What's new
Note
Azure Defender for IoT has been renamed to Microsoft Defender for IoT.
This article lists new features and feature enhancements in Microsoft Defender for IoT for device builders.
Noted features are in PREVIEW. The Azure Preview Supplemental Terms include other legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
For more information, see Upgrade the Microsoft Defender for IoT micro agent.
March 2024
Updates to Defender for IoT Firmware Analysis:
Azure CLI and PowerShell commands: Automate your workflow of analyzing firmware images by using the Firmware Analysis Azure CLI or the Firmware Analysis PowerShell commands.
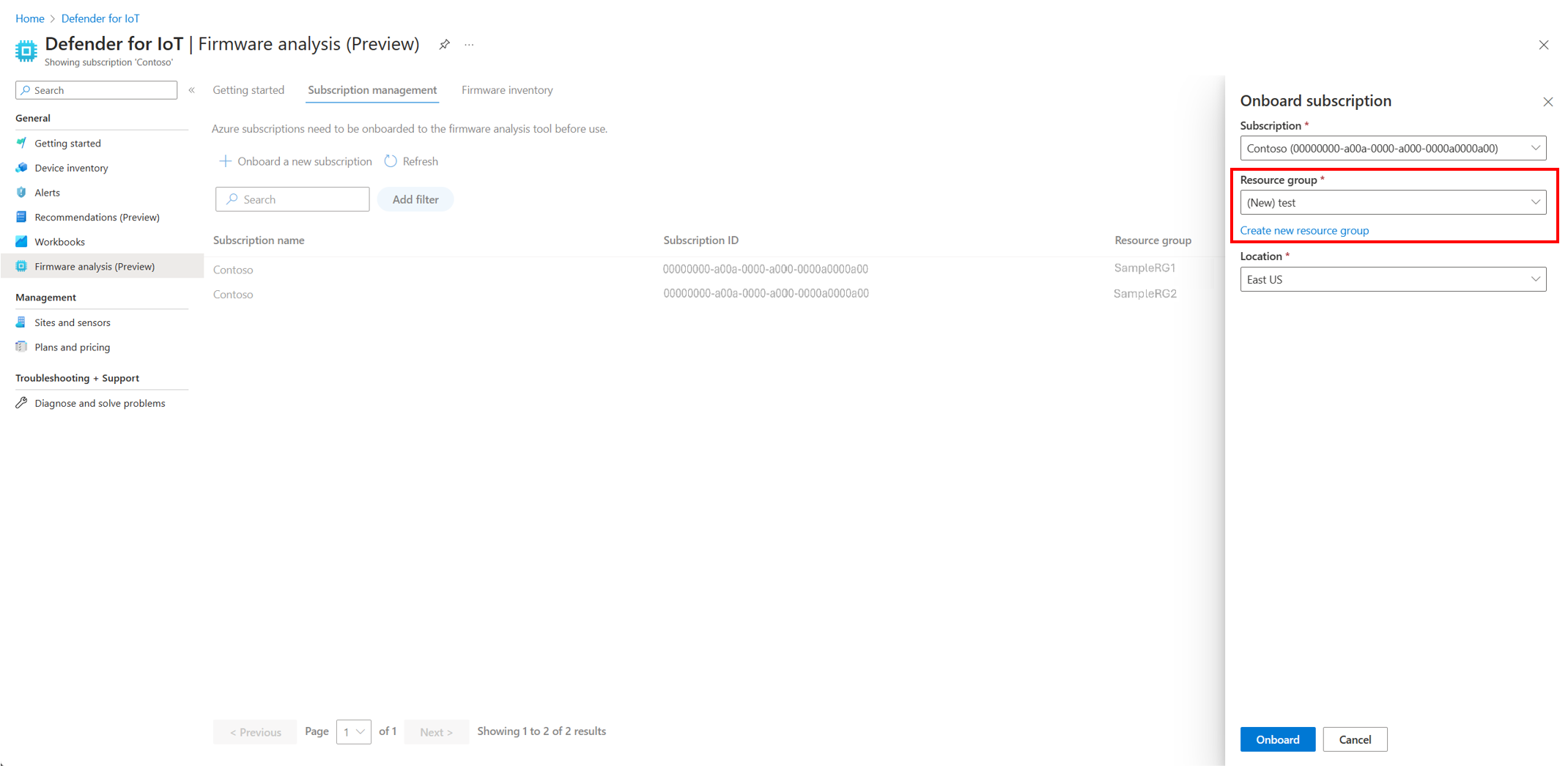
User choice in resource group: Pick your own resource group or create a new resource group to use Defender for IoT Firmware Analysis during the onboarding process.
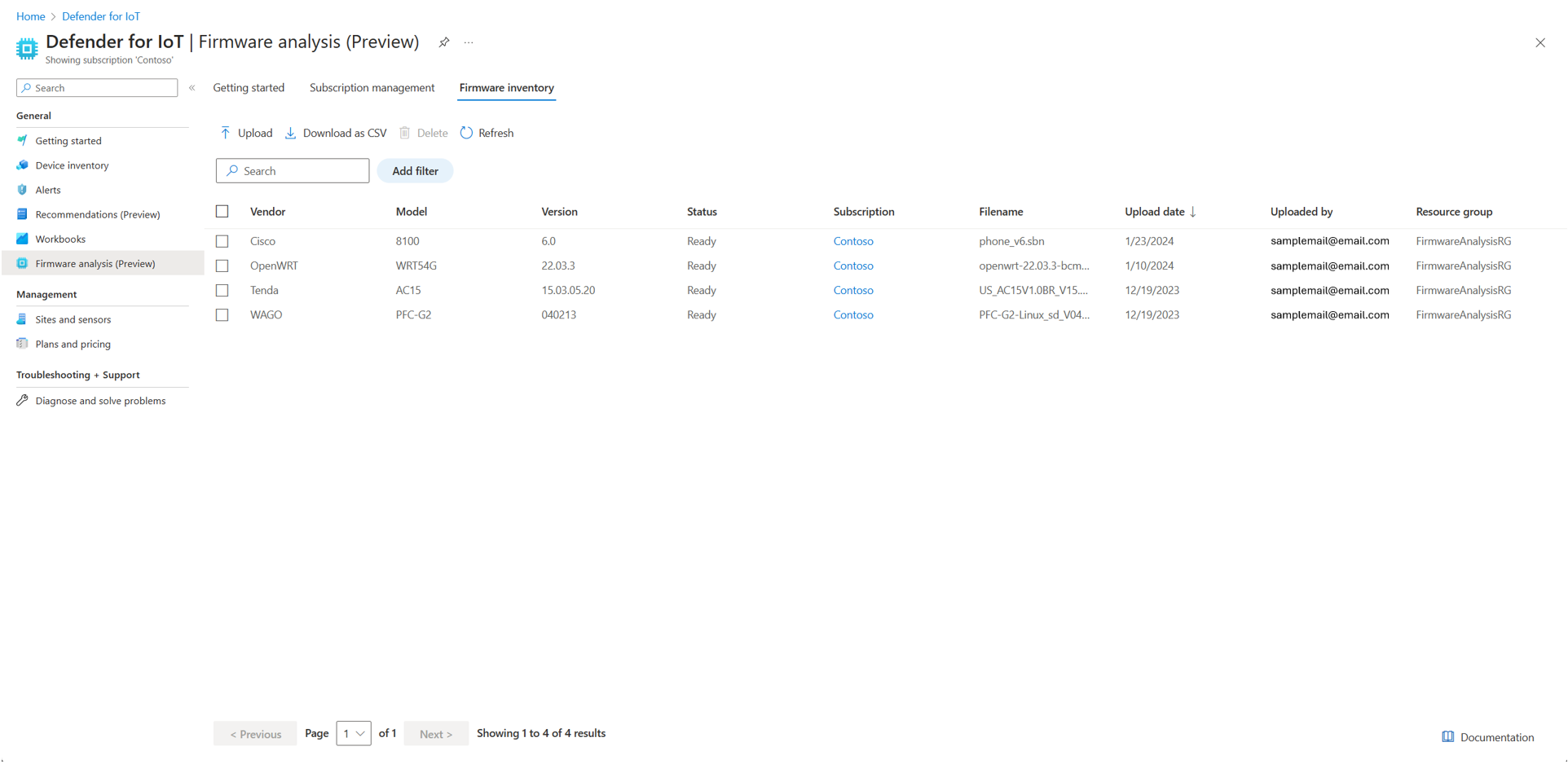
New UI format with Firmware inventory: Subtabs to organize Getting started, Subscription management, and Firmware inventory.
