Azure Policy for Microsoft Entra-only authentication with Azure SQL
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure Policy can enforce the creation of an Azure SQL Database or Azure SQL Managed Instance with Microsoft Entra-only authentication enabled during provisioning. With this policy in place, any attempts to create a logical server in Azure or managed instance will fail if it isn't created with Microsoft Entra-only authentication enabled.
Note
Although Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) has been renamed to Microsoft Entra ID, the policy names currently contain the original Azure AD name, so Microsoft Entra-only and Azure AD-only authentication is used interchangeably in this article.
The Azure Policy can be applied to the whole Azure subscription, or just within a resource group.
Two new built-in policies have been introduced in Azure Policy:
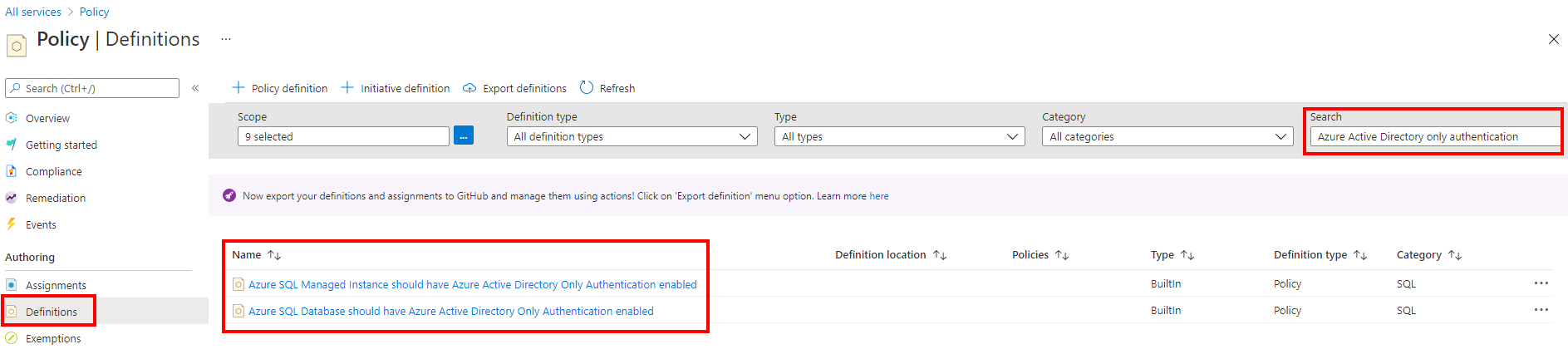
- Azure SQL Database should have Azure Active Directory Only Authentication enabled
- Azure SQL Managed Instance should have Azure Active Directory Only Authentication enabled
For more information on Azure Policy, see What is Azure Policy? and Azure Policy definition structure.
Permissions
For an overview of the permissions needed to manage Azure Policy, see Azure RBAC permissions in Azure Policy.
Actions
If you're using a custom role to manage Azure Policy, the following Actions are needed.
- */read
- Microsoft.Authorization/policyassignments/*
- Microsoft.Authorization/policydefinitions/*
- Microsoft.Authorization/policyexemptions/*
- Microsoft.Authorization/policysetdefinitions/*
- Microsoft.PolicyInsights/*
For more information on custom roles, see Azure custom roles.
Manage Azure Policy for Azure AD-only authentication
The Azure AD-only authentication policies can be managed by going to the Azure portal, and searching for the Policy service. Under Definitions, search for Azure Active Directory-only authentication.
For a guide, see Using Azure Policy to enforce Microsoft Entra-only authentication with Azure SQL.
There are three effects for these policies:
- Audit - The default setting, and will only capture an audit report in the Azure Policy activity logs
- Deny - Prevents logical server or managed instance creation without Microsoft Entra-only authentication with Azure SQL enabled
- Disabled - Will disable the policy, and won't restrict users from creating a logical server or managed instance without Microsoft Entra-only authentication enabled
If the Azure Policy for Azure AD-only authentication is set to Deny, creating a logical server or managed instance fails. The details of this failure are recorded in the Activity log of the resource group.
