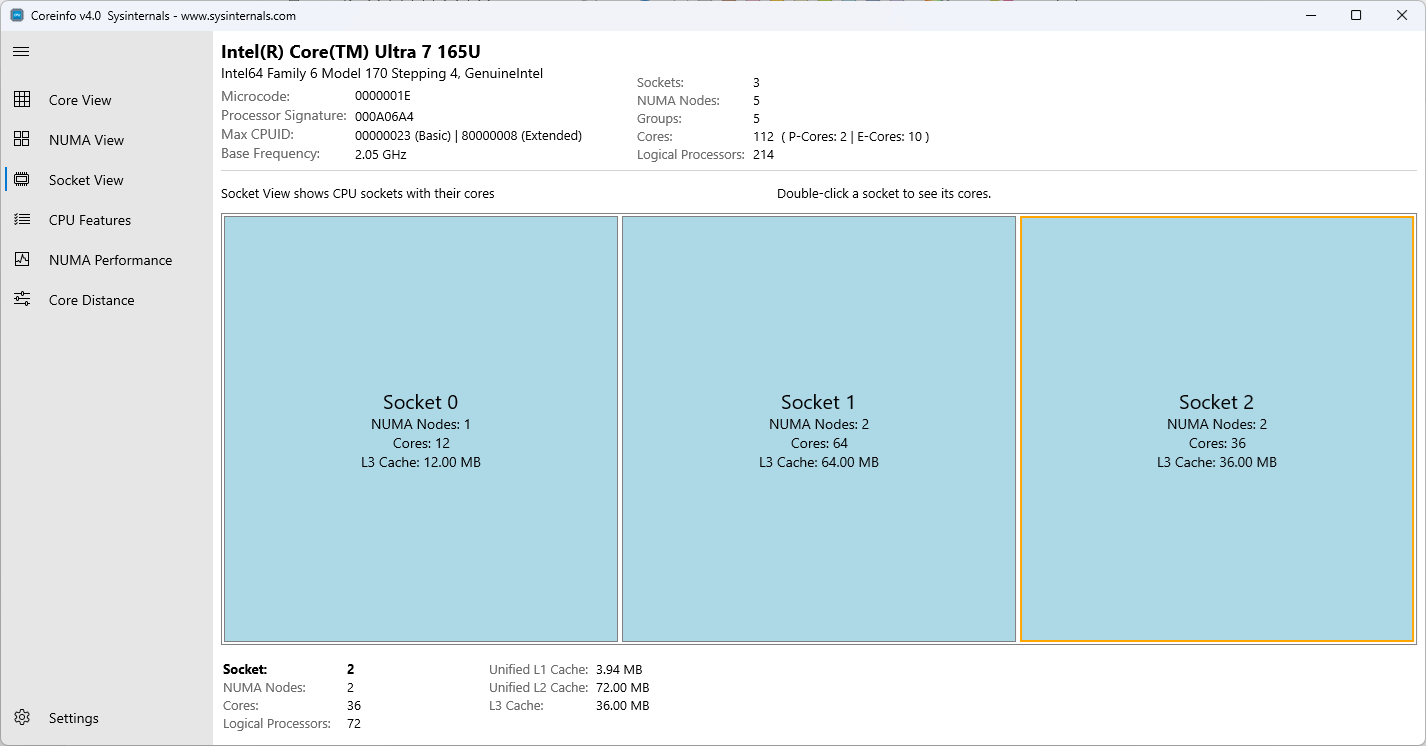 Socketansicht mit nach CPU-Sockets organisierten Kernen
Socketansicht mit nach CPU-Sockets organisierten Kernen
Anwendungsfälle:
- Multi-Socket-Systemanalyse
- Verständnis der Kosten für die Kommunikation über Sockets hinweg
- Planen der Workloadverteilung in Multisocketservern
4. Ansicht der CPU-Features
In der Ansicht "CPU-Features" wird eine umfassende Liste der Prozessorfunktionen, Anweisungssatzerweiterungen und Hardwarefeatures angezeigt, die von Ihrer CPU unterstützt werden.
Features:
- Durchsuchbare Liste: Schnelle Suche nach bestimmten CPU-Features mithilfe der Suchleiste
-
Statusindikatoren: Klare visuelle Anzeige unterstützter/nicht unterstützter Features mithilfe von Farbcodierung
- Unterstützte Features werden in normaler Farbe angezeigt.
