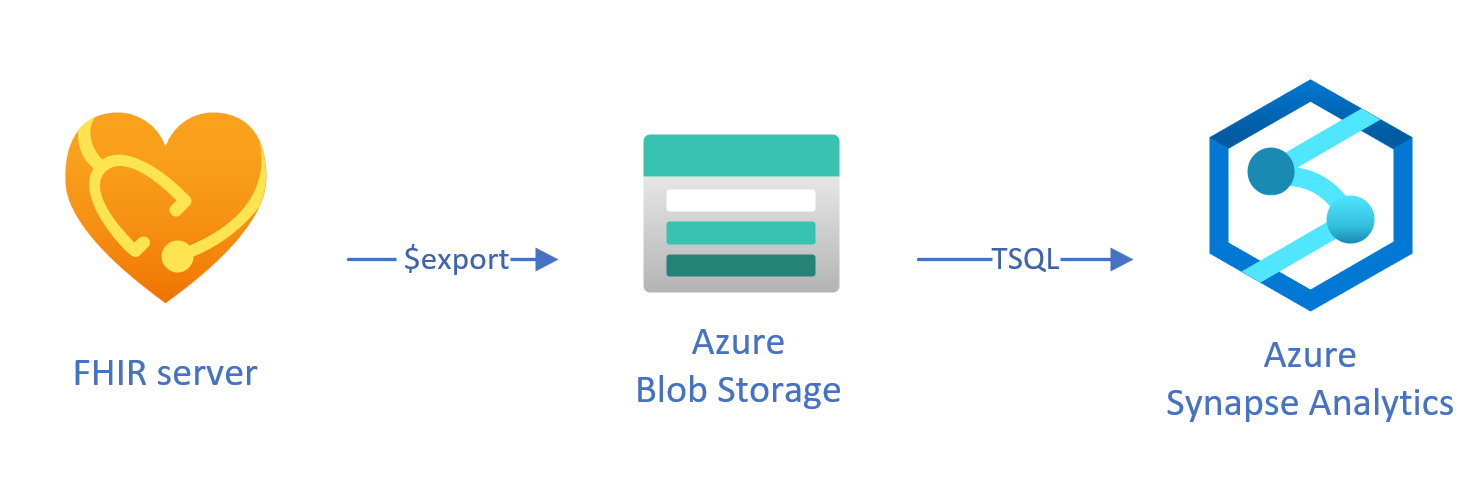
Copy data from FHIR service to Azure Synapse Analytics
In this article, you learn three ways to copy data from the FHIR® service in Azure Health Data Services to Azure Synapse Analytics, which is a limitless analytics service that brings together data integration, enterprise data warehousing, and big data analytics.
- Use the FHIR to Synapse Sync Agent OSS tool
- Use the FHIR to CDM pipeline generator OSS tool
- Use $export and load data to Synapse using T-SQL
Using the FHIR to Synapse Sync Agent OSS tool
Note
FHIR to Synapse Sync Agent is an open source tool released under MIT license, and is not covered by the Microsoft SLA for Azure services.
The FHIR to Synapse Sync Agent is a Microsoft OSS project released under MIT License. It's an Azure function that extracts data from a FHIR server using FHIR Resource APIs, converts it to hierarchical Parquet files, and writes it to Azure Data Lake in near real time. This also contains a script to create external tables and views in Synapse Serverless SQL pool pointing to the Parquet files.
This solution enables you to query against the entire FHIR data with tools such as Synapse Studio, SSMS, and Power BI. You can also access the Parquet files directly from a Synapse Spark pool. You should consider this solution if you want to access all of your FHIR data in near real time, and want to defer custom transformation to downstream systems.
Follow the OSS documentation for installation and usage instructions.
Using the FHIR to CDM pipeline generator OSS tool
Note
FHIR to CDM pipeline generator is an open source tool released under MIT license, and is not covered by the Microsoft SLA for Azure services.
