Explore how Power Platform works with Microsoft Teams
When COVID-19 hit the world, organizations were forced to rethink how their work force gets things done. Many organizations switched their workers to work remotely. This introduced a need for better collaborative tools organizations can utilize.
Microsoft Teams fills that need for many organizations. It provides a central point where users can collaborate with other users, have meetings, manage projects, and more. One key advantage of Microsoft Teams is how extensible and adaptable it is. This means organizations can build custom applications for Teams based on the needs of their users. Microsoft Power Platform is the innovative gateway to rapidly build Teams compatible apps using low-code attributes. All Power Platform components can be used with Microsoft Teams.
Let’s examine them in a little more detail.
Power BI: The Power BI tab for Microsoft Teams adds support for reports in the Teams workspace and allows users to share interactive Power BI content and collaborate with others in Teams channels and chats. You can create packaged Power BI app content from scratch and distribute it as an app or create a template app in Power BI. Additionally, use the new Power BI app in Teams to bring your entire basic Power BI service experience into Teams.
Power Apps: The Power Apps app in Teams provides an integrated experience for app makers to create and edit apps and workflows within Teams. They can quickly publish and share the apps with team members. The members can use the apps without having to switch between multiple apps and services. For example, a company might create an incident reporting application that can be accessed directly from Microsoft Teams. When a user needs to report an incident, they can do so without ever needing to leave Microsoft Teams.
Power Automate: You can create flows to automate repetitive work tasks directly within the Teams environment with the Power Automate app in Teams. You can trigger a flow from any message in Microsoft Teams and use Adaptive Cards within Power Automate. Additionally, you can build flows to customize and add further value to Microsoft Teams from within the new Power Apps app in Teams.
Copilot Studio: You can create, manage, and publish conversational copilots (chatbots) easily from within Teams. You can share copilots with other people in your organization to chat and get answers for their questions.
Dataverse for Teams: Dataverse for Teams is a built-in, low-code data platform that empowers users to build custom apps, bots, and flows directly in Microsoft Teams with Power Apps, Power Virtual Agents, and Power Automate.
Let’s look at an example.
Since the global pandemic hit in 2020, real estate companies have dramatically changed how they do business. First, all their real estate agents are remote workers now. Most of them come into the office once per month at the most. Since most of their workforce is mobile, being able to collaborate with team members is more important than ever. Their agents spend most of their day working in Microsoft Teams. It's important that they not only collaborate with other employees, but also perform day-to-day activities. By using Power Platform with Teams, we can provide real estate agents with the following capabilities:
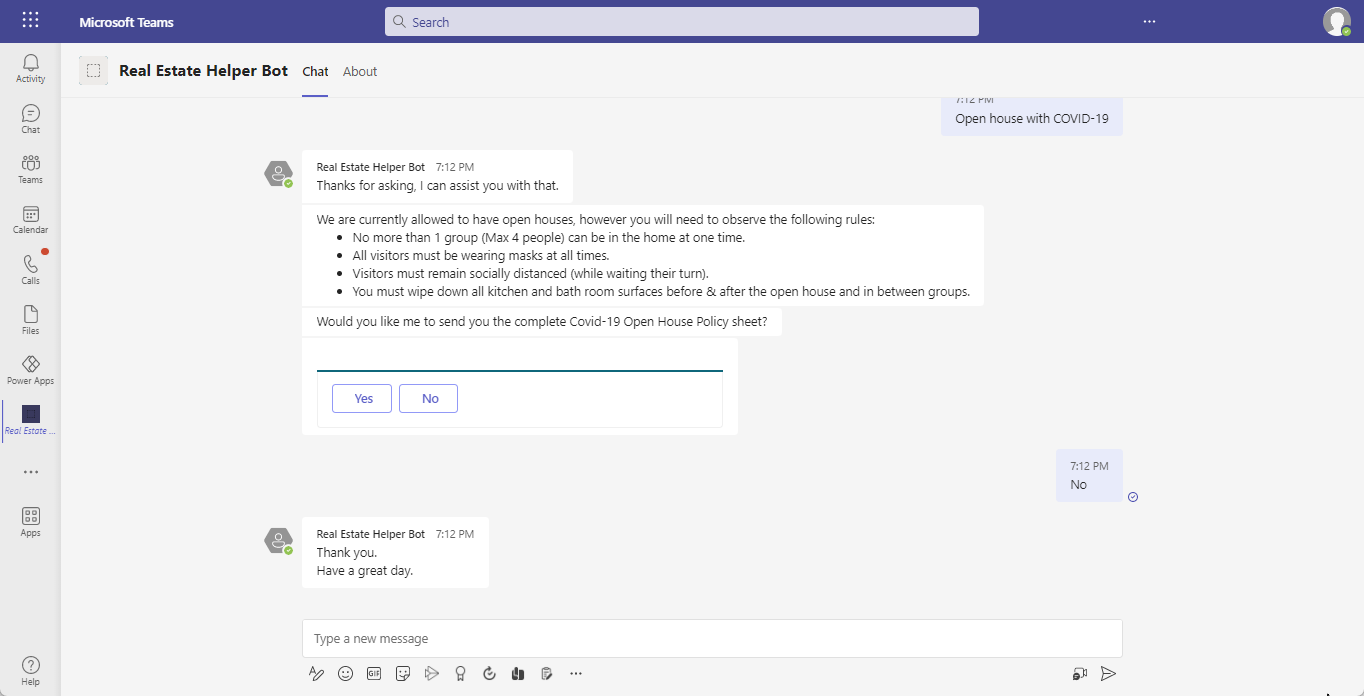
Dedicated Copilots embedded in Microsoft Teams can answer agent questions and help them with day-to-day tasks. For example, a copilot can answer questions about open house protocols and assist agents with scheduling open houses.
A dedicated expense submission app can be built using Dataverse for Teams to help agents submit expenses related to travel, staging, and open houses right for Teams.
Power BI reports that provide analytics around properties can be easily embedded inside Microsoft Teams.
In the image, we can see a dedicated chat bot inside Microsoft Teams that helps answer agents’ questions related to different things such as open house scheduling protocols.
Clickthrough demo: Accessing Power Platform components from within Teams
In this clickthrough demonstration, you're guided through the process of accessing Power Platform components from within Teams.
Accessing Power Platform components from within Teams