- Nicht unterstützte/deaktivierte Features sind abgeblendet
-
Featurekategorien:
- Virtualisierung (VMX, SVM, HYPERVISOR)
- 64-Bit-Unterstützung (EM64T, NX)
- Anweisungssätze (SSE, AVX, AES usw.)
- Energieverwaltung (EIST, ACPI, Thermal)
- Sicherheitsfeatures (SMX, SKINIT)
- Speicherfunktionen (PAE, PAT, PSE)
- Debug- und Überwachungsfunktionen
Angezeigte Informationen:
- Featureabkürzung
- Featurestatus (unterstützt/nicht unterstützt)
- Beschreibung des vollständigen Features (im Detailbereich)
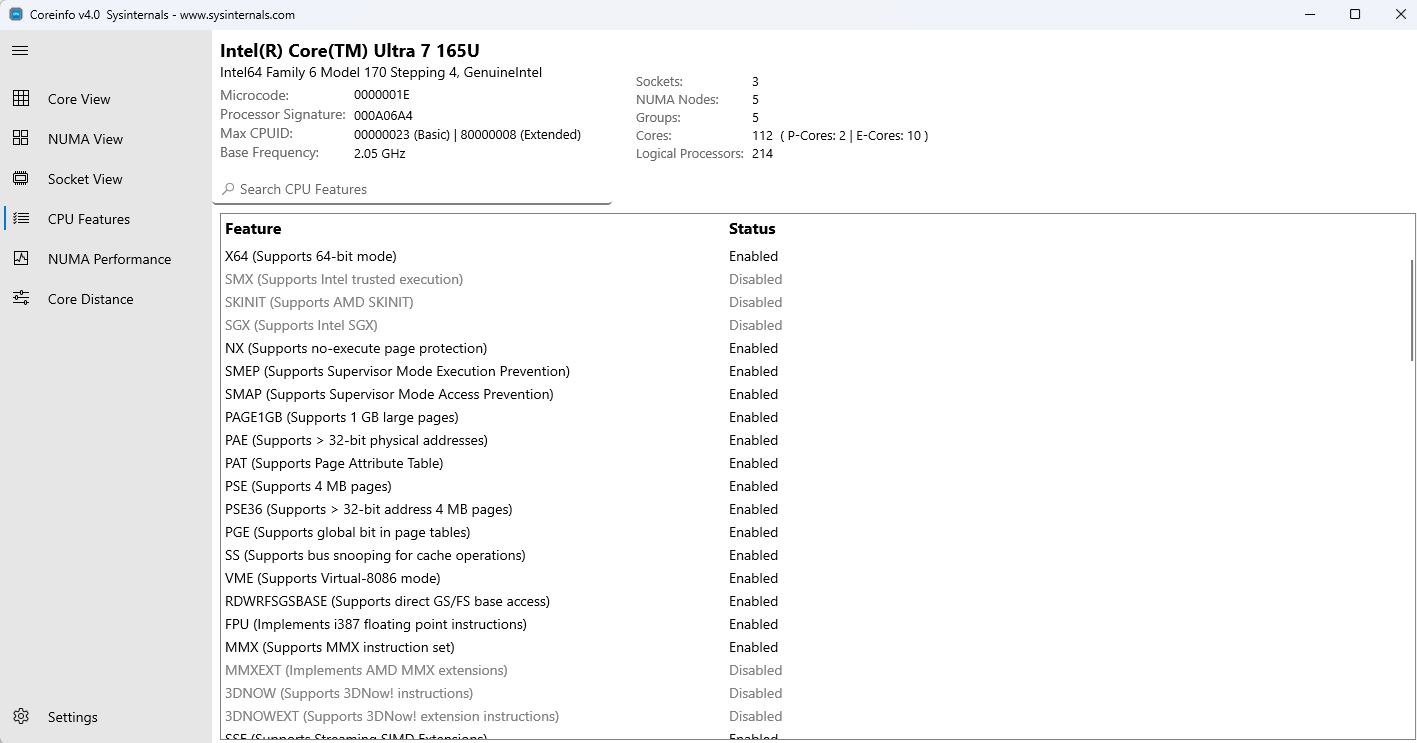 CPU-Features-Ansicht mit der Liste der Prozessorfähigkeiten
CPU-Features-Ansicht mit der Liste der Prozessorfähigkeiten
Hinweis: Einige Virtualisierungsfeatures (z. B. VMX, SVM) können fälschlicherweise als nicht verfügbar gemeldet werden, wenn ein Hypervisor aktiv ausgeführt wird oder von einem virtuellen Computer aus ausgeführt wird. Coreinfo muss auf einem System ohne einen laufenden Hypervisor ausgeführt werden, um genaue Ergebnisse zu erzielen.