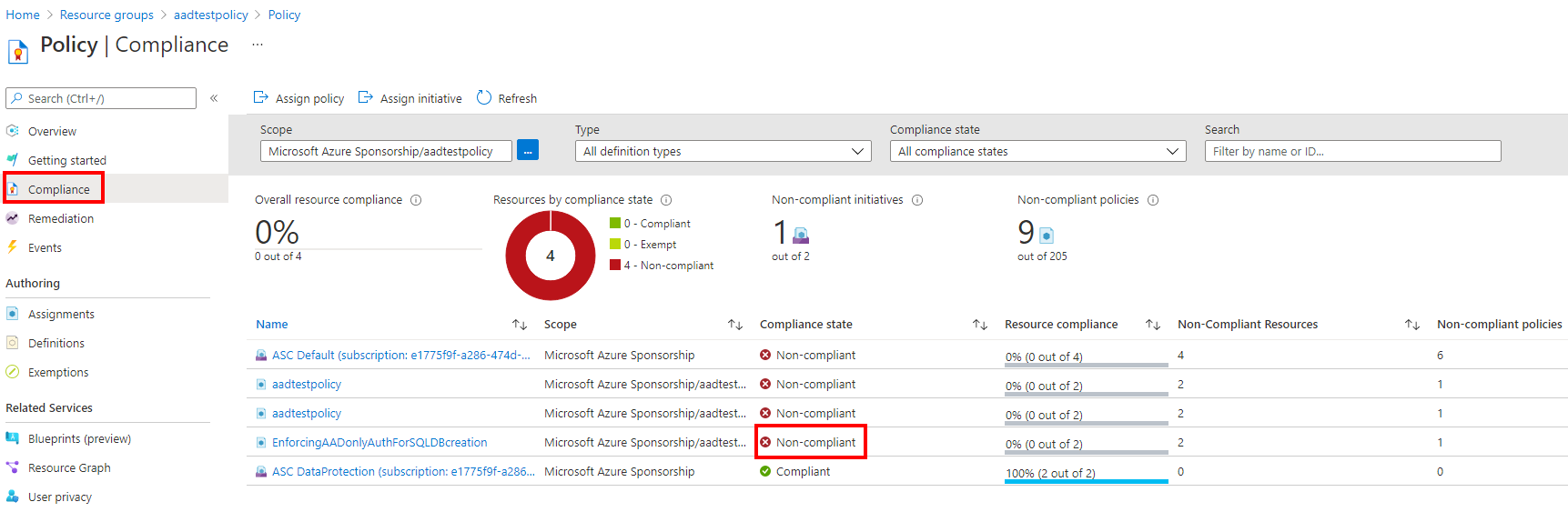
Policy compliance
You can view the Compliance setting under the Policy service to see the compliance state. The Compliance state will tell you whether the server or managed instance is currently in compliance with having Microsoft Entra-only authentication enabled.
The Azure Policy can prevent a new logical server or managed instance from being created without having Microsoft Entra-only authentication enabled, but the feature can be changed after server or managed instance creation. If a user has disabled Microsoft Entra-only authentication after the server or managed instance was created, the compliance state will be Non-compliant if the Azure Policy is set to Deny.
Limitations
- Azure Policy enforces Azure AD-only authentication during logical server or managed instance creation. Once the server is created, authorized Microsoft Entra users with special roles (for example, SQL Security Manager) can disable the Azure AD-only authentication feature. The Azure Policy allows it, but in this case, the server or managed instance will be listed in the compliance report as
Non-compliantand the report will indicate the server or managed instance name. - For more remarks, known issues, and permissions needed, see Microsoft Entra-only authentication with Azure SQL.