What is custom Text Analytics for health?
Note
Custom text analytics for health (preview) will be retired on 10 January 2025, please transition to other custom model training services, such as custom named entity recognition in Azure AI Language, by that date. From now to 10 January 2025, you can continue to use custom text analytics for health (preview) in your existing projects without disruption. You can’t create new projects. On 10 January 2025 – workloads running on custom text analytics for health (preview) will be deleted and associated project data will be lost.
Custom Text Analytics for health is one of the custom features offered by Azure AI Language. It is a cloud-based API service that applies machine-learning intelligence to enable you to build custom models on top of Text Analytics for health for custom healthcare entity recognition tasks.
Custom Text Analytics for health enables users to build custom AI models to extract healthcare specific entities from unstructured text, such as clinical notes and reports. By creating a custom Text Analytics for health project, developers can iteratively define new vocabulary, label data, train, evaluate, and improve model performance before making it available for consumption. The quality of the labeled data greatly impacts model performance. To simplify building and customizing your model, the service offers a web portal that can be accessed through the Language studio. You can easily get started with the service by following the steps in this quickstart.
This documentation contains the following article types:
- Quickstarts are getting-started instructions to guide you through creating making requests to the service.
- Concepts provide explanations of the service functionality and features.
- How-to guides contain instructions for using the service in more specific or customized ways.
Example usage scenarios
Similarly to Text Analytics for health, custom Text Analytics for health can be used in multiple scenarios across a variety of healthcare industries. However, the main usage of this feature is to provide a layer of customization on top of Text Analytics for health to extend its existing entity map.
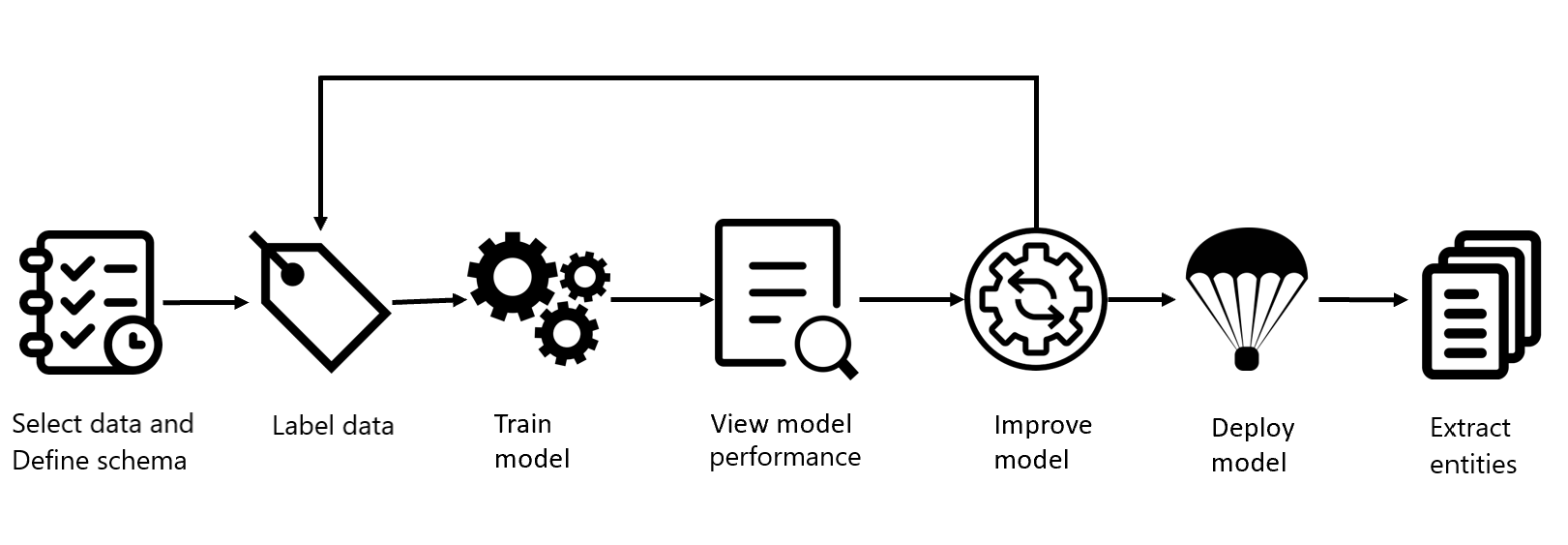
Project development lifecycle
Using custom Text Analytics for health typically involves several different steps.
Define your schema: Know your data and define the new entities you want extracted on top of the existing Text Analytics for health entity map. Avoid ambiguity.
Label your data: Labeling data is a key factor in determining model performance. Label precisely, consistently and completely.
- Label precisely: Label each entity to its right type always. Only include what you want extracted, avoid unnecessary data in your labels.
- Label consistently: The same entity should have the same label across all the files.
- Label completely: Label all the instances of the entity in all your files.
Train the model: Your model starts learning from your labeled data.
View the model's performance: After training is completed, view the model's evaluation details, its performance and guidance on how to improve it.
Deploy the model: Deploying a model makes it available for use via an API.
Extract entities: Use your custom models for entity extraction tasks.
Reference documentation and code samples
As you use custom Text Analytics for health, see the following reference documentation for Azure AI Language:
| APIs | Reference documentation |
|---|---|
| REST APIs (Authoring) | REST API documentation |
| REST APIs (Runtime) | REST API documentation |
Responsible AI
An AI system includes not only the technology, but also the people who will use it, the people who will be affected by it, and the environment in which it is deployed. Read the transparency note for Text Analytics for health to learn about responsible AI use and deployment in your systems. You can also see the following articles for more information:
Next steps
Use the quickstart article to start using custom Text Analytics for health.
As you go through the project development lifecycle, review the glossary to learn more about the terms used throughout the documentation for this feature.
Remember to view the service limits for information such as regional availability.