Anwendungsfälle:
- Überprüfen der Verfügbarkeit des Befehlssatzes vor der Bereitstellung von Anwendungen
- Überprüfen der Virtualisierungsunterstützung
- Grundlegendes zur Prozessorgenerierung und -funktionen
- Debuggen von Leistungsproblemen im Zusammenhang mit fehlenden CPU-Features
5. NUMA-Leistungsansicht
Die NUMA-Leistungsansicht bietet eine Rastervisualisierung mit Speicherzugriffskosten zwischen NUMA-Knoten und hilft dabei, Leistungsengpässe in NUMA-Systemen zu identifizieren.
Features:
- Rastervisualisierung: Matrix mit relativen Speicherzugriffskosten zwischen NUMA-Knoten
- Interaktive Matrix: Zeigen Sie mit dem Mauszeiger auf Zellen, um detaillierte Leistungsinformationen anzuzeigen
- Real-Time Updates: Leistungsdatenaktualisierungen dynamisch durch Auswählen der Schaltfläche "Aktualisieren"
- Relative Kostenanzeige: Zeigt die relativen Kosten für den Zugriff auf den Arbeitsspeicher von verschiedenen NUMA-Knoten an.
Angezeigte Informationen:
- NxN-Matrix, wobei N = Anzahl der NUMA-Knoten
- Speicherzugriffskosten vom Quellknoten NUMA (Zeile) bis zum Ziel-NUMA-Knoten (Spalte)
- Numerische Werte mit relativen Leistungskosten
- Diagonale Zellen zeigen lokalen Speicherzugriff (in der Regel niedrigste Kosten)
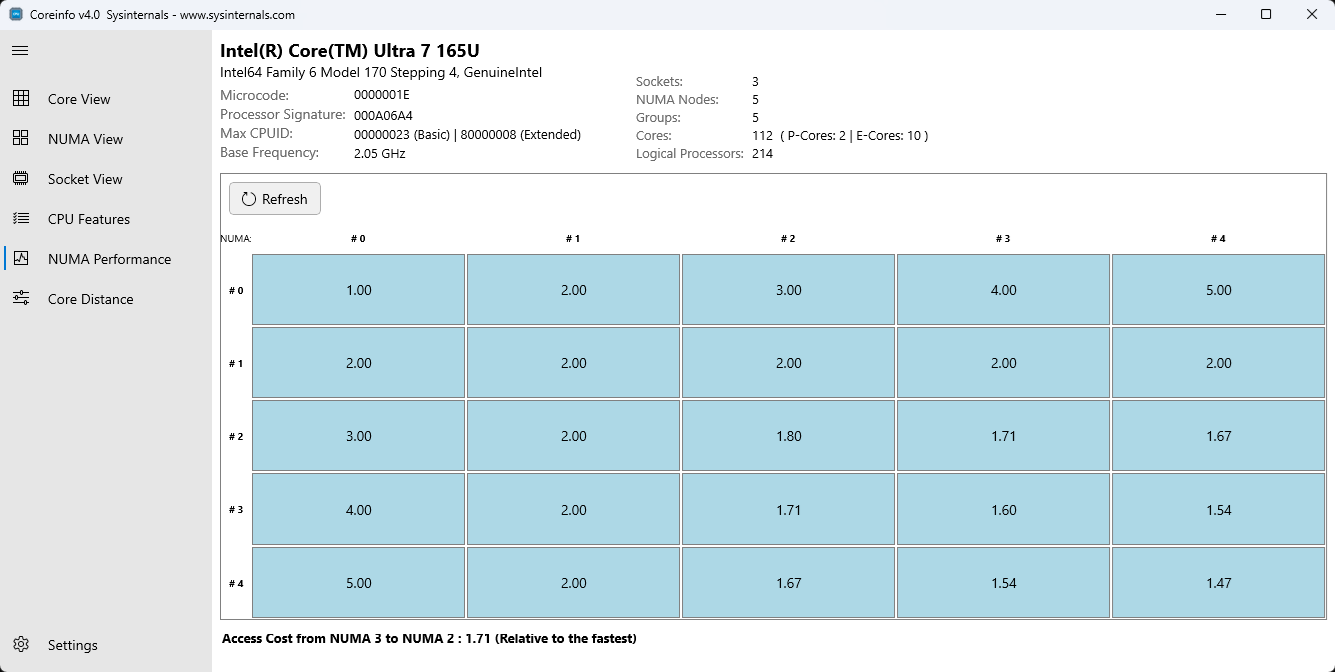 NUMA Performance Grid mit Speicherzugriffskosten
NUMA Performance Grid mit Speicherzugriffskosten
Grundlegendes zum Raster:
- Diagonale Elemente: Stellen den lokalen Speicherzugriff dar (Knoten, der auf seinen eigenen Speicher zugreift) – in der Regel die niedrigsten Werte
- Off-diagonale Elemente: Sie stellen den Zugriff auf entfernten Speicher mit höheren relativen Kosten dar.