The FHIR to CDM pipeline generator is a Microsoft OSS project released under MIT License. It's a tool to generate an ADF pipeline for copying a snapshot of data from a FHIR server using $export API, transforming it to csv format, and writing to a CDM folder in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen 2. The tool requires a user-created configuration file containing instructions to project and flatten FHIR Resources and fields into tables. You can also follow the instructions for creating a downstream pipeline in Synapse workspace to move data from a CDM folder to a Synapse dedicated SQL pool.
This solution enables you to transform the data into tabular format as it gets written to CDM folder. You should consider this solution if you want to transform FHIR data into a custom schema after it's extracted from the FHIR server.
Follow the OSS documentation for installation and usage instructions.
Loading exported data to Synapse using T-SQL
In this approach, you use the FHIR $export operation to copy FHIR resources into a Azure Data Lake Gen 2 (ADL Gen 2) blob storage in NDJSON format. Then, you load the data from the storage into serverless or dedicated SQL pools in Synapse using T-SQL. You can convert these steps into a robust data movement pipeline using Synapse pipelines.
Using $export to copy data
Configuring $export in the FHIR server
The FHIR server in Azure Health Data Services implements the $export operation defined by the FHIR specification to export all or a filtered subset of FHIR data in NDJSON format. In addition, it supports de-identified export to anonymize FHIR data during the export.
To export FHIR data to Azure blob storage, you first need to configure your FHIR server to export data to the storage account. You'll need to (1) enable Managed Identity, (2) go to Access Control in the storage account and add role assignment, (3) select your storage account for $export. More step by step can be found here.
You can configure the server to export the data to any kind of Azure storage account, but we recommend exporting to ADL Gen 2 for best alignment with Synapse.
Using $export command
After configuring your FHIR server, you can follow the documentation to export your FHIR resources at System, Patient, or Group level. For example, you can export all of your FHIR data related to the patients in a Group with the following $export command, in which you specify your ADL Gen 2 blob storage name in the field {{BlobContainer}}:
https://{{FHIR service base URL}}/Group/{{GroupId}}/$export?_container={{BlobContainer}}
You can also use _type parameter in the preceding $export call to restrict the resources that you want to export. For example, the following call exports only Patient, MedicationRequest, and Observation resources:
https://{{FHIR service base URL}}/Group/{{GroupId}}/$export?_container={{BlobContainer}}&
_type=Patient,MedicationRequest,Condition
For more information on the different parameters supported, check out our $export page section on the query parameters.
Using Synapse for Analytics
Creating a Synapse workspace
Before using Synapse, you'll need a Synapse workspace. Create an Azure Synapse Analytics service on Azure portal. More step-by-step guidance can be found here. You need an ADLSGEN2 account to create a workspace. Your Azure Synapse workspace will use this storage account to store your Synapse workspace data.
After creating a workspace, you can view your workspace in Synapse Studio by signing into your workspace on https://web.azuresynapse.net, or launching Synapse Studio in the Azure portal.
Creating a linked service between Azure storage and Synapse
To copy your data to Synapse, you need to create a linked service that connects your Azure Storage account, where you've exported your data, with Synapse. More step-by-step instructions can be found here.
- In Synapse Studio, browse to the Manage tab and under External connections, select Linked services.
- Select New to add a new linked service.
- Select Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 from the list and select Continue.
- Enter your authentication credentials. Select Create when finished.
Now that you have a linked service between your ADL Gen 2 storage and Synapse, you're ready to use Synapse SQL pools to load and analyze your FHIR data.
Decide between serverless and dedicated SQL pool
Azure Synapse Analytics offers two different SQL pools: serverless SQL pool and dedicated SQL pool. Serverless SQL pool gives the flexibility of querying data directly in the blob storage using the serverless SQL endpoint without any resource provisioning. Dedicated SQL pool has the processing power for high performance and concurrency, and is recommended for enterprise-scale data warehousing capabilities. For more details on the two SQL pools, check out the Synapse documentation page on SQL architecture.
Using serverless SQL pool
Since it's serverless, there's no infrastructure to setup or clusters to maintain. You can start querying data from Synapse Studio as soon as the workspace is created.
For example, the following query can be used to transform selected fields from Patient.ndjson into a tabular structure:
SELECT * FROM
OPENROWSET(bulk 'https://{{youraccount}}.blob.core.windows.net/{{yourcontainer}}/Patient.ndjson',
FORMAT = 'csv',
FIELDTERMINATOR ='0x0b',
FIELDQUOTE = '0x0b')
WITH (doc NVARCHAR(MAX)) AS rows
CROSS APPLY OPENJSON(doc)
WITH (
ResourceId VARCHAR(64) '$.id',
Active VARCHAR(10) '$.active',
FullName VARCHAR(100) '$.name[0].text',
Gender VARCHAR(20) '$.gender',
...
)
In the preceding query, the OPENROWSET function accesses files in Azure Storage, and OPENJSON parses JSON text and returns the JSON input properties as rows and columns. Every time this query is executed, the serverless SQL pool reads the file from the blob storage, parses the JSON, and extracts the fields.
You can also materialize the results in Parquet format in an External Table to get better query performance, as follows.
-- Create External data source where the parquet file will be written
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE [MyDataSource] WITH (
LOCATION = 'https://{{youraccount}}.blob.core.windows.net/{{exttblcontainer}}'
);
GO
-- Create External File Format
CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT [ParquetFF] WITH (
FORMAT_TYPE = PARQUET,
DATA_COMPRESSION = 'org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec'
);
GO
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[Patient] WITH (
LOCATION = 'PatientParquet/',
DATA_SOURCE = [MyDataSource],
FILE_FORMAT = [ParquetFF]
) AS
SELECT * FROM
OPENROWSET(bulk 'https://{{youraccount}}.blob.core.windows.net/{{yourcontainer}}/Patient.ndjson'
-- Use rest of the SQL statement from the previous example --
Using dedicated SQL pool
Dedicated SQL pool supports managed tables and a hierarchical cache for in-memory performance. You can import big data with simple T-SQL queries, and then use the power of the distributed query engine to run high-performance analytics.
The simplest and fastest way to load data from your storage to a dedicated SQL pool is to use the COPY command in T-SQL, which can read CSV, Parquet, and ORC files. As in the following example query, use the COPY command to load the NDJSON rows into a tabular structure.
-- Create table with HEAP, which is not indexed and does not have a column width limitation of NVARCHAR(4000)
CREATE TABLE StagingPatient (
Resource NVARCHAR(MAX)
) WITH (HEAP)
COPY INTO StagingPatient
FROM 'https://{{yourblobaccount}}.blob.core.windows.net/{{yourcontainer}}/Patient.ndjson'
WITH (
FILE_TYPE = 'CSV',
ROWTERMINATOR='0x0a',
FIELDQUOTE = '',
FIELDTERMINATOR = '0x00'
)
GO
Once you have the JSON rows in the preceding StagingPatient table, you can create different tabular formats of the data using the OPENJSON function and storing the results into tables. Here's a sample SQL query to create a Patient table by extracting a few fields from the Patient resource:
SELECT RES.*
INTO Patient
FROM StagingPatient
CROSS APPLY OPENJSON(Resource)
WITH (
ResourceId VARCHAR(64) '$.id',
FullName VARCHAR(100) '$.name[0].text',
FamilyName VARCHAR(50) '$.name[0].family',
GivenName VARCHAR(50) '$.name[0].given[0]',
Gender VARCHAR(20) '$.gender',
DOB DATETIME2 '$.birthDate',
MaritalStatus VARCHAR(20) '$.maritalStatus.coding[0].display',
LanguageOfCommunication VARCHAR(20) '$.communication[0].language.text'
) AS RES
GO
Next steps
In this article, you learned three different ways to copy your FHIR data into Synapse.
Next, you can learn about how you can de-identify your FHIR data while exporting it to Synapse in order to protect PHI.
Note
FHIR® is a registered trademark of HL7 and is used with the permission of HL7.