Enhanced documentation: Updates to Tutorial: Analyze an IoT/OT firmware image documentation addressing the new onboarding experience.
January 2024
Updates to Defender for IoT Firmware Analysis since public preview in July 2023:
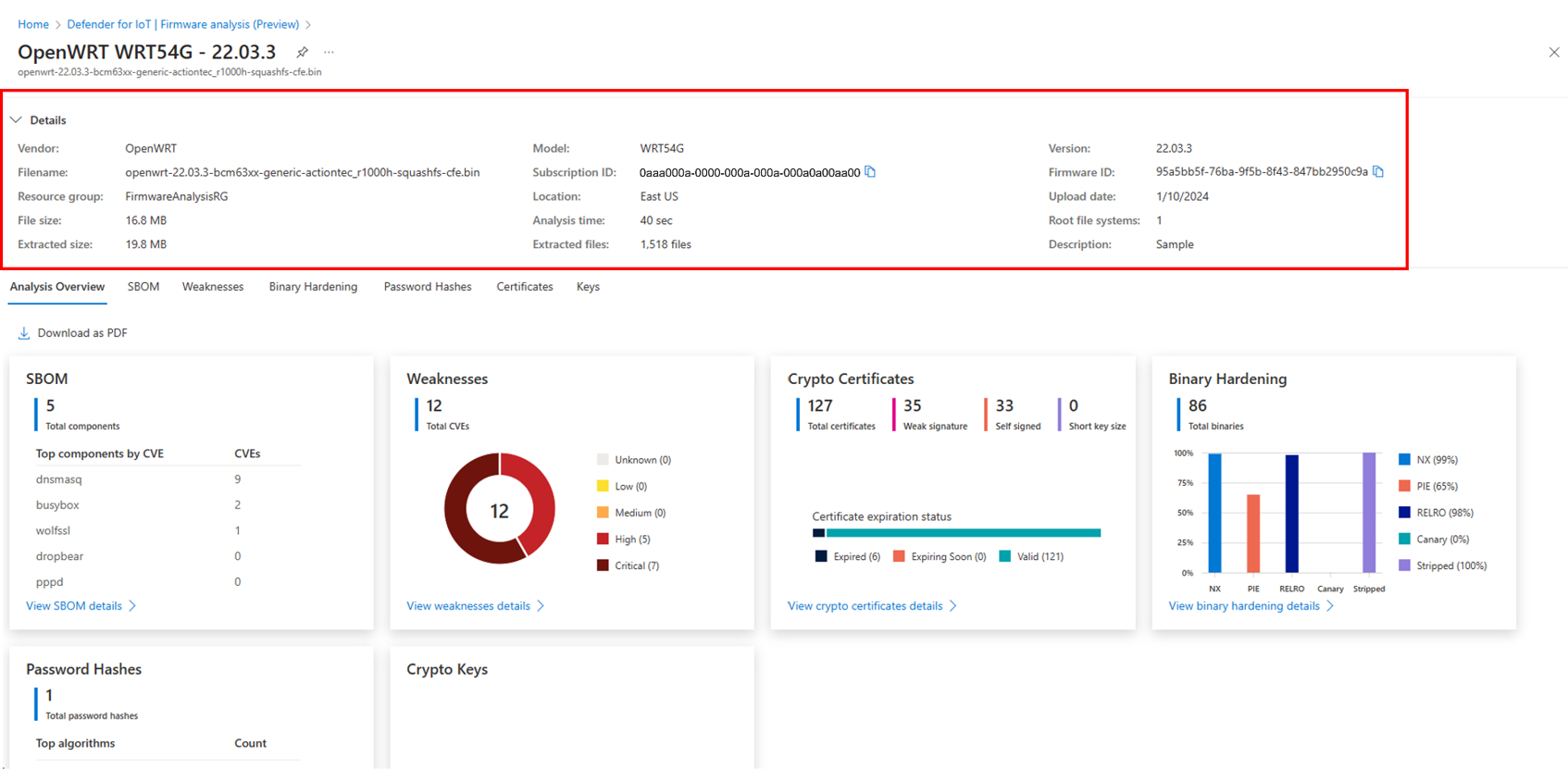