- Symmetrie: Die Matrix ist möglicherweise nicht perfekt symmetrisch, da die Zugriffskosten je nach Richtung variieren können.
Anwendungsfälle:
- Identifizieren von Leistungsengpässen bei NUMA
- Optimieren von Speicherzuweisungsstrategien
- Planungsprozess/Thread-Pinning für NUMA-Systeme
- Grundlegendes zu Knotenübergreifenden Speicherzugriffsstrafen
6. Kernabstandsansicht
Die Core Distance View zeigt eine detaillierte Wärmekarte der Kommunikationskosten zwischen einzelnen CPU-Kernen an und bietet Einblicke in die Kern-zu-Core-Latenz und Kommunikationseffizienz.
Features:
-
Core-Level Heatmap: Farbcodierte Matrix mit relativen Abständen zwischen Kernen
- Grün/Blau = Niedrige Latenz (derselbe Kerncluster, freigegebener Cache)
- Gelb/Orange = mittlere Latenz (selben Socket, unterschiedliche Cluster)
- Rot = Hohe Latenz (unterschiedliche Sockets oder NUMA-Knoten)
- Interaktive Erkundung: Zeigen Sie auf den Rasterbereich, um detaillierte Entfernungsinformationen anzuzeigen
- Granulare Analyse: Zeigt Kern-zu-Kern-Beziehungen auf der besten Granularität
- Dynamische Aktualisierung: Verwenden Der Schaltfläche "Aktualisieren" zum dynamischen Abrufen aktualisierter Kernabstandsdaten
Angezeigte Informationen:
- NxN-Matrix, wobei N = Anzahl der logischen Prozessoren
- Relative Entfernung/Latenz vom Quellkern (Zeile) zum Zielkern (Spalte)
- Farbcodierung für schnelle visuelle Identifizierung von Kernbeziehungen
- Detaillierte Entfernungsmetriken im Detailbereich
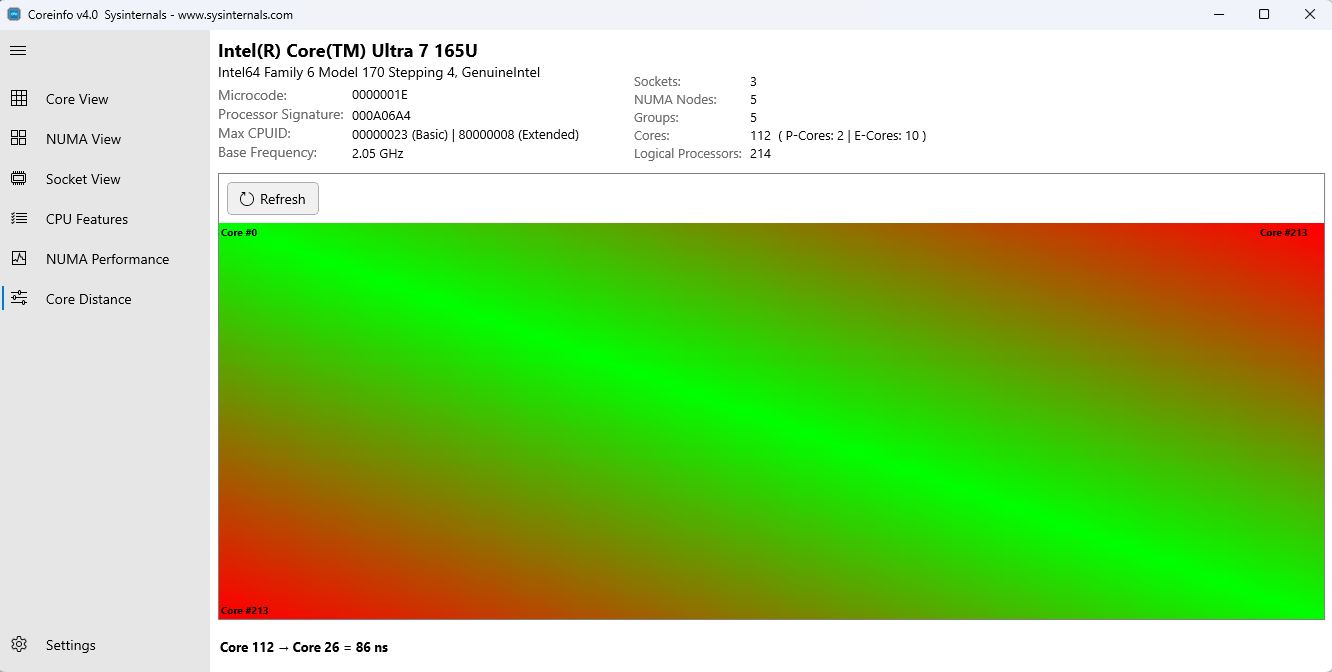 Abstand Heatmap mit Kern-zu-Kern-Kommunikationskosten
Abstand Heatmap mit Kern-zu-Kern-Kommunikationskosten
Grundlegendes zur Entfernungskarte:
- Diagonale Elemente: Immer Null (Kern für sich selbst)
- Geringer Abstand (grün): Kerne teilen L2- oder L3-Cache
- Mittlerer Abstand (gelb):Kerne auf demselben Socket, aber unterschiedliche Cachedomänen
