Understand support for disconnected device updates (preview)
The Microsoft Connected Cache (MCC) module for IoT Edge devices enables Device Update capabilities on disconnected devices behind gateways. In a transparent gateway scenario, one or more devices can pass their messages through a single gateway device that maintains the connection to Azure IoT Hub. In these cases, the child devices may not have internet connectivity or may not be allowed to download content from the internet. The MCC module provides Device Update for IoT Hub customers with the capability of an intelligent in-network cache. The cache enables image-based and package-based updates of Linux OS-based devices that are behind an IoT Edge gateway (also called downstream IoT devices). The cache also helps reduce the bandwidth used for updates.
Note
This information relates to a preview feature that's available for early testing and use in a production environment. This feature is fully supported but it's still in active development and may receive substantial changes until it becomes generally available.
If you aren't familiar with IoT Edge gateways, learn more about How an IoT Edge device can be used as a gateway.
What is Microsoft Connected Cache
Microsoft Connected Cache is an intelligent, transparent cache for content published for Device Update for IoT Hub and can be customized to cache content from other sources like package repositories as well. Microsoft Connected Cache is a cold cache that is warmed by client requests for the exact file ranges requested by the Delivery Optimization client and doesn't pre-seed content. The following diagram and step-by-step description explain how Microsoft Connected Cache works within the Device Update infrastructure.
Note
This flow assumes that the IoT Edge gateway has internet connectivity. For the downstream IoT Edge gateway (nested edge) scenario, the content delivery network (CDN) can be considered the MCC hosted on the parent IoT Edge gateway.
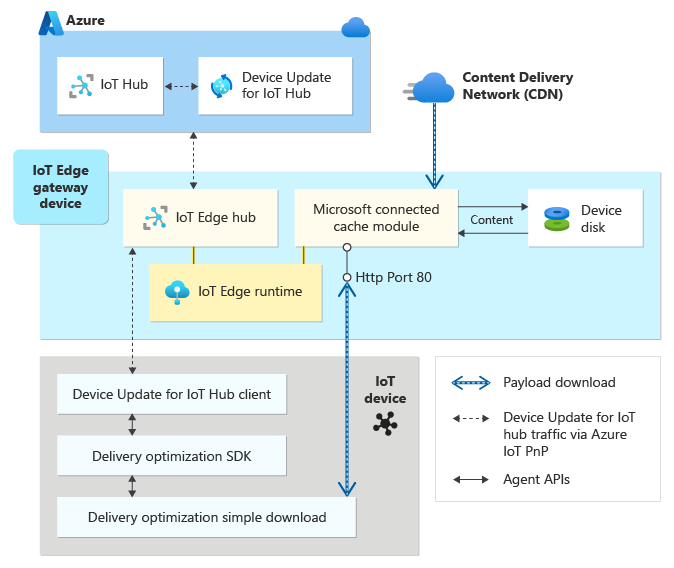
Microsoft Connected Cache is deployed as an IoT Edge module to the on-premises gateway server.
Device Update for IoT Hub clients are configured to download content from Microsoft Connected Cache by using either the GatewayHostName attribute of the device connection string for IoT leaf devices or the parent_hostname set in the config.toml for IoT Edge child devices.
Device Update for IoT Hub clients receive download commands from the Device Update service and request update content from the Microsoft Connected Cache instead of the CDN. Microsoft Connected Cache listens on HTTP port 80 by default, and the Delivery Optimization client makes the content request on port 80 so the parent must be configured to listen on this port. Only the HTTP protocol is supported at this time.
The Microsoft Connected Cache server downloads content from the CDN, seeds its local cache stored on disk and delivers the content to the Device Update client.
Note
When using package-based updates, the Microsoft Connected Cache server will be configured by the admin with the required package hostname.
Subsequent requests from other Device Update clients for the same update content now come from cache and Microsoft Connected Cache won't make requests to the CDN for the same content.
Supporting industrial IoT (IIoT) with parent/child hosting scenarios
Industrial IoT (IIoT) scenarios often involve multiple levels of IoT Edge gateways, with only the top level having internet access. In this scenario, each gateway hosts a Microsoft Connected Cache service that is configured to request update content from its parent gateway.
When a child (or downstream) IoT Edge gateway makes a request for update content from its parent gateway, this request is repeated for as many levels as necessary before reaching the topmost IoT Edge gateway hosting a Microsoft Connected Cache server that has internet access. From the internet connected server, the content is requested from the CDN at which point the content is delivered back to the child IoT Edge gateway that originally requested the content. The content is stored on disk at every level.
Request access to the preview
The Microsoft Connected Cache IoT Edge module is released as a preview for customers who are deploying solutions using Device Update for IoT Hub. Access to the preview is by invitation. Request Access to the Microsoft Connected Cache preview for Device Update for IoT Hub and provide the information requested if you would like access to the module.
Microsoft Connected Cache module configuration
Microsoft Connected Cache is deployed to Azure IoT Edge gateways as an IoT Edge module. Like other IoT Edge modules, environment variables and container create options are used to configure MCC modules. This section defines the environment variables and container create options that are required to successfully deploy the MCC module for use by Device Update for IoT Hub.
There's no naming requirement for the Microsoft Connected Cache module since no other module or service interactions rely on the name of the MCC module for communication. Additionally, the parent-child relationship of the Microsoft Connected Cache servers isn't dependent on this module name, but rather the FQDN or IP address of the IoT Edge gateway.
Module environment variables
Microsoft Connected Cache module environment variables are used to pass basic module identity information and functional module settings to the container.
| Variable name | Value format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CUSTOMER_ID | Azure subscription ID GUID | Required This value is the customer's ID, which provides secure authentication of the cache node to Delivery Optimization services. |
| CACHE_NODE_ID | Cache node ID GUID | Required Uniquely identifies the MCC node to Delivery Optimization services. |
| CUSTOMER_KEY | Customer Key GUID | Required This value is the customer's key, which provides secure authentication of the cache node to Delivery Optimization services. |
| STORAGE_N_SIZE_GB (Where N is the cache drive) | Integer | Required Specify up to nine drives to cache content and specify the maximum space in gigabytes to allocate for content on each cache drive. The number of the drive must match the cache drive binding values specified in the container create option MicrosoftConnectedCacheN value. Examples: STORAGE_1_SIZE_GB = 150 STORAGE_2_SIZE_GB = 50 Minimum size of the cache is 10 GB. |
| UPSTREAM_HOST | FQDN/IP | Optional This value can specify an upstream MCC node that acts as a proxy if the Connected Cache node is disconnected from the internet. This setting is used to support the nested IoT scenario. Note: MCC listens on http default port 80. |
| UPSTREAM_PROXY | FQDN/IP:PORT | Optional The outbound internet proxy. This value could also be the OT DMZ proxy of an ISA 95 network. |
| CACHEABLE_CUSTOM_N_HOST | HOST/IP FQDN |
Optional Required to support custom package repositories. Repositories could be hosted locally or on the internet. There's no limit to the number of custom hosts that can be configured. Examples: Name = CACHEABLE_CUSTOM_1_HOST Value = packages.foo.com Name = CACHEABLE_CUSTOM_2_HOST Value = packages.bar.com |
| CACHEABLE_CUSTOM_N_CANONICAL | Alias | Optional Required to support custom package repositories. This value can be used as an alias and will be used by the cache server to reference different DNS names. For example, repository content hostname may be packages.foo.com, but for different regions there could be an extra prefix that is added to the hostname like westuscdn.packages.foo.com and eastuscdn.packages.foo.com. By setting the canonical alias, you ensure that content isn't duplicated for content coming from the same host, but different CDN sources. The format of the canonical value isn't important, but it must be unique to the host. It may be easiest to set the value to match the host value. Examples based on the previous custom host examples: Name = CACHEABLE_CUSTOM_1_CANONICAL Value = foopackages Name = CACHEABLE_CUSTOM_2_CANONICAL Value = packages.bar.com |
| IS_SUMMARY_PUBLIC | True or False | Optional Enables viewing of the summary report on the local network or internet. Use of an API key (discussed later) is required to view the summary report if set to true. |
| IS_SUMMARY_ACCESS_UNRESTRICTED | True or False | Optional Enables viewing of summary report on the local network or internet without use of API key from any device in the network. Use if you don't want to lock down access to viewing cache server summary data via the browser. |
Module container create options
Container create options provide control of the settings related to storage and ports used by the Microsoft Connected Cache module.
Sample container create options:
{
"HostConfig": {
"Binds": [
"/microsoftConnectedCache1/:/nginx/cache1/"
],
"PortBindings": {
"8081/tcp": [
{
"HostPort": "80"
}
],
"5000/tcp": [
{
"HostPort": "5100"
}
]
}
}
}
The following sections list the required container create variables used to deploy the MCC module.
HostConfig
The HostConfig parameters are required to map the container storage location to the storage location on the disk. Up to nine locations can be specified.
Note
The number of the drive must match the cache drive binding values specified in the environment variable STORAGE_N_SIZE_GB value, /MicrosoftConnectedCache*N*/:/nginx/cache*N*/.
PortBindings
The PortBindings parameters map container ports to ports on the host device.
The first port binding specifies the external machine HTTP port that MCC listens on for content requests. The default HostPort is port 80 and other ports aren't supported at this time as the ADU client makes requests on port 80 today. TCP port 8081 is the internal container port that the MCC listens on and can't be changed.
The second port binding ensures that the container isn't listening on host port 5000. The Microsoft Connected Cache module has a .NET Core service, which is used by the caching engine for various functions. To support nested edge, the HostPort must not be set to 5000 because the registry proxy module is already listening on host port 5000.
Microsoft Connected Cache summary report
The summary report is currently the only way for a customer to view caching data for the Microsoft Connected Cache instances deployed to IoT Edge gateways. The report is generated at 15-second intervals and includes averaged stats for the period and aggregated stats for the lifetime of the module. The key stats that the report provides are:
- hitBytes - The sum of bytes delivered that came directly from cache.
- missBytes - The sum of bytes delivered that Microsoft Connected Cache had to download from CDN to see the cache.
- eggressBytes - The sum of hitBytes and missBytes and is the total bytes delivered to clients.
- hitRatioBytes - The ratio of hitBytes to egressBytes. For example, if 100% of eggressBytes delivered in a period were equal to the hitBytes, this value would be 1.
The summary report is available at http://<IoT Edge gateway>:5001/summary Replace <IoT Edge Gateway> with the IP address or hostname of the IoT Edge gateway hosting the MCC module.
Next steps
Learn how to implement Microsoft Connected Cache in single gateways or nested and industrial IoT gateways.