Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article shows you how to scale your app in Azure App Service. There are two workflows for scaling, scale up and scale out, and this article explains the scale up workflow.
- Scale up: Get more CPU, memory, or disk space, or extra features like dedicated virtual machines (VMs), custom domains and certificates, staging slots, autoscaling, and more. You scale up by changing the pricing tier of the App Service plan that your app belongs to.
- Scale out: Increase the number of VM instances that run your app. Basic, Standard, and Premium service plans scale out to as many as 3, 10, and 30 instances, respectively. App Service Environments in the Isolated tier further increase your scale-out count to 100 instances. For more information about scaling out, see Scale instance count manually or automatically. There, you find out how to use autoscaling, which is to scale instance count automatically based on predefined rules and schedules.
Important
App Service offers an automatic scale-out option to handle varying incoming HTTP requests.
The scale settings take only seconds to apply and affect all apps in your App Service plan. They don't require you to change your code or redeploy your application.
For information about the pricing and features of individual App Service plans, see App Service Pricing Details.
Note
Before you switch an App Service plan from the Free tier, you must first remove the spending limits in place for your Azure subscription. To view or change options for your App Service subscription, see Cost Management + Billing in the Azure portal.
Scale up your pricing tier
Note
To scale up to Premium V4 tier, see Configure Premium V4 tier for App Service.
In your browser, open the Azure portal.
In the left navigation of your App Service app page, select Scale up (App Service plan).
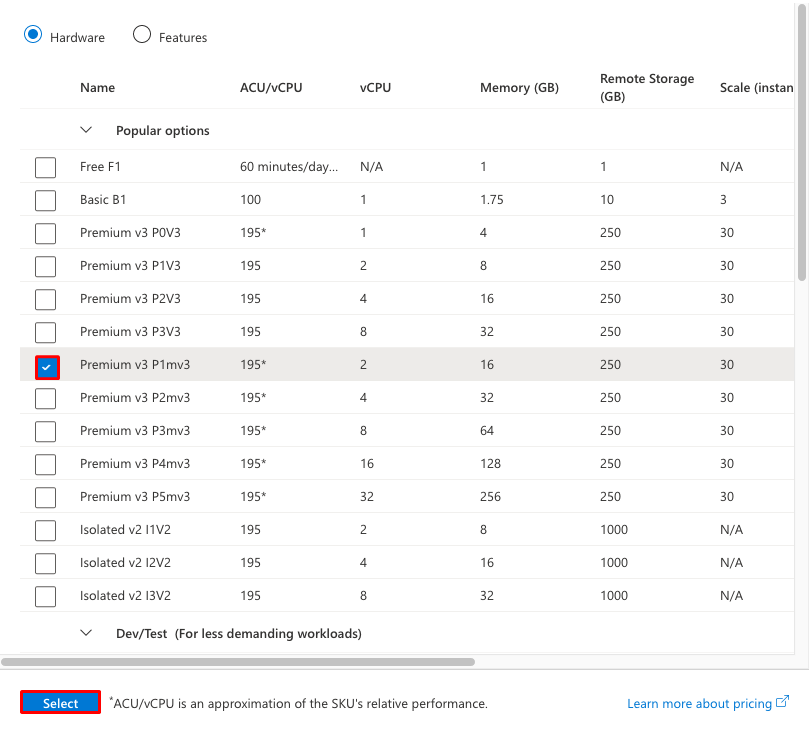
Select one of the pricing tiers and select Select.
When the operation is complete, you see a notification pop-up with a green success check mark.
Scale related resources
If your app depends on other services, such as Azure SQL Database or Azure Storage, you can scale up these resources separately. These resources aren't managed by the App Service plan.
In the Overview page for your app, select the Resource group link.
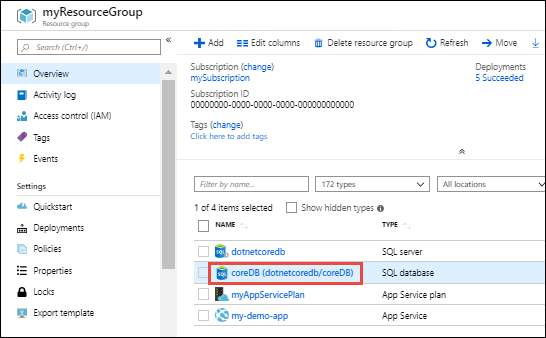
On the Overview page for the resource group, select a resource that you want to scale. The following screenshot shows a SQL Database resource.
To scale up the related resource, see the documentation for the specific resource type. For example, to scale up a single SQL database, see Scale single database resources in Azure SQL Database. To scale up an Azure Database for MySQL resource, see Scale Azure Database for MySQL resources.
Compare pricing tiers
For detailed information, such as VM sizes for each pricing tier, see App Service Pricing Details.
For a table of service limits, quotas, and constraints, and supported features in each tier, see App Service limits.