- Hoher Abstand (rot): Kerne auf verschiedenen Sockets oder NUMA-Knoten
Anwendungsfälle:
- Optimierung der Threadaffinität
- Grundlegendes zu Cachekoherenzdomänen
- Identifizieren optimaler Kernpaare für die Kommunikation von Threads
- Analysieren der Multithread-Anwendungsleistung
- Planung von CPU-Zuordnungsstrategien für Anwendungen mit niedriger Latenz
Interaktive Funktionen
Kernauswahl und Details
Durch Klicken auf einen Kern in einer beliebigen Ansicht (Core, NUMA oder Socket) werden detaillierte Informationen im unteren Detailbereich angezeigt:
- Prozessorinformationen: Logische Prozessornummer, Maske und Affinität
-
Cachehierarchie:
- L1-Datencache (Größe, Zuordnung, Zeilengröße)
- L1-Anweisungscache (Größe, Zuordnung, Zeilengröße)
- L2-Cache (Größe, Zuordnung, Zeilengröße)
- L3-Cache (Größe, Zuordnung, Zeilengröße)
- Topologieinformationen: NUMA-Knoten-, Socket- und Gruppenzuweisungen
- Kerntyp: P-Core, E-Core oder Standardkernbezeichnung
Suchfunktionalität
Die Ansicht "CPU-Features" enthält eine Suchleiste, mit der Sie bestimmte Prozessorfeatures schnell finden können:
- Klicken Sie auf das Suchsymbol
- Geben Sie den Featurenamen oder die Abkürzung ein.
- Die Liste filtert automatisch, um übereinstimmende Features anzuzeigen.
- Löschen der Suche zum Wiederherstellen der vollständigen Liste
Cachezuordnungs-Umschalter
Wechseln Sie in der Kernansicht zwischen zwei Visualisierungsmodi:
- Standardmodus: Zeigt Kerne in ihrer logischen Anordnung an
- Cache-Kartierungsmodus: Organisiert Kerne neu, um die Beziehungen zur Cache-Freigabe zu visualisieren
Navigation zwischen Ansichten
- Verwenden des linken Navigationsbereichs zum Wechseln zwischen Ansichten
- Wenn Sie einen bestimmten NUMA-Knoten oder Socket anzeigen, kehren Sie durch erneutes Klicken auf dieselbe Ansicht zur Gesamtansicht zurück.
- Die aktuelle Ansicht ist im Navigationsbereich hervorgehoben.
Einstellungen und Anpassungen
Greifen Sie auf die Einstellungen über die Option "Einstellungen" im Navigationsmenü zu.
Darstellungseinstellungen
Designoptionen:
- Licht: Lichtfarbschema optimiert für helle Umgebungen
- Dunkel: Dunkles Farbschema zur Reduzierung der Augenbelastung
- Systemstandard: Entspricht automatisch Ihrer Windows-Designeinstellung
In Datei speichern
Exportieren von Kerntopologiedaten:
- Verwenden Sie die Option Speichern unter, um Kerntopologiedaten in einer Datei abzulegen.
- Das Ausgabeformat ist identisch mit der Befehlszeilentoolausgabe.
Verständnis Ihrer Systemtopologie
Kerntypen (Hybridarchitektur)
Moderne CPUs können Hybridarchitekturen mit unterschiedlichen Kerntypen aufweisen:
- P-Cores (Performance): Hochleistungskerne, die für Singlethreads und anspruchsvolle Workloads optimiert sind
- E-Cores (Effizienz):Energieeffiziente Kerne, die für Hintergrundaufgaben und Multithread-Workloads optimiert sind
Die Coreinfo-Benutzeroberfläche identifiziert und unterscheidet diese Kerntypen in allen anwendbaren Ansichten eindeutig.
NUMA-Architektur
Was ist NUMA? Nicht-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) ist ein Speicherdesign, bei dem jeder Prozessor über lokalen Speicher verfügt, auf den er schnell zugreifen kann, und Remotespeicher, der die Kommunikation zwischen Prozessor erfordert.
Warum es wichtig ist:
- Der Zugriff auf den lokalen Speicher ist wesentlich schneller als der Remotezugriff.
- Die Anwendungsleistung kann erheblich von der NUMA-Platzierung beeinflusst werden.
- Das Verständnis der NUMA-Topologie ist für das Hochleistungsrechnen von entscheidender Bedeutung.
Verwenden der Coreinfo-Benutzeroberfläche für NUMA-Optimierung:
- Verwenden der NUMA-Ansicht zum Verständnis der NUMA-Topologie Ihres Systems
- Überprüfen der NUMA-Leistungsansicht , um Speicherzugriffskosten anzuzeigen
- Optimieren der Thread-/Prozessplatzierung basierend auf NUMA-Knotenzuweisungen
- Verwenden Sie die Core Distance View, um die Core-zu-Core-Kommunikation innerhalb und über NUMA-Knoten hinweg zu verstehen.
Cachehierarchie
Cacheebenen:
- L1-Cache: Kleinste und schnellste, in Daten- und Anweisungscaches aufgeteilt
- L2-Cache: Größerer einheitlicher Cache, in der Regel privat für jeden Kern
- L3-Cache: Größter einheitlicher Cache, häufig gemeinsam mit mehreren Kernen
Verwenden von Cacheinformationen:
- Verstehen, welche Kerne Cacheressourcen gemeinsam nutzen
- Optimieren der Datenlokalität für Cachefreigabekerne
- Verwenden des Cachezuordnungsmodus in der Kernansicht zum Visualisieren von Cachedomänen
Verwenden von Coreinfo über die Befehlszeile
Für jede Ressource wird eine Zuordnung der für das Betriebssystem sichtbaren Prozessoren angezeigt, die den angegebenen Ressourcen entsprechen. Dabei steht „*“ für die entsprechenden Prozessoren. Bei einem System mit vier Kernen beispielsweise eine Zeile in der Cacheausgabe mit einer Zuordnung, die gemeinsam von den Kernen 3 und 4 genutzt wird.
Syntax:
coreinfo [-c][-f][-g][-l][-n][-s][-m][-v]
| Parameter | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| -c | Sichert Informationen zu Kernen. |
| -f | Sichert Informationen zu Hauptfunktionen. |
| -g | Sichert Informationen zu Gruppen. |
| -l | Sichert Informationen zu Caches. |
| -n | Sichert Informationen zu NUMA-Knoten. |
| -s | Sichert Informationen zu Sockets. |
| -m | Sichert NUMA-Zugriffskosten. |
| -v | Sichert nur virtualisierungsbezogene Features, einschließlich Unterstützung für die Adressübersetzung der zweiten Ebene. (erfordert Administratorrechte auf Intel-Systemen.) |
Alle Optionen außer -v standardmäßig ausgewählt.
Coreinfo-Ausgabe:
Coreinfo v4.0 - Dump information on system CPU and memory topology
Copyright © 2008-2025 Mark Russinovich
Sysinternals - www.sysinternals.com
Intel(R) Core(TM) Ultra 7 165U
Intel64 Family 6 Model 170 Stepping 4, GenuineIntel
Microcode signature: 0000001E
Processor signature: 000A06A4
Maximum implemented CPUID leaves: 00000023 (Basic), 80000008 (Extended).
Maximum implemented address width: 48 bits (virtual), 46 bits (physical).
HTT * Hyperthreading enabled
CET * Supports Control Flow Enforcement Technology
Kernel CET - Kernel-mode CET Enabled
User CET * User-mode CET Allowed
X64 * Supports 64-bit mode
SMX - Supports Intel trusted execution
SKINIT - Supports AMD SKINIT
SGX - Supports Intel SGX
NX * Supports no-execute page protection
SMEP * Supports Supervisor Mode Execution Prevention
SMAP * Supports Supervisor Mode Access Prevention
PAGE1GB * Supports 1 GB large pages
PAE * Supports > 32-bit physical addresses
PAT * Supports Page Attribute Table
PSE * Supports 4 MB pages
PSE36 * Supports > 32-bit address 4 MB pages
PGE * Supports global bit in page tables
SS * Supports bus snooping for cache operations
VME * Supports Virtual-8086 mode
RDWRFSGSBASE * Supports direct GS/FS base access
FPU * Implements i387 floating point instructions
MMX * Supports MMX instruction set
MMXEXT - Implements AMD MMX extensions
3DNOW - Supports 3DNow! instructions
3DNOWEXT - Supports 3DNow! extension instructions
SSE * Supports Streaming SIMD Extensions
SSE2 * Supports Streaming SIMD Extensions 2
SSE3 * Supports Streaming SIMD Extensions 3
SSSE3 * Supports Supplemental SIMD Extensions 3
SSE4a - Supports Streaming SIMDR Extensions 4a
SSE4.1 * Supports Streaming SIMD Extensions 4.1
SSE4.2 * Supports Streaming SIMD Extensions 4.2
AES * Supports AES extensions
AVX * Supports AVX instruction extensions
AVX2 * Supports AVX2 instruction extensions
AVX-512-F - Supports AVX-512 Foundation instructions
AVX-512-DQ - Supports AVX-512 double and quadword instructions
AVX-512-IFAMA - Supports AVX-512 integer Fused multiply-add instructions
AVX-512-PF - Supports AVX-512 prefetch instructions
AVX-512-ER - Supports AVX-512 exponential and reciprocal instructions
AVX-512-CD - Supports AVX-512 conflict detection instructions
AVX-512-BW - Supports AVX-512 byte and word instructions
AVX-512-VL - Supports AVX-512 vector length instructions
FMA * Supports FMA extensions using YMM state
MSR * Implements RDMSR/WRMSR instructions
MTRR * Supports Memory Type Range Registers
XSAVE * Supports XSAVE/XRSTOR instructions
OSXSAVE * Supports XSETBV/XGETBV instructions
RDRAND * Supports RDRAND instruction
RDSEED * Supports RDSEED instruction
CMOV * Supports CMOVcc instruction
CLFSH * Supports CLFLUSH instruction
CX8 * Supports compare and exchange 8-byte instructions
CX16 * Supports CMPXCHG16B instruction
BMI1 * Supports bit manipulation extensions 1
BMI2 * Supports bit manipulation extensions 2
ADX * Supports ADCX/ADOX instructions
DCA - Supports prefetch from memory-mapped device
F16C * Supports half-precision instruction
FXSR * Supports FXSAVE/FXSTOR instructions
FFXSR - Supports optimized FXSAVE/FSRSTOR instruction
MONITOR * Supports MONITOR and MWAIT instructions
MOVBE * Supports MOVBE instruction
ERMSB * Supports Enhanced REP MOVSB/STOSB
PCLMULDQ * Supports PCLMULDQ instruction
POPCNT * Supports POPCNT instruction
LZCNT * Supports LZCNT instruction
SEP * Supports fast system call instructions
LAHF-SAHF * Supports LAHF/SAHF instructions in 64-bit mode
HLE - Supports Hardware Lock Elision instructions
RTM - Supports Restricted Transactional Memory instructions
DE * Supports I/O breakpoints including CR4.DE
DTES64 - Can write history of 64-bit branch addresses
DS - Implements memory-resident debug buffer
DS-CPL - Supports Debug Store feature with CPL
PCID * Supports PCIDs and settable CR4.PCIDE
INVPCID * Supports INVPCID instruction
PDCM * Supports Performance Capabilities MSR
RDTSCP * Supports RDTSCP instruction
TSC * Supports RDTSC instruction
TSC-DEADLINE * Local APIC supports one-shot deadline timer
TSC-INVARIANT * TSC runs at constant rate
xTPR * Supports disabling task priority messages
