Azure Cosmos DB dedicated gateway - Overview
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
A dedicated gateway is server-side compute that is a front-end to your Azure Cosmos DB account. When you connect to the dedicated gateway, it both routes requests and caches data. Like provisioned throughput, the dedicated gateway is billed hourly.
Overview
You can provision a dedicated gateway to improve performance at scale. The most common reason that you would want to provision a dedicated gateway is for caching. When you provision a dedicated gateway, an integrated cache is automatically configured within the dedicated gateway. Point reads and queries that hit the integrated cache don't use any of your RUs. Provisioning a dedicated gateway with an integrated cache can help reduce costs for read-heavy workloads on Azure Cosmos DB.
The dedicated gateway is built into Azure Cosmos DB. When you provision a dedicated gateway, you have a fully managed node that routes requests to backend partitions. Connecting to Azure Cosmos DB with the dedicated gateway provides lower and more predictable latency than connecting to Azure Cosmos DB with the standard gateway. Even cache misses see latency improvements when comparing the dedicated gateway and standard gateway.
There are only minimal code changes required in order for your application to use a dedicated gateway. Both new and existing Azure Cosmos DB accounts can provision a dedicated gateway for improved read performance.
Note
Do you have any feedback about the dedicated gateway? We want to hear it! Feel free to share feedback directly with the Azure Cosmos DB engineering team: cosmoscachefeedback@microsoft.com
Connection modes
There are two connectivity modes for Azure Cosmos DB, Direct mode and Gateway mode. With Gateway mode you can connect to either the standard gateway or the dedicated gateway depending on the endpoint you configure.
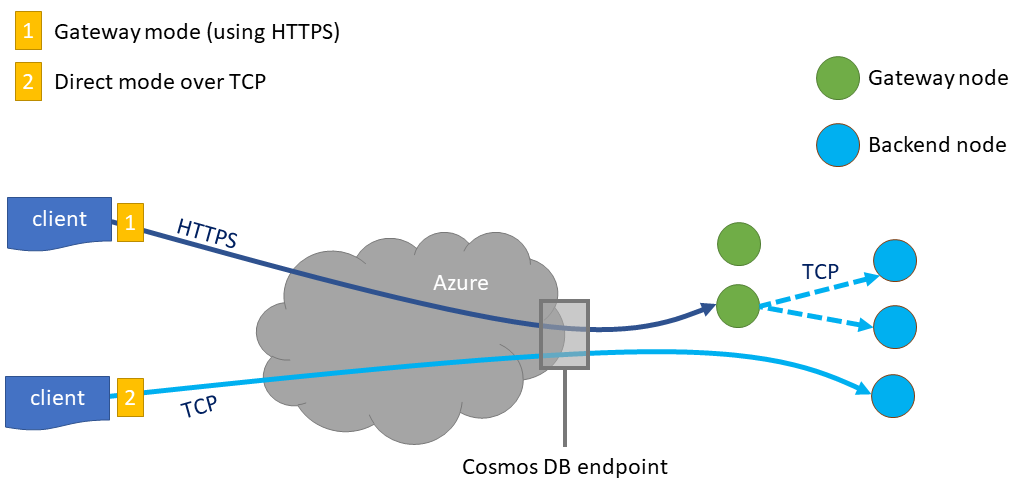
Connect to Azure Cosmos DB using direct mode
When you connect to Azure Cosmos DB using direct mode, your application connects directly to the Azure Cosmos DB backend. Even if you have many physical partitions, request routing is handled entirely client-side. Direct mode offers low latency because your application can communicate directly with the Azure Cosmos DB backend and doesn't need an intermediate network hop. If you choose to connect with direct mode, your requests won't use the dedicated gateway or the integrated cache.
Connect to Azure Cosmos DB using gateway mode
If you connect to Azure Cosmos DB using gateway mode, your application connects to a front-end node first, which handles routing the request to the appropriate backend nodes. Because gateway mode involves an extra network hop, you may observe slightly higher latency when compared to direct mode.
When connecting to Azure Cosmos DB with gateway mode, you can connect with either of the following options:
- Standard gateway - While the backend, which includes your provisioned throughput and storage, has dedicated capacity per container, the standard gateway is shared between many Azure Cosmos DB accounts. It's practical for many customers to share a standard gateway since the compute resources consumed by each individual customer are small.
- Dedicated gateway - In this gateway, the backend and gateway both have dedicated capacity. The integrated cache requires a dedicated gateway because it requires significant CPU and memory that is specific to your Azure Cosmos DB account.
You must connect to Azure Cosmos DB using the dedicated gateway in order to use the integrated cache. The dedicated gateway has a different endpoint from the standard one provided with your Azure Cosmos DB account, but requests are routed in the same way. When you connect to your dedicated gateway endpoint, your application sends a request to the dedicated gateway, which then routes the request to different backend nodes. If possible, the integrated cache serves the result.
Diagram of gateway mode connection with a dedicated gateway:

Provisioning the dedicated gateway
A dedicated gateway cluster can be provisioned in API for NoSQL accounts. A dedicated gateway cluster can have up to five nodes by default and you can add or remove nodes at any time. All dedicated gateway nodes within your account share the same dedicated gateway endpoint.
Dedicated gateway nodes are independent from one another. When you provision multiple dedicated gateway nodes, any single node can route any given request. In addition, each node has a separate integrated cache from the others. The cached data within each node depends on the data that was recently written or read through that specific node. If an item or query is cached on one node, it isn't necessarily cached on the others.
For development, we recommend starting with one node but for production, you should provision three or more nodes for high availability. Learn how to provision a dedicated gateway cluster with an integrated cache. Provisioning multiple dedicated gateway nodes allows the dedicated gateway cluster to continue to route requests and serve cached data, even when one of the dedicated gateway nodes is unavailable.
The dedicated gateway is available in the following sizes. The integrated cache uses approximately 50% of the memory and the rest is reserved for metadata and routing requests to backend partitions.
| Sku Name | vCPU | Memory |
|---|---|---|
| D4s | 4 | 16 GB |
| D8s | 8 | 32 GB |
| D16s | 16 | 64 GB |
Tip
Once created, you can add or remove dedicated gateway nodes, but you can't modify the size of the nodes. To change the size of your dedicated gateway nodes you can deprovision the cluster and provision it again in a different size. This will result in a short period of downtime unless you change the endpoint in your application to use the standard gateway during reprovisioning.
There are many different ways to provision a dedicated gateway:
- Provision a dedicated gateway using the Azure portal
- Use Azure Cosmos DB's REST API
- Azure CLI
- ARM template
- Note: You can't deprovision a dedicated gateway using ARM templates
Note
You can provision a dedicated gateway in Azure Cosmos DB accounts with availability zones by request. Reach out to cosmoscachefeedback@microsoft.com for more information.
Dedicated gateway in multi-region accounts
When you provision a dedicated gateway cluster in multi-region accounts, identical dedicated gateway clusters are provisioned in each region. For example, consider an Azure Cosmos DB account in East US and North Europe. If you provision a dedicated gateway cluster with two D8 nodes in this account, you'd have four D8 nodes in total - two in East US and two in North Europe. You don't need to explicitly configure dedicated gateways in each region and your dedicated gateway endpoint remains the same. There are also no changes to best practices for performing failovers.
Like nodes within a cluster, dedicated gateway nodes across regions are independent. It's possible that the cached data in each region is different, depending on the recent reads or writes to that region.
Limitations
Dedicated gateways are only supported on API for NoSQL accounts.
Next steps
Read more about dedicated gateway usage in the following articles:
- Integrated cache
- Configure the integrated cache
- Integrated cache FAQ
- Trying to do capacity planning for a migration to Azure Cosmos DB? You can use information about your existing database cluster for capacity planning.
- If all you know is the number of vCores and servers in your existing database cluster, read about estimating request units using vCores or vCPUs
- If you know typical request rates for your current database workload, read about estimating request units using Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner