Tutorial: Configure network for Azure Stack Edge Pro R
This tutorial describes how to configure network for your Azure Stack Edge Pro R device by using the local web UI.
The connection process can take around 20 minutes to complete.
In this tutorial, you learn about:
- Prerequisites
- Configure network
- Configure advanced networking
- Configure web proxy
- Validate network settings
Prerequisites
Before you configure and set up your Azure Stack Edge Pro R device, make sure that you:
- Install the physical device as detailed in Install Azure Stack Edge Pro R.
- Connect to the local web UI of the device as detailed in Connect to Azure Stack Edge Pro R
Configure network
Your Get started page displays the various settings that are required to configure and register the physical device with the Azure Stack Edge service.
Follow these steps to configure the network for your device.
In the local web UI of your device, go to the Get started page.
On the Network tile, select Configure to go to the Network page.
On your physical device, there are four network interfaces. PORT 1 and PORT 2 are 1-Gbps network interfaces. PORT 3 and PORT 4 are all 10/25-Gbps network interfaces. PORT 1 is automatically configured as a management-only port, and PORT 2 to PORT 4 are all data ports. The Network page is as shown as follows:
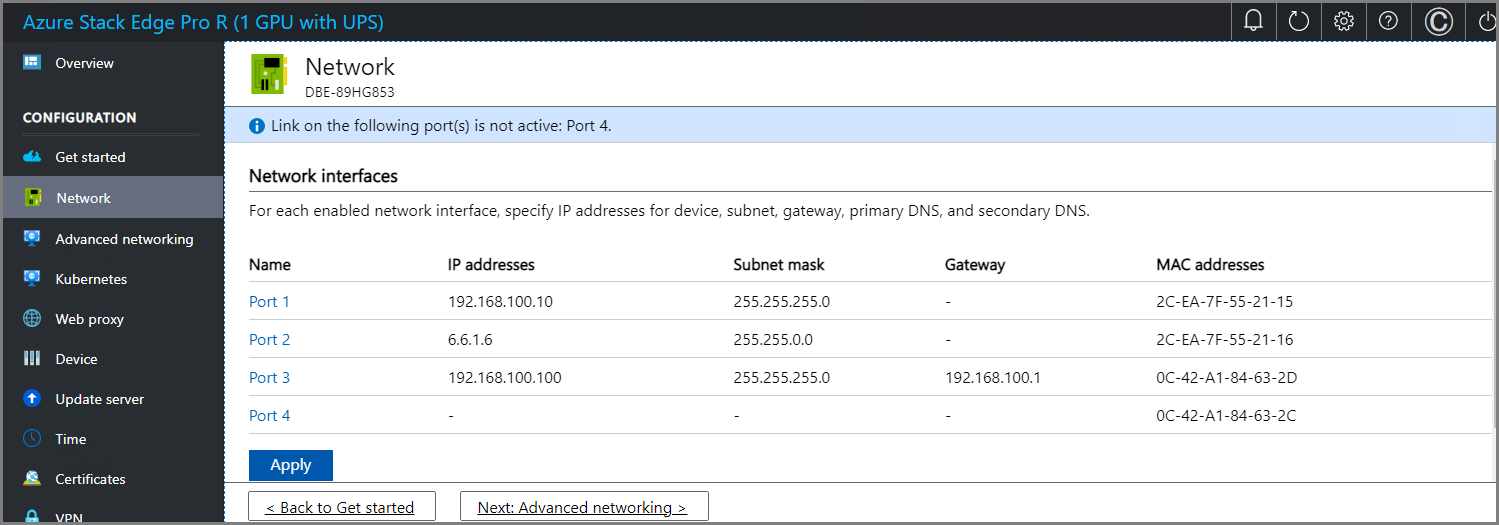
To change the network settings, select a port and in the right pane that appears, modify the IP address, subnet, gateway, primary DNS, and secondary DNS.
If you select Port 1, you can see that it's preconfigured as static.
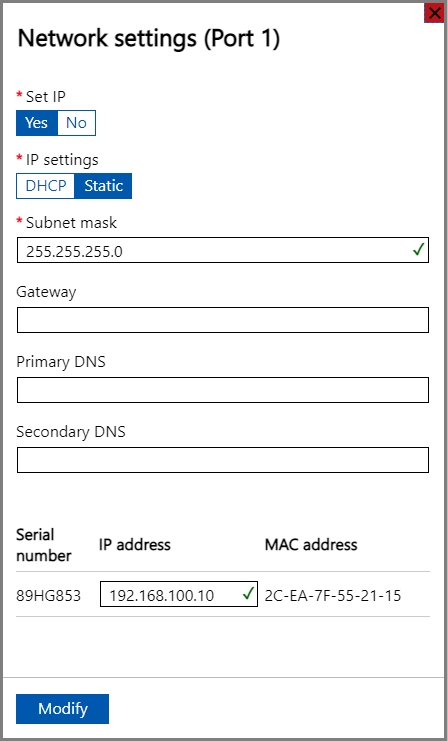
If you select Port 2, Port 3, or Port 4, all of these ports are configured as DHCP by default.
As you configure the network settings, keep in mind:
- If DHCP is enabled in your environment, network interfaces are automatically configured. An IP address, subnet, gateway, and DNS are automatically assigned.
- If DHCP isn't enabled, you can assign static IPs if needed.
- You can configure your network interface as IPv4.
- Network Interface Card (NIC) Teaming or link aggregation isn't supported with Azure Stack Edge.
- Serial number for any port corresponds to the node serial number.
Note
If you need to connect to your device from an outside network, see Enable device access from outside network for additional network settings.
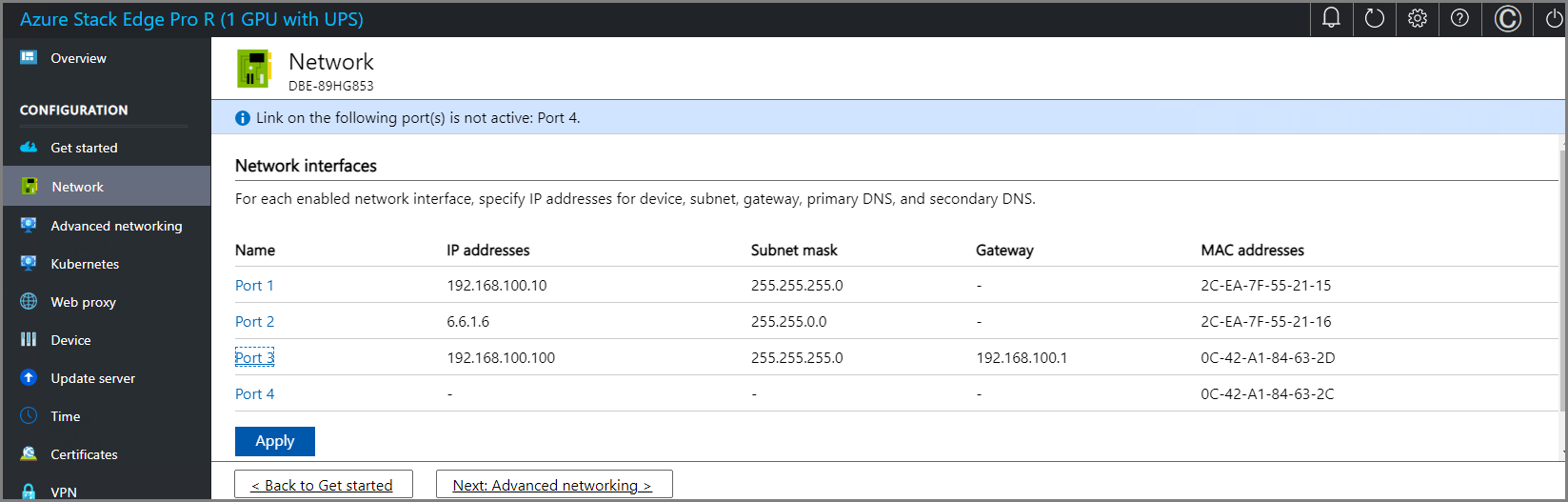
Once the device network is configured, the page updates as shown below.
Note
We recommend that you do not switch the local IP address of the network interface from static to DCHP, unless you have another IP address to connect to the device. If using one network interface and you switch to DHCP, there would be no way to determine the DHCP address. If you want to change to a DHCP address, wait until after the device has activated with the service, and then change. You can then view the IPs of all the adapters in the Device properties in the Azure portal for your service.
After you have configured and applied the network settings, select Next: Advanced networking to configure compute network.
Enable compute network
Follow these steps to enable compute and configure compute network.
In the Advanced networking page, select a network interface that you want to enable for compute.
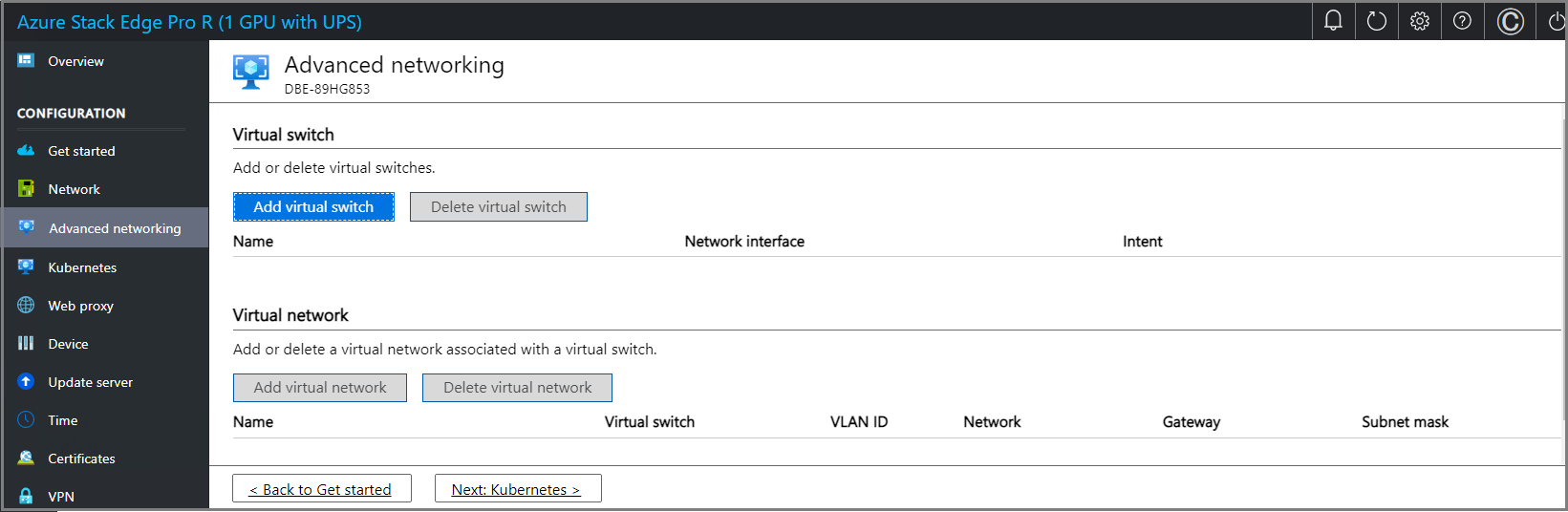
Configure virtual switches
Follow these steps to add or delete virtual switches and virtual networks.
In the local UI, go to Advanced networking page.
In the Virtual switch section, you add or delete virtual switches. Select Add virtual switch to create a new switch.
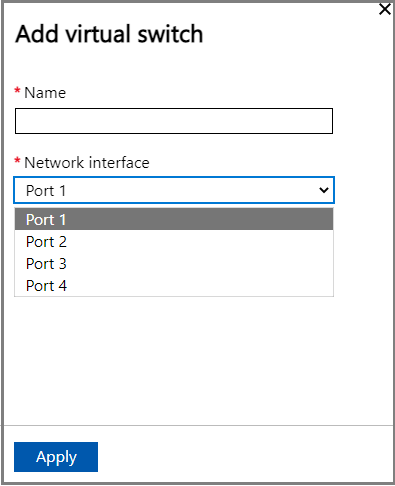
In the Network settings blade, if using a new switch, provide the following:
- Provide a name for your virtual switch.
- Choose the network interface on which the virtual switch should be created.
- If deploying 5G workloads, set Supports accelerated networking to Yes.
- Select Apply. You can see that the specified virtual switch is created.

You can create more than one switch by following the steps described earlier.
To delete a virtual switch, under the Virtual switch section, select Delete virtual switch. When a virtual switch is deleted, the associated virtual networks are also deleted.
You can now create virtual networks and associate with the virtual switches you created.
Configure virtual networks
You can add or delete virtual networks associated with your virtual switches. To add a virtual switch, follow these steps:
In the local UI on the Advanced networking page, under the Virtual network section, select Add virtual network.
In the Add virtual network blade, input the following information:
- Select a virtual switch for which you want to create a virtual network.
- Provide a Name for your virtual network. The name you specify must conform to Naming rules and restrictions for Azure resources.
- Enter a VLAN ID as a unique number in 1-4094 range. The VLAN ID that you provide should be in your trunk configuration. For more information about trunk configuration for your switch, refer to the instructions from your physical switch manufacturer.
- Specify the Subnet mask and Gateway for your virtual LAN network as per the physical network configuration.
- Select Apply. A virtual network is created on the specified virtual switch.
To delete a virtual network, under the Virtual network section, select Delete virtual network and select the virtual network you want to delete.
Select Next: Kubernetes > to next configure your compute IPs for Kubernetes.
Configure compute IPs
After the virtual switches are created, you can enable the switches for Kubernetes compute traffic.
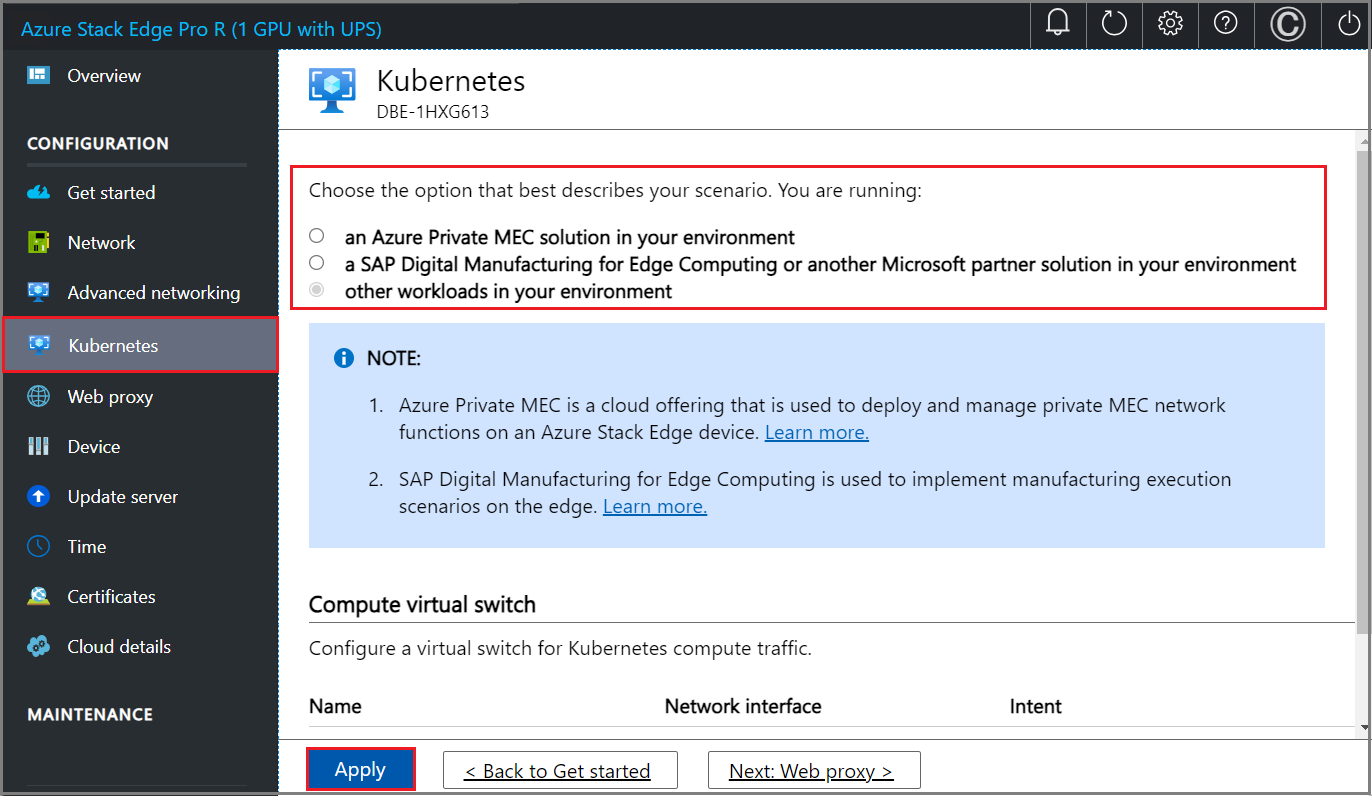
In the local UI, go to the Kubernetes page.
Specify a workload from the options provided.
- If you're working with an Azure Private MEC solution, select the option for an Azure Private MEC solution in your environment.
- If you're working with an SAP Digital Manufacturing solution or another Microsoft partner solution, select the option for a SAP Digital Manufacturing for Edge Computing or another Microsoft partner solution in your environment.
- For other workloads, select the option for other workloads in your environment.
If prompted, confirm the option you specified and then select Apply.
To use PowerShell to specify the workload, see detailed steps in Change Kubernetes workload profiles.
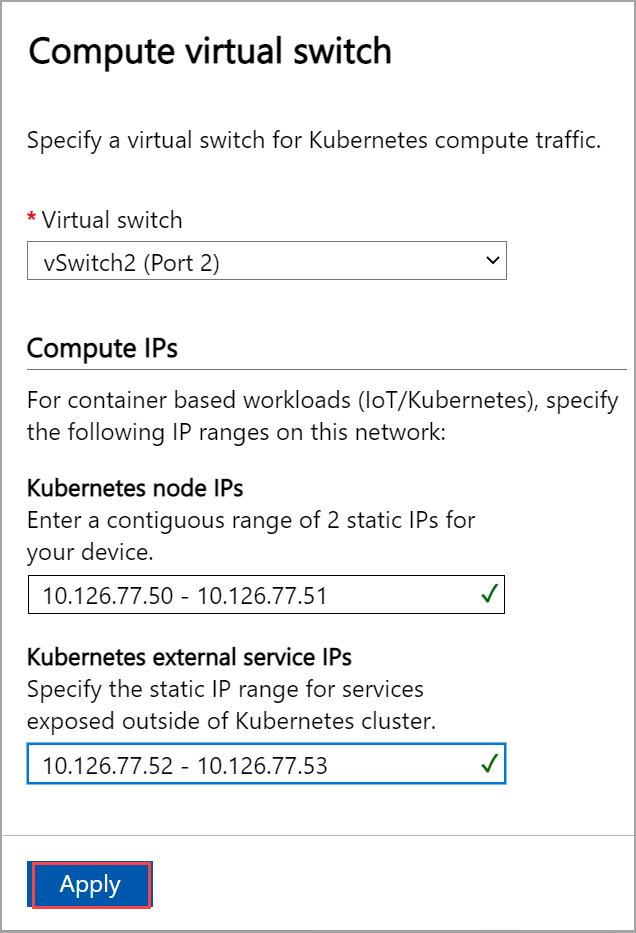
From the dropdown list, select the virtual switch you want to enable for Kubernetes compute traffic.
Assign Kubernetes node IPs. These static IP addresses are for the Kubernetes VMs.
If you select the Azure Private MEC solution or SAP Digital Manufacturing for Edge Computing or another Microsoft partner workload option for your environment, you must provide a contiguous range of a minimum of 6 IPv4 addresses (or more) for a 1-node configuration.
If you select the other workloads option for an n-node device, a contiguous range of a minimum of n+1 IPv4 addresses (or more) are provided for the compute VM using the start and end IP addresses. For a 1-node device, provide a minimum of 2 free, contiguous IPv4 addresses.
Important
- If you're running other workloads in your environment, Kubernetes on Azure Stack Edge uses 172.27.0.0/16 subnet for pod and 172.28.0.0/16 subnet for service. Make sure that these are not in use in your network. For more information, see Change Kubernetes pod and service subnets.
- DHCP mode is not supported for Kubernetes node IPs.
Assign Kubernetes external service IPs. These are also the load-balancing IP addresses. These contiguous IP addresses are for services that you want to expose outside of the Kubernetes cluster and you specify the static IP range depending on the number of services exposed.
Important
We strongly recommend that you specify a minimum of 1 IP address for Azure Stack Edge Hub service to access compute modules. The service IP addresses can be updated later.
Select Apply.
The configuration takes a couple minutes to apply and you may need to refresh the browser.
Select Next: Web proxy to configure web proxy.
Configure web proxy
This is an optional configuration.
Important
Proxy-auto config (PAC) files are not supported. A PAC file defines how web browsers and other user agents can automatically choose the appropriate proxy server (access method) for fetching a given URL. Proxies that try to intercept and read all the traffic (then re-sign everything with their own certification) aren't compatible since the proxy's certificate is not trusted. Typically, transparent proxies work well with Azure Stack Edge Pro R. Non-transparent web proxies are not supported.
On the Web proxy settings page, take the following steps:
In the Web proxy URL box, enter the URL in this format:
http://host-IP address or FQDN:Port number. HTTPS URLs aren't supported.To validate and apply the configured web proxy settings, select Apply.
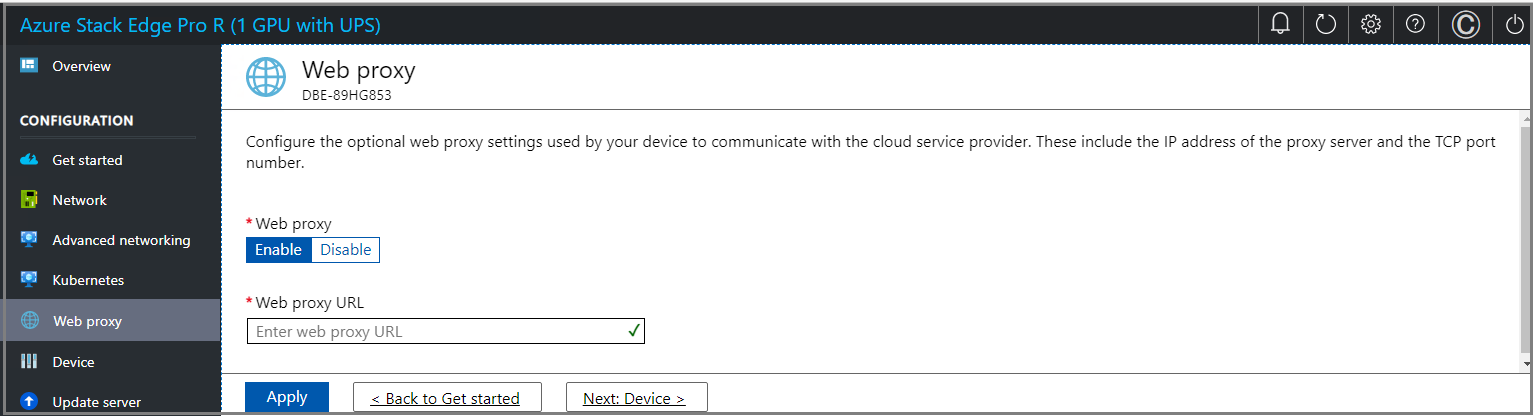
After the settings are applied, select Next: Device.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned about:
- Prerequisites
- Configure network
- Configure advanced networking
- Configure web proxy
- Validate network settings
To learn how to set up your Azure Stack Edge Pro R device, see:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for