Use the Dependency Tracker extension
Azure DevOps Services
Note
We recommend that you use Delivery Plans to track dependencies instead of Dependency Tracker. The Dependency Tracker extension is not a supported feature of Azure Boards and isn't supported by any product team. For questions, suggestions, or issues you have when using the extension, visit the Marketplace for Azure DevOps, Dependency Tracker extension page. The Dependency Tracker extension is only available on Azure DevOps Services.
The Dependency Tracker extension helps you manage dependencies across teams, projects, and organizations. It provides filterable views to show all dependencies a team is consuming and producing. These views allow you to track the state and schedule of dependencies to support you in assessing the risk of dependencies to product deliverables.
Use the Dependency Tracker to plan dependencies at the beginning of an iteration or release, and to track the status during development. For any given dependency, the following parties are involved:
- Consumer: Feature team that has a need and starts a request for work.
- Producer: Feature team that makes a commitment to deliver work.
Each work request and work deliverable is defined as a work item. The work items get linked by the Successor-Predecessor link type or other directional link type. For more information, see Link type reference Producing for/Consuming from link.
Tip
While any work item type can participate in dependency tracking, you might want to limit dependencies to specific types, such as Features, Epics, User Stories, or Bugs. You can create the restriction by configuring Dependency Tracker.
From the Dependency Tracker, you can choose different views and filters, and drill down to obtain specific details. These views and options are described in the following sections:
Recommended use and key terms
Use Dependency Tracker to visualize and track the following work items:
- Dependencies on deliverables for work that your team is delivering.
- Dependencies you have on other teams for work that your team is delivering.
- Dependencies that other teams have on work your team is delivering.
All teams across organizations can participate in tracking dependencies.
Note
Dependency Tracker doesn't replace the in-person interactions that are required to agree to doing the work. It provides easier planning and tracking capabilities. Dependencies should be agreed upon by all parties before they enter into the Dependency Tracker.
Key terms
- Dependency: Work that Team A requires from Team B to do the work Team A is trying to do.
- Consumer: The team that asks to have work done.
- The consumer owns the engagement and tracking of that work – since it's the work their scenario requires, the burden is on the consumer to file, monitor, and track the status of the work
- The consumer owns entering the work into Azure Boards and submitting that work request to the producer
- The consumer is in charge of managing the work they requested so that they're aware of any material changes and adjustments
- Producer: The team that is doing the work.
- Once the work gets submitted to the producer, the producer owns the work item,
- The producer is responsible for maintaining the work item in Azure Boards
- The producer owns the state of the work item and iteration
- The consumer shouldn't touch these values once the work item gets handed off
- Once the work gets submitted to the producer, the producer owns the work item,
- Sequencing: A producing team's work is needed before the consuming team can start their work.
Prerequisites
| Category | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Tools | Dependency Tracker extension installed for the organization for which you want to track dependencies. |
| Permissions | - To view dependencies: Member of the Project Valid Users group for the project. - To create a dependency: Member of the Contributors group for both projects that participate in the dependency linking. - To modify configuration: Member of the Project Collection Administrators group. |
| Authentication | All organizations authenticate users through the same Microsoft Entra ID. |
| Services | Azure Boards as a service enabled. |
| Configuration and customization tasks | - Area paths and teams set up to participate in dependency tracking. - Iteration paths/sprints configured for the project and assigned to work items participating in dependency tracking. This requirement is essential for the Timeline view to yield meaningful data. - Customize your process as needed to support any other work items or fields. - Dependency Tracker configured to support your business needs and address any customizations. |
Important
The default configuration for Dependency Tracker supports the Agile process. If your project(s) are based on a different process or you have customized your process, you may need to modify the configuration. See Configure the Dependency Tracker later in this article.
Open the Dependency Tracker extension
Open the web portal for the project where your team is defined.
Select Boards > Dependency Tracker.

Choose the Area that corresponds to the team you want to view dependencies for from the dropdown menu.

You can only filter on those Area paths defined for the project.
Filter options
Filter each supported view by entering a keyword or using one or more of the fields. Provided fields include State, Work item type, and Iteration Path. Based on the keyword that you enter, the filter function lists work items based on any displayed column field.
To show the filter toolbar, choose the ![]() filter icon.
filter icon.