EIST * Supports Enhanced Intel Speedstep
ACPI * Implements MSR for power management
TM * Implements thermal monitor circuitry
TM2 * Implements Thermal Monitor 2 control
APIC * Implements software-accessible local APIC
x2APIC * Supports x2APIC
CNXT-ID - L1 data cache mode adaptive or BIOS
MCE * Supports Machine Check, INT18 and CR4.MCE
MCA * Implements Machine Check Architecture
PBE * Supports use of FERR#/PBE# pin
PSN - Implements 96-bit processor serial number
HTT * Hyperthreading
PREFETCHW * PrefetchW instruction support
HYPERVISOR * Hypervisor is present
VMX - Supports Intel hardware-assisted virtualization
EPT - Supports Intel extended page tables (SLAT)
URG - Supports Intel unrestricted guest
Logical to Physical Processor Map:
**------------ Physical Processor 0 (Hyperthreaded)
--*----------- Physical Processor 1
---*---------- Physical Processor 2
----*--------- Physical Processor 3
-----*-------- Physical Processor 4
------*------- Physical Processor 5
-------*------ Physical Processor 6
--------*----- Physical Processor 7
---------*---- Physical Processor 8
----------**-- Physical Processor 9 (Hyperthreaded)
------------*- Physical Processor 10
-------------* Physical Processor 11
Logical Processor to Socket Map:
************** Socket 0
Logical Processor to NUMA Node Map:
************** NUMA Node 0
No NUMA nodes.
Logical Processor to Cache Map:
**------------ Data Cache 0, Level 1, 48 KB, Assoc 12, LineSize 64
**------------ Instruction Cache 0, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 16, LineSize 64
**------------ Unified Cache 0, Level 2, 2 MB, Assoc 16, LineSize 64
************-- Unified Cache 1, Level 3, 12 MB, Assoc 12, LineSize 64
--*----------- Data Cache 1, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
--*----------- Instruction Cache 1, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
--****-------- Unified Cache 2, Level 2, 2 MB, Assoc 16, LineSize 64
---*---------- Data Cache 2, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
---*---------- Instruction Cache 2, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
----*--------- Data Cache 3, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
----*--------- Instruction Cache 3, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
-----*-------- Data Cache 4, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
-----*-------- Instruction Cache 4, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
------*------- Data Cache 5, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
------*------- Instruction Cache 5, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
------****---- Unified Cache 3, Level 2, 2 MB, Assoc 16, LineSize 64
-------*------ Data Cache 6, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
-------*------ Instruction Cache 6, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
--------*----- Data Cache 7, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
--------*----- Instruction Cache 7, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
---------*---- Data Cache 8, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
---------*---- Instruction Cache 8, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
----------**-- Data Cache 9, Level 1, 48 KB, Assoc 12, LineSize 64
----------**-- Instruction Cache 9, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 16, LineSize 64
----------**-- Unified Cache 4, Level 2, 2 MB, Assoc 16, LineSize 64
------------*- Data Cache 10, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
------------*- Instruction Cache 10, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
------------** Unified Cache 5, Level 2, 2 MB, Assoc 16, LineSize 64
-------------* Data Cache 11, Level 1, 32 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
-------------* Instruction Cache 11, Level 1, 64 KB, Assoc 8, LineSize 64
Logical Processor to Group Map:
************** Group 0
 Coreinfo herunterladen(3 MB)Jetzt ausSysinternals Liveausführen.
Coreinfo herunterladen(3 MB)Jetzt ausSysinternals Liveausführen.
Läuft auf:
- Client: Windows 11 und höher.
- Server: Windows Server 2016 und höher.