Hello @Anas Elnashar ,
The address space for a virtual network is composed of one or more non-overlapping address ranges that are specified in CIDR notation. Although you can define only one address range when you create the virtual network in the portal, you can add more address ranges to the address space after the virtual network is created. To learn how to add an address range to an existing virtual network, see Add or remove an address range.
Sometimes, when you end up using the entire range of address space of your Vnet and are not willing to create a new Vnet, you can simply add a new address space to the existing Vnet. It completely depends upon the user's requirement. Another benefit is, if you create a new Vnet and would like to connect the machines on both your old and new Vnet, you would have to setup a Vnet peering but if you add an additional address space in the old Vnet and create the VMs, they can by default talk to the existing VMs since they belong to the same Vnet. Vnet peering is charged but Virtual network is free of charge.
As far as routing is concerned, Azure automatically creates a route table for each subnet within an Azure virtual network and adds system default routes to the table. Each route contains an address prefix and next hop type. The default route for Virtual Network is as below:
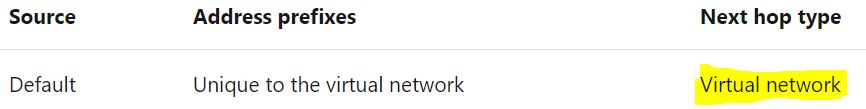
Virtual network: Routes traffic between address ranges within the address space of a virtual network. Azure creates a route with an address prefix that corresponds to each address range defined within the address space of a virtual network. If the virtual network address space has multiple address ranges defined, Azure creates an individual route for each address range. Azure automatically routes traffic between subnets using the routes created for each address range. So you do not need to worry about the routing even when there are multiple address spaces as Azure takes care of it by adding default routes for each address space that exists within the Vnet.
Please refer : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-networks-udr-overview
Kindly let us know if you need any further assistance on this issue from our end.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Please don’t forget to "Accept the answer" wherever the information provided helps you, this can be beneficial to other community members.