![]()
Toggle filters on and off by choosing the filter icon. To see more filters use the arrows at the end of the list of filters.
Choose one or more values from the drop-down menu for each field. These fields populate with the following values:
- Work item type: Check one or more check boxes for the Work item types you want to view. Work item types configured to participate in dependency tracking. The default work item types are: Epic, Feature, User Story, and Bug. To modify the configuration, see Configuration of Dependency Tracker.
- State: Check one or more check boxes for the work item states you want to view. The drop-down list should include all workflow States defined for all work item types shown in the selected view.
- Iteration: Check one or more check boxes for the Iteration Paths you want to view. The drop-down list should include all Iteration Paths configured for the project and for which there are work items listed in the current view.
- Priority: Check one or more check boxes for the Priorities you want to view. The priority values assigned to work items
- Partner: The partner organization for which the work item is defined.
Your filtering options are dependent on the configuration defined for the Dependency Tracker and that correspond to work items shown in the selected view that meet the filter criteria. For example, if you don't have any work items assigned to Sprint 4, then the Sprint 4 option doesn't appear in the filter options for the Iteration Path.
You can drop dependencies within the selected area, which excludes dependencies inside your team.
View drill-down options
Several views provide interactive visualizations through drill-downs. These features are addressed in the tabbed views descriptions later in this article.
![]()
Create a dependency
A dependency represents work where one team is dependent on another team. Both teams should track their own work in their own area path. By linking the work that is dependent on the other teams work, the dependencies can be visualized and tracked.
Select New Dependency.

If the partner team is in a different organization, then first choose the Partner Account. The Partner Account option can be enabled or disabled by configuring the Dependency Tracker.
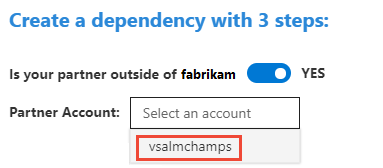
Search for work items by ID or enter a keyword contained within the work item title. In the following example, we link a user story and a bug.

- The Producer is the team that commits to delivering the work.
- The Consumer is the team that needs or is dependent on the work.
- The fastest way to create a dependency link is to type the Producer and Consumer work item IDs in the search boxes and then choose Save.
Optionally, you can choose Create New to add work items that you then link as dependent upon each other. Here we create two new features and link them.

If no work items exist for one half of the dependency, you can create a new work item as needed.
Select Save. The Save button is available only after two work items get chosen to link.
From the success confirmation dialog, select View dependency.
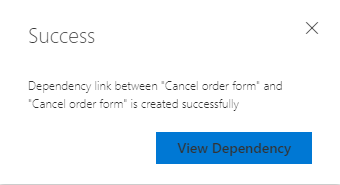
The work items that you linked are highlighted.
In the following example, the Fabrikam Fiber/Service Delivery/Voice team is dependent on the MyFirstProject team to deliver their
User Story 706: Cancel order formto completeBug 390: Cancel order form.
Create links manually
You can also link work items using the Links tab to create Successor/Predecessor links. A Predecessor is the producer of the work item, or the item that must come first. A Successor is the consumer of the work item, or the item that is dependent on the first item.
![]()
Note
The Successor/Predecessor (consumes/produces) link types are the default link types used by the Dependency Tracker. If you customized your projects using a Hosted XML process model, it's possible to specify different link types in the Dependency Tracker configuration. For more information, see Configure the Dependency Tracker later in this article, and Link user stories, issues, bugs, and other work items.
Remove dependency links
You can remove a dependency by choosing the ![]() actions icon from the linked work item and choose Remove Dependency Link option from the menu.
actions icon from the linked work item and choose Remove Dependency Link option from the menu.
![]()
Optionally, you can remove the link from the work item's Links tab.
Create a query of dependencies
To open a set of dependent work items, select them in the same way you would via a bulk edit, choose the ![]() actions icon from one of the selected linked work items and choose Open in Query option from the menu.
actions icon from one of the selected linked work items and choose Open in Query option from the menu.
![]()
A new tab opens to the Query Results page.
You can also create a custom query by selecting the Work items and direct links query type and choose any work item type.
Choose Copy to HTML to copy the selected work items to the clipboard as a formatted table.
Consuming Dependencies view
The Consuming Dependencies view shows work that a team is dependent upon by other teams or area paths.
![]()
Each column on the bar chart represents another area path that is producing dependencies by workflow state for the selected Area View. The table shows the number of unique dependencies. It also lists all work items participating in the filtered view of tracked dependencies.
Within the table, you can complete the following actions.
- Filter the list of work items by choosing one of the area path bars and progress states in the bar chart graph
- Expand or collapse the list of work items to show the full list of dependent work items using the
 expand and
expand and  collapse icons
collapse icons - Add or remove column fields by opening Column Options
- Switch the sequence of work items by choosing the Display: Consumer on top or Producer on top
Producing Dependencies view
The Producing Dependencies view shows work that other teams or area paths are dependent on per the selected area.
![]()
Each column on the bar chart represents another area path that is consuming dependencies by workflow state for the selected Area View. The table shows the number of unique dependencies and lists all work items included in the filtered view of tracked dependencies.
Within the table, you can complete the same actions as in the Consuming Dependencies view.
Timeline tab
The Timeline tab provides a calendar view of dependencies. The Timeline view is in Beta.
Important
For the Timeline to show meaningful data, have assigned the dependent work items to Iteration Paths, and the Iteration Paths must have start and end dates assigned.
There are two versions of the Timeline view: Correct Flow and Incorrect Flow. Each version shows the color-coded workflow state. You can customize color codes within the Dependency Tracker configuration.
Correct Flow view
The Correct Flow view shows those dependencies that are in the correct sequence. Successor work items get completed after their predecessor work item.
![]()
Incorrect Flow view
The Incorrect Flow view shows those dependencies that are out of order. At least one predecessor work item gets completed after its successor work item.
![]()
Risk Graph
The Risk Graph provides a visualization of how dependencies flow from Consumer team to Producer team, or from Producer to Consumer. The graph lets a team understand the number of dependencies and level of risks associated at a glance. Also, the risk graph view demonstrates the value of linking dependencies and laddering them up to Stories.
![]()
There are two views: Consuming From and Producing For. The workflow state color coding is configurable. The width of the lines indicates how many dependencies exist in that area, the thicker the link the more dependencies as indicated in the legend.
Consuming From
![]()
Producing For
![]()
Filtered on a specific dependency
You can drill down into specifics by choosing one of the dependencies.
![]()
Configure the Dependency Tracker
Be a member of the Project Collection Administrator Group to modify the configuration. All changes to the configuration apply to all projects defined in the organization.
To change the configuration, choose the ![]() gear icon and modify the syntax listed. Choose Save when you're done.
gear icon and modify the syntax listed. Choose Save when you're done.
The main properties you can modify are summarized as follows:
- The link types to use to create dependency links. Defaults are the Successor/Predecessor link types. Only customize when you use the Hosted XML process model to customize work tracking.
- Work items and work item types
- Work item types to participate in dependency tracking
- Mapping of work item category states to colors
- Mapping of work item workflow states and colors
- Default field columns in dependency list tables
- Default filter selections:
- Selected dependency work item types
- Selected Iteration Paths
- Enabled options:
- Timeline
- New Dependency link
- Cross account (organization) dependencies
- Cross account dependency toggle default state
- Risk graph configuration:
- Work item states associated with at risk (Red color) work items
- Work item states associated with neutral (Gray color) work items
- Work item states associates with on track (Green color) work items
For a full list and description, see the Property descriptions provided later in this section.
Enable or disable the New Dependency option
The newDependencyButtonEnabled property enables or disables the New Dependency link option. When enabled, the link appears on the Dependency Tracker page. When disabled, users can't create dependencies from the tracker, only review the dependencies created through other means. The default value is set to true (enabled).
Enable or disable cross-organization linking
The crossAccountConfigs property enables or disables cross-organization dependency linking from the New dependency dialog. The default value is set to true (enabled).
To disable, set the following syntax in the JSON configuration to false.
{
"crossAccountConfigs": {
"crossAccountDependencyEnabled": false,
"crossAccountDependencyToggleDefaultState": false, //default state for cross account toggle
"crossAccountDependencyToggleOnText": "Cross-account dependencies on",
"crossAccountDependencyToggleOffText": "Cross-account dependencies off"}
}
Cross account linking requires the use of a special link type and should only be used in coordination with the New Dependency option.
Property descriptions
The following table describes each of the property items specified in the configuration file.
Property/Description
Default/Example
consumesLinkName
Specifies the link type used to create the link from producer to consumer.
System.LinkTypes.Dependency-Reverse
producesLinkName
Specifies the link type used to create the link from consumer to producer.
System.LinkTypes.Dependency-Forward
queryFields
Specifies the custom fields to use in place of the system fields used by the dependency tracker to return linked work item results. By default. system reference names are used to return values for the following fields:
- areaPath - Area Path
- assignedTo - Assigned To
- id - ID
- areapath - IterationID
- areapath - Iteration Path
- areapath - Priority
- areapath - State
- areapath - Tags
- teamProject - Team Project
- title - Title
- workItemType - Work Item Type
If a custom field is used in place of one of the system fields, you specify the substitution by entering:
{
title: "Custom.Title",
assignedTo: "Custom.AssignedTo"
}
dependencyWorkItemTypes
Specifies the work item types that participate in dependency tracking. From the Create a dependency dialog, only those work item types listed can be created.
Default:
[
"Epic",
"Feature",
"User Story",
"Bug"
]
If using the Scrum process, you would change the entry to:
[
"Epic",
"Feature",
"Product Backlog Item",
"Bug"
]
selectedDependencyWorkItemTypes
Restricts the initial focus to just those work item types that the dependency tracker displays or lists. Based on the default "Any", any work item type that contains a dependency link type is displayed or listed. Users can change the focus through filtering.
Default:
Any
To restrict the work item types to just Epics and Features, specify:
[
"Epic",
"Feature"
]
selectedReleases
Restricts the initial focus to just those work items that are assigned to those Iteration Paths equal to or under the specified releases. Based on the blank default, no restrictions are applied. Users can change the focus through filtering.
Default:
[]
To restrict the work item types to just Release 1 and Release 2 for the Fabrikam project, specify:
[
"Fabrikam/Release 1",
"Fabrikam/Release 2",
]
workItemCategoriesAndColors
Specifies the colors used to represent work items based on their category and workflow state. For more information, see How workflow states and state categories are used in Backlogs and Boards.
Default:
{
"Proposed": {
"displayName": "Proposed",
"color": "#a6a6a6"
},
"InProgress": {
"displayName": "In Progress",
"color": "#00bcf2"
},
"Completed": {
"displayName": "Completed",
"color": "#9ac70b"
},
"Removed": {
"displayName": "Removed",
"color": "#d9242c"
},
"Resolved": {
"displayName": "Resolved",
"color": "#ff9d00"
}
}
workItemDislayStatesAndDisplayColors
Maps the workflow states to colors used to display them. If you customize the workflow states, or use a process that uses different workflow states, you must update this property.
Default:
{
"New": {
"textColor": "rgb(112, 112, 112)",
"chartColor": "rgb(112, 112, 112)",
"states": [
"New"
]
},
"Active": {
"textColor": "rgb(0, 122, 204)",
"chartColor": "rgb(0, 122, 204)",
"states": [
"Active",
"Resolved"
]
},
"Closed": {
"textColor": "rgb(16, 124, 16)",
"chartColor": "rgb(16, 124, 16)",
"states": [
"Closed"
]
},
"Removed": {
"textColor": "rgb(204, 41, 61)",
"chartColor": "rgb(204, 41, 61)",
"states": [
"Removed"
]
},
"Other": {
"textColor": "rgb(178, 178, 178)",
"chartColor": "rgb(178, 178, 178)",
"states": []
}
}
riskAssessmentValues
Specifies the Risk field values. The Risk field specifies a subjective rating of the relative uncertainty around the successful completion of a user story. It is defined for the Agile process, but can be added to work item types used in other processes.
Default:
["1-High", "2-Medium", "3-Low"]
partnerAccounts
Optional configuration that specifies which Azure DevOps organizations are selectable from the Dependency dialog when creating a Cross account dependency. If not specified generates a list based on previous organizations that the user has visited.
Default:
[]
Example:
["account-1", "account-2"]
timelineEnabled
Enables or disables the Timeline view.
Default:
true
newDependencyButtonEnabled
Enables or disables the New Dependency link to create a new linked dependency.
Default:
true
crossAccountConfigs
(1) Enables or disables the support of creating new dependencies to work items in other partner accounts, and (2) specifies the default state of the Partner account options in the Create a dependency dialog.
Default:
{
"crossAccountDependencyEnabled": true,
"crossAccountDependencyToggleDefaultState": false
}
If you don't want any dependencies created that belong to other organizations, then change this configuration to:
{
"crossAccountDependencyEnabled": false,
"crossAccountDependencyToggleDefaultState": false
}
priorityValues
Specifies the Priority field values. The Priority field specifies a subjective rating of a bug, issue, task, or user story as it relates to the business. It is defined for most backlog work item types and processes, but can be added to work item types used in other processes.
Default:
["0","1","2","3","4","(blank)"]
defaultColumns
Specifies the field columns and order used to display dependency lists.
Default:
[
"Id",
"Area Path",
"Dependency Title",
"State",
"Consumers",
"Producers"
]
riskAnalysisEnabled
Specifies whether or not Risk functionality is enabled. If set to true, then the riskAssessmentValues property must be defined.
Default:
False
riskAssessmentValues
Default:
[]
riskGraphConfig
Maps the workflow States to one of the three Risk areas displayed on the Graph:
atRiskis Red,neutralis Gray, andonTrackis Green.
Default: 8
{
"atRisk": [
"Removed"
],
"neutral": [
"New"
],
"onTrack": [
"Active",
"Resolved",
"Closed",
"Other"
]
}
Add or remove workflow states used in work item types participating in dependency tracking.
iterationDepth
Specifies the hierarchical depth of Iteration Paths that the Dependency Tracker queries to build the Timeline view.
Default: 8A depth of 3 would correspond to: Fabrikam/Release 1/Sprint 20.
Default configuration syntax
{
"consumesLinkName": "System.LinkTypes.Dependency-Reverse",
"producesLinkName": "System.LinkTypes.Dependency-Forward",
"queryFields": {},
"dependencyWorkItemTypes": [
"Epic",
"Feature",
"User Story",
"Bug"
],
"selectedDependencyWorkItemTypes": "Any",
"selectedReleases": "",
"workItemCategoriesAndColors": {
"Proposed": {
"displayName": "Proposed",
"color": "#a6a6a6"
},
"InProgress": {
"displayName": "In Progress",
"color": "#00bcf2"
},
"Completed": {
"displayName": "Completed",
"color": "#9ac70b"
},
"Removed": {
"displayName": "Removed",
"color": "#d9242c"
},
"Resolved": {
"displayName": "Resolved",
"color": "#ff9d00"
}
},
"workItemDislayStatesAndDisplayColors": {
"New": {
"textColor": "rgb(112, 112, 112)",
"chartColor": "rgb(112, 112, 112)",
"states": [
"New"
]
},
"Active": {
"textColor": "rgb(0, 122, 204)",
"chartColor": "rgb(0, 122, 204)",
"states": [
"Active",
"Resolved"
]
},
"Closed": {
"textColor": "rgb(16, 124, 16)",
"chartColor": "rgb(16, 124, 16)",
"states": [
"Closed"
]
},
"Removed": {
"textColor": "rgb(204, 41, 61)",
"chartColor": "rgb(204, 41, 61)",
"states": [
"Removed"
]
},
"Other": {
"textColor": "rgb(178, 178, 178)",
"chartColor": "rgb(178, 178, 178)",
"states": []
}
},
"riskAssessmentValues": [],
"releases": [],
"partnerAccounts": [],
"timelineEnabled": true,
"newDependencyButtonEnabled": true,
"crossAccountConfigs": {
"crossAccountDependencyEnabled": true,
"crossAccountDependencyToggleDefaultState": false
},
"priorityValues": [
"0",
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"(blank)"
],
"defaultColumns": [
"Id",
"Area Path",
"Dependency Title",
"State",
"Consumers",
"Producers"
],
"riskGraphConfig": {
"atRisk": [
"Removed"
],
"neutral": [
"New"
],
"onTrack": [
"Active",
"Resolved",
"Closed",
"Other"
]
},
"iterationDepth": 8
}
Related articles
- Manage work item fields
- Review team delivery plans
- Use the inheritance process model
- Use the hosted XML process model
- Understand workflow states and state categories in Backlogs and Boards