Routing MQTT Messages in Azure Event Grid
Event Grid allows you to route your MQTT messages to Azure services or webhooks for further processing. Accordingly, you can build end-to-end solutions by using your IoT data for data analysis, storage, and visualizations, among other use cases.
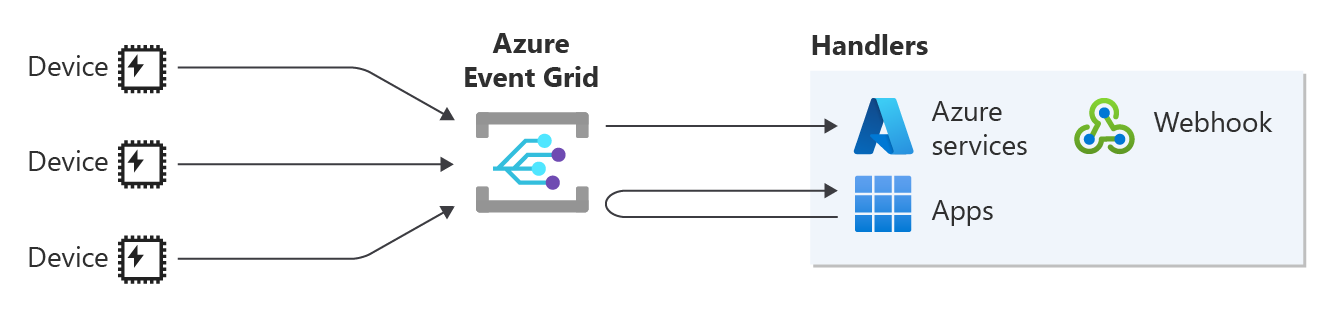
How can I use the routing feature?
Routing the messages from your clients to an Azure service or your custom endpoint enables you to maximize the benefits of this data. The following are some of many use cases to take advantage of this feature:
- Data Analysis: extract and analyze the routed messages from your clients to optimize your solution. For example, analyze your machines' telemetry to predict when to schedule maintenance before failures happen to avoid delays and further damage.
- Serverless applications: trigger a serverless function based on the routed messages from your clients. For example, when a motion sensor detects a motion, send a notification to security personnel to address it.
- Data Visualizations: build visualizations of the routed data from your clients to easily represent and understand the data as well as highlight trends and outliers.
Routing configuration:
The routing configuration enables you to send all your MQTT messages from your clients to either an Event Grid namespace topic or an Event Grid custom topic. Once the messages are in the topic, you can configure an event subscription to consume the messages from the topic. Use the following high-level steps to achieve this configuration:
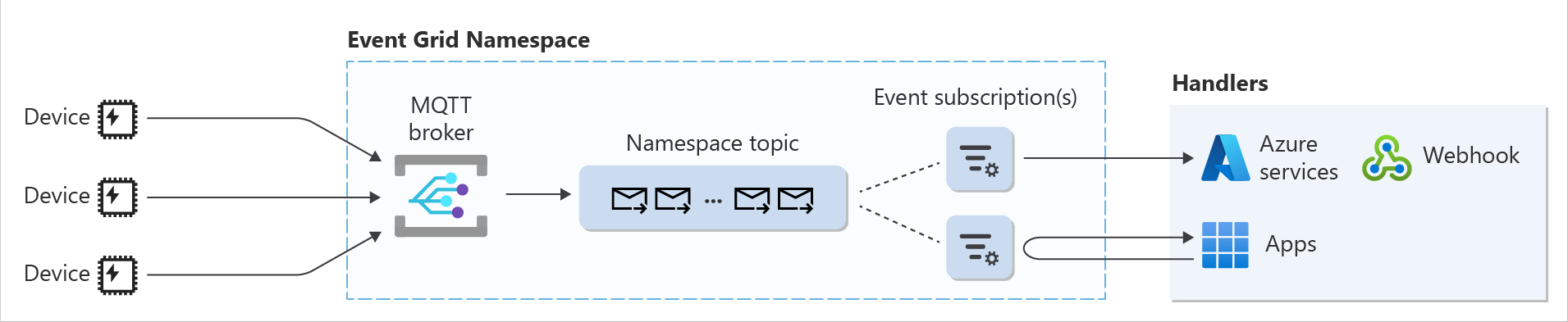
- Namespace topic as a routing destination:
- Create an Event Grid namespace topic where all MQTT messages are routed.
- Create an event subscription of push type to route these messages to one of the supported Azure services or a custom webhooks or an event subscription of queue type to pull the messages directly from the namespace topic through your application.
- Set the routing configuration referring to the topic that you created in the first step.
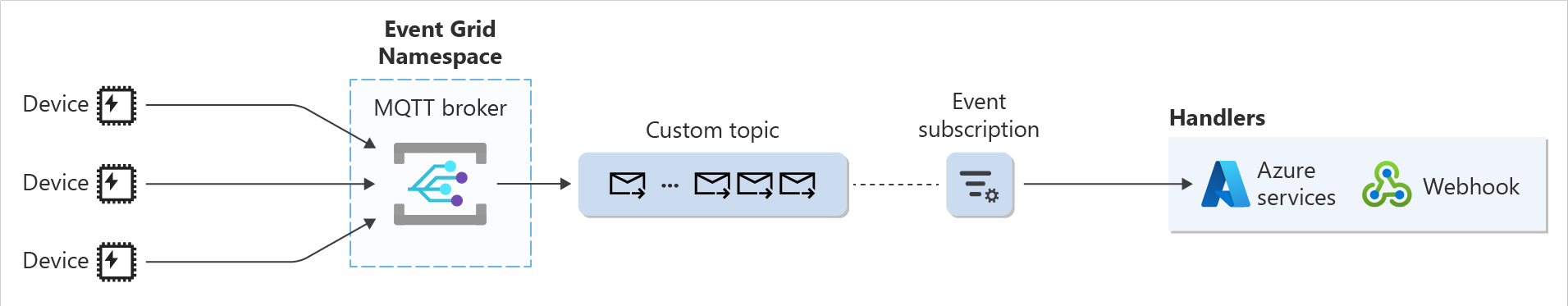
- Custom topic as a routing destination:
- Create an Event Grid custom topic where all MQTT messages are routed. This topic needs to fulfill the Event Grid custom topic requirements for routing
- Create an Event Grid event subscription to route these messages to one of the supported Azure services or a custom endpoint.
- Set the routing configuration referring to the topic that you created in the first step.
Note
Disabling public network access on the namespace will cause the MQTT routing to fail.
Difference between namespace topics and custom topics as a routing destination
The following table shows the difference between namespace topics and custom topics as a routing destination. For a detailed breakdown of which quotas and limits are included in each Event Grid resource, see Quotas and limits.
| Point of comparison | Namespace topic | Custom topic |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | High, up to 40 MB/s (ingress) and 80 MB/s (egress) | Low, up to 5 MB/s (ingress and egress) |
| Pull delivery | Yes | |
| Push delivery to Event Hubs | Yes | Yes |
| Push delivery to Azure services (Functions, Webhooks, Service Bus queues and topics, relay hybrid connections, and storage queues) | Yes | |
| Message retention | 7 days | 1 day |
| Role assignment requirement | Not needed since the MQTT broker and the namespace topic are under the same namespace | Required since the namespace hosting the MQTT broker functionality and the custom topic are different resources |
Event Grid custom topic requirements for routing
The Event Grid custom topic that is used for routing need to fulfill the following requirements:
- It needs to be set to use the Cloud Event Schema v1.0
- It needs to be in the same region as the namespace.
- You need to assign "Event Grid Data Sender" role to yourself or to the selected managed identity on the Event Grid custom topic before the routing configuration is applied.
- In the portal, go to the created Event Grid topic resource.
- In the "Access control (IAM)" menu item, select Add a role assignment.
- In the "Role" tab, select "Event Grid Data Sender", then select Next.
- In the "Members" tab, select +Select members, then type your AD user name in the "Select" box that appears (for example, user@contoso.com).
- Select your AD user name, then select "Review + assign"
Azure portal configuration
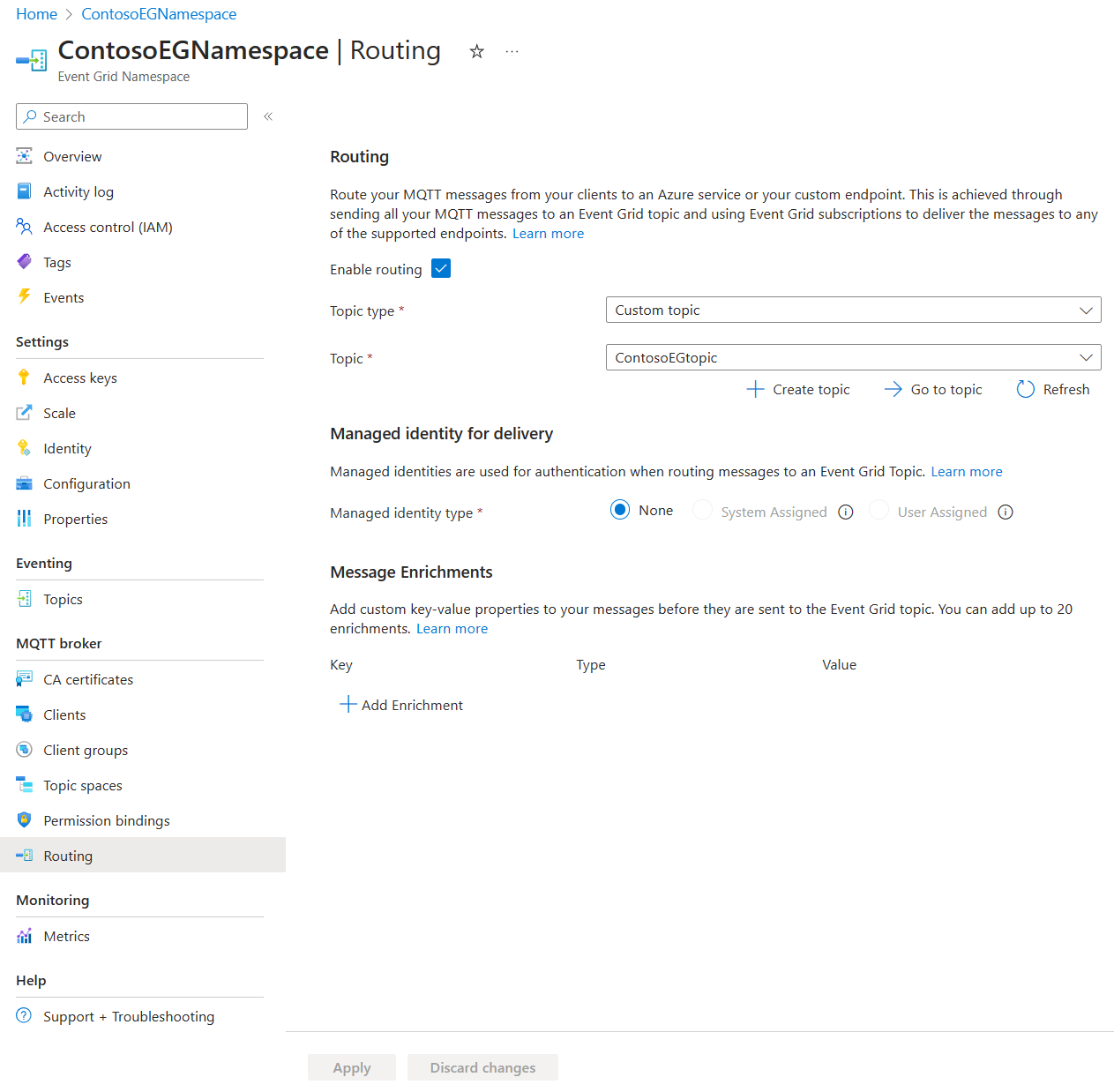
Use the following steps to configure routing:
- Go to your namespace in the Azure portal.
- Under Routing, Check Enable Routing.
- Under topic type, select either Namespace topic or Custom topic
- Under topic, select the topic that you created where all MQTT messages are routed.
- For custom topics, the list shows only the topics that fulfill the Event Grid custom topic requirements for routing
- If custom topic was selected, the Managed Identity for Delivery section appears. Select one of the following options for the identity that is used to authenticate the MQTT broker while delivering the MQTT messages to the custom topic:
- None: in this case, you need to assign the "Event Grid Data Sender" role to yourself on the custom topic.
- System-assigned identity: in this case, you need to enable system-assigned identity on the namespace as a prerequisite and assign the "EventGrid Data Sender" role to the system-assigned identity on the custom topic.
- User-assigned identity: in this case, you need to enable user-assigned identity on the namespace as a prerequisite and assign the "EventGrid Data Sender" role to the selected identity on the custom topic.
- If User-assigned identity was selected, a drop-down appears to enable you to select the desired identity.
- Select Apply.
For enrichments configuration instructions, go to Enrichment portal configuration.
Azure CLI configuration
az resource create --resource-type Microsoft.EventGrid/namespaces --id /subscriptions/<Subscription ID>/resourceGroups/<Resource Group>/providers/Microsoft.EventGrid/namespaces/<Namespace Name> --is-full-object --api-version 2023-06-01-preview --properties @./resources/NS.json
NS.json
"properties": {
"inputSchema": "CloudEventSchemaV1_0",
"topicSpacesConfiguration": {
"state": "Enabled",
"routeTopicResourceId": "/subscriptions/<Subscription ID>/resourceGroups/<Resource Group>/providers/Microsoft.EventGrid/topics/<Event Grid topic name>",
"routingIdentityInfo": {
"type": "UserAssigned", //Allowed values: None, SystemAssigned, UserAssigned
"userAssignedIdentity": "/subscriptions/<Subscription ID>/resourceGroups/<Resource Group>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<User-assigned identity>" //needed only if UserAssigned was the value of type
},
}
}
For enrichments configuration instructions, go to Enrichment CLI configuration.
MQTT message routing behavior
While routing MQTT messages to custom topics, Event Grid provides durable delivery as it tries to deliver each message at least once immediately. If there's a failure, Event Grid either retries delivery or drops the message that was meant to be routed. Event Grid doesn't guarantee order for event delivery, so subscribers might receive them out of order.
The following table describes the behavior of MQTT message routing based on different errors.
| Error | Error description | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| TopicNotFoundError | The custom topic that is configured to receive all the MQTT routed messages was deleted. | Event Grid drops the MQTT message that was meant to be routed. |
| AuthenticationError | The Event Grid Data Sender role for the custom topic configured as the destination for MQTT routed messages was deleted. | Event Grid drops the MQTT message that was meant to be routed. |
| TooManyRequests | The number of MQTT routed messages per second exceeds the publish limit for the custom topic. | Event Grid retries to route the MQTT message. |
| ServiceError | An unexpected server error for a server's operational reason. | Event Grid retries to route the MQTT message. |
During retries, Event Grid uses an exponential backoff retry policy for MQTT message routing. Event Grid retries delivery on the following schedule on a best effort basis:
- 10 seconds
- 30 seconds
- 1 minute
- 5 minutes
- 10 minutes
- 30 minutes
- 1 hour
- 3 hours
- 6 hours
- Every 12 hours
If a routed MQTT message that was queued for redelivery succeeded, Event Grid attempts to remove the message from the retry queue on a best effort basis, but duplicates might still be received.
Next steps:
Use the following articles to learn more about routing:
QuickStart:
- Tutorial: Route MQTT messages to Azure Event Hubs using namespace topics
- Tutorial: Route MQTT messages to Azure Functions using custom topics