Customize a Hosted XML process
Azure DevOps Services
Azure DevOps Services supports adding and updating processes through an administrative experience that is a web-based import process. After you add a process, you can create one or more projects from it. You can update the process at any time by importing it again. The changes made to the process template are then applied to all projects that use the process.
Important
With the Hosted XML process model, you customize work tracking by updating select XML definition files of a process template. This feature is available only when data is migrated to Azure DevOps Services by use of Team Foundation Server Database Import Service.
To learn more about customization and process models, see Customize work tracking.
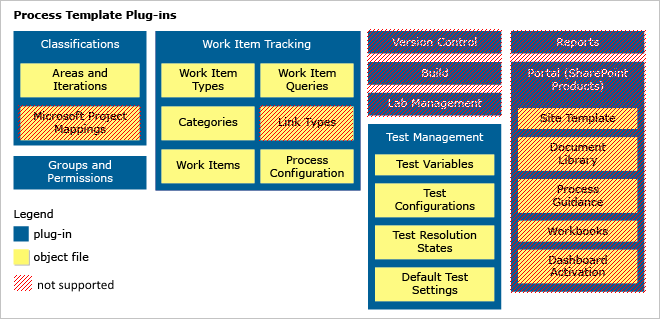
A process is a zip file that contains a set of interdependent files. These files define the building blocks of the work-item tracking system and other subsystems in Azure DevOps Services. Some building blocks update existing projects, while others apply only to new projects. See the following table for the full list of building blocks.
Used when importing/updating a process
Used when creating a new project
Replaced by system defaults
Ignored
Work Item Tracking
WITs
Categories
Process Configuration
Areas and Iterations
Test Management
Work Items
Work Item Queries
Build
Lab Management
Version Control
Microsoft Project Mappings
Reports
Portal (SharePoint Products)
There are differences between what Azure DevOps Services supports and what on-premises Team Foundation Server supports. For a summary of these differences, see Process template customizations differences.
How to customize a process
When you customize a process, starting with a well-defined process is easier than building a new one.
If you update an existing process you've used with on-premises Team Foundation Server, make sure it conforms to the constraints placed on templates for import.
Open Settings>Process
You create, manage, and make customizations to processes from Organization settings>Process.
Choose the
 Azure DevOps logo to open Projects. Then choose Organization settings.
Azure DevOps logo to open Projects. Then choose Organization settings.
Then, choose Process.
Important
If you don't see Process, then you're working from TFS-2018 or earlier version. The Process page isn't supported. You must use the features supported for the On-premises XML process model.
Export and import a process
From the Processes tab, select the ellipsis (...) to open the shortcut menu for the Hosted XML process that you want to export. You can export only Hosted XML processes.
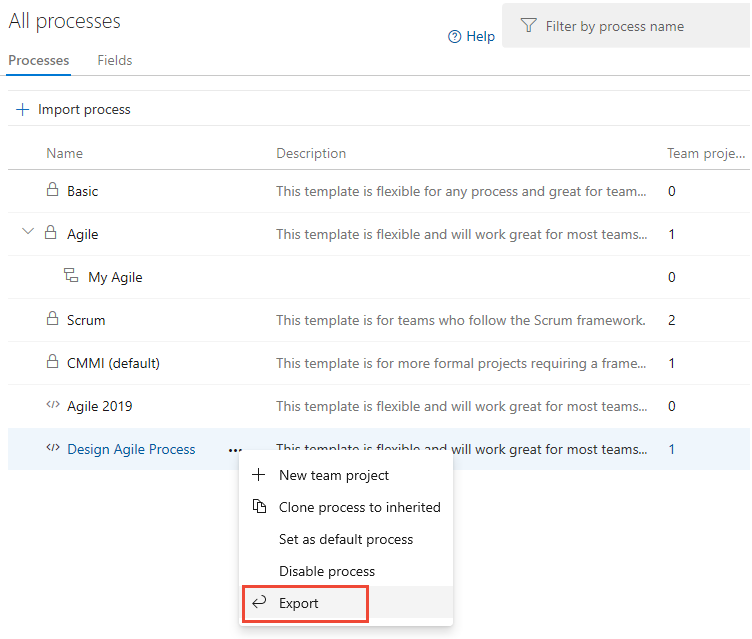
Save the zip file and extract all files from it.
Rename the process within the ProcessTemplate.xml file located in the root directory.
Name the process to distinguish it from existing ones.
<name>MyCompany Agile Process </name>Change the version type, and change the major and minor numbers. Provide a distinct GUID for the type as in this example:
<version type="F50EFC58-C2FC-4C66-9814-E395D90778A3" major="1" minor="1"/>Apply supported customizations.
Create a zip file of all files and folders in the root directory.
Supported customizations
You can apply the following customizations to your process:
- Add, remove, or modify a WIT.
- Add or modify a field.
- Add up to five portfolio backlogs.
- Add categories that you'll use in your process configuration.
- Modify process configuration.
- Add global lists.
The following section lists limitations that the system imposes.
Restrictions
You can import up to 32 processes into Azure DevOps Services. Your custom processes must conform to all of the following summarized rules. Otherwise, validation error messages might appear upon import.
- Customize a Hosted XML process
Process template
Your ProcessTemplate.xml file must conform to the syntax and rules described in ProcessTemplate XML element reference. Also, it must meet the following conditions:
- Limits the number of defined WITs to 64
- Contains only one Categories.xml definition file
- Contains only one ProcessConfiguration.xml definition file
- Uses unique friendly names across all fields and WIT definitions
Also, your process must pass the following validation checks:
- Process names are unique and contain at most 155 Unicode characters.
- A template with the same name and version GUID as an existing process overwrites that process.
- A template with the same name but a different version GUID generates an error.
- Process names can't contain the following special characters:
. , ; ' ` : / \ * | ? " & % $ ! + = ( ) [ ] { } < >.
See Naming restrictions for additional constraints.
- Process folders contain no .exe files. Even if you can import a process that contains an .exe file, project creation fails.
- The process's total size is at most 2 GB. Otherwise, project creation fails.
Process configuration
The ProcessConfiguration.xml definition file must conform to the syntax and rules described in ProcessConfiguration XML element reference. Also, it must meet the following conditions:
- Specifies all TypeFields elements
- Is limited to five portfolio backlogs
- Contains only one unparented portfolio backlog
- Specifies only one parent portfolio backlog for each subordinate portfolio backlog
- Contains required workflow state-to-metastate mappings and doesn't reference unsupported metastates
Categories
The Categories.xml definition file must conform to the syntax and rules described in Categories XML element reference. Also, it must meet the following conditions:
- Is limited to 32 categories
- Defines all categories referenced in the ProcessConfiguration.xml file
Work item types
A WITD element and its child elements must conform to the syntax and rules described in WITD XML element reference. Also, it must meet the following conditions:
- There are at most 1024 fields within a single WIT and 1024 fields across all WITs.
- The friendly name and required refname attribute assigned to a WIT are unique within the set of WIT definition files.
- The required refname attribute value doesn't contain disallowed characters or use the disallowed namespaces System.Name and Microsoft.Name.
- Reference names contain at least one period (.), and all other characters are letters with no spaces.
- The WITD element contains a FORM element that defines a WebLayout element conforming to the syntax specified in WebLayout and Control elements.
Work item fields
A FIELDS element and its child elements must conform to the syntax and rules described in FIELD XML element reference. Also, it must meet the following conditions:
- The friendly name and required refname attribute assigned to a WIT are unique within the set of WIT definition files.
- The required refname attribute value doesn't contain disallowed characters or use the disallowed namespaces System.Name and Microsoft.Name.
- Reference names contain at least one period (.), and all other characters are letters with no spaces.
A FIELD element and its child elements can contain a GLOBALLIST element.
Limit restrictions
- A FIELDS element is limited to 1024 fields.
- A work item type is limited to 64 person-name fields. A person-name field is one with the attribute and value
syncnamechanges=true. - An ALLOWEDVALUES or SUGGESTEDVALUES element is limited to 512 LISTITEM elements.
- A field is limited to 1,024 rules.
Required fields
The following fields are specified in the ProcessConfiguration.xml file:
- For all WITs in a category that defines a process-configuration backlog, specify the fields used for the attributes and values
type=Teamandtype=Order. - For all WITs in a category that defines a regular backlog or portfolio backlog, specify the field used for
type=Effort. - For all WITs in the category that defines the TaskBacklog element, specify:
- The field used for
type=RemainingWork. - The field used for
type=Activity. - The ALLOWEDVALUES rule for the field used for
type=Activity.
- The field used for
Rule restrictions
In addition to the standard field-rule restrictions, the following restrictions are enforced:
- Field-rule elements can't specify the for and not attributes.
- FIELD elements can't contain the child-rule elements CANNOTLOSEVALUE, NOTSAMEAS, MATCH, and PROHIBITEDVALUES.
- Except for the following fields, FIELD definitions for System.Name fields can't contain field rules.
- System.Title can contain the rules REQUIRED and DEFAULT.
- System.Description can contain the rules REQUIRED and DEFAULT.
- System.AssignedTo can contain the rules REQUIRED, DEFAULT, ALLOWEXISTINGVALUE, and VALIDUSER.
- System.ChangedBy can contain the rules REQUIRED, DEFAULT, ALLOWEXISTINGVALUE, and VALIDUSER.
Consistent names and attributes
Within a process or a project collection, name, type, and other attributes that a FIELD element defines must be the same across all WIT definitions.
Identity fields
Identity fields correspond to fields used to contain account, user, or group names. The following core system fields are hard-coded as identity fields:
- Assigned To (System.AssignedTo)
- Authorized As (System.AuthorizedAs)
- Changed By (System.ChangedBy)
- Created By (System.CreatedBy)
- Activated By (Microsoft.VSTS.Common.ActivatedBy)
- Closed By (Microsoft.VSTS.Common.ClosedBy)
- Resolved By (Microsoft.VSTS.Common.ResolvedBy)
Add a custom identity field
A string field is recognized as an identity field when you specify the attribute syncnamechanges as True.
Rule restrictions on identity fields
For the current release of process import, don't specify any of the following rules within a FIELD definition.
- SUGGESTEDVALUES
- Rules that contain nonidentity values.
Correct example
To limit the account names that are valid within an identity field, specify the VALIDUSER element with a group name attribute.
<FIELD name="Project Manager" refname="Fabrikam.ProgramManager" type="String" reportable="dimension" syncnamechanges="true">
<ALLOWEXISTINGVALUE />
<VALIDUSER group="[PROJECT]\Program Manager Group" />
<HELPTEXT>The program manager responsible for signing off on the user story.</HELPTEXT>
</FIELD>
Before you import the process, make sure you've created the group in the projects that the process updates.
Incorrect example
The following example isn't valid because it specifies:
- An
ALLOWEDVALUESelement. - A
DEFAULTelement that specifies the nonidentity stringvalue="Not Assigned".
<FIELD name="Project Manager" refname="Fabrikam.ProgramManager" type="String" reportable="dimension" syncnamechanges="true">
<ALLOWEXISTINGVALUE />
<ALLOWEDVALUES>
<LISTITEM value="[PROJECT]\Program Manager Group" />
<LISTITEM value="Not Assigned" />
</ALLOWEDVALUES>
<DEFAULT from="value" value="Not Assigned" />
<VALIDUSER />
<HELPTEXT>The program manager responsible for signing off on the user story.</HELPTEXT>
</FIELD>
Workflow
A WORKFLOW element and its child elements must conform to the syntax and rules described in WORKFLOW XML element reference. Also, it must meet the following conditions:
- Limits each WIT to 16 workflow states
- Defines all workflow states that are mapped to metastates in the ProcessConfiguration definition file
- Defines a transition between all workflow states mapped to the "Proposed" state category and workflow states mapped to the "InProgress" state category
- Defines a transition between all workflow states mapped to the "InProgress" state category and workflow states mapped to the "Complete" state category.
For a description of state category and mappings, see Workflow states and state categories.
Global lists
For the Hosted XML process model, the following limits are placed on global-list import:
- There are at most 64 global lists.
- There are at most 1,024 items per list.
- Approximately 10,000 items can be defined in total among all global lists that are specified across all WITs.
Form layout
A FORM element and its child elements must conform to the syntax and rules described in FORM XML element reference.
A Control element can't specify a custom control. Custom controls aren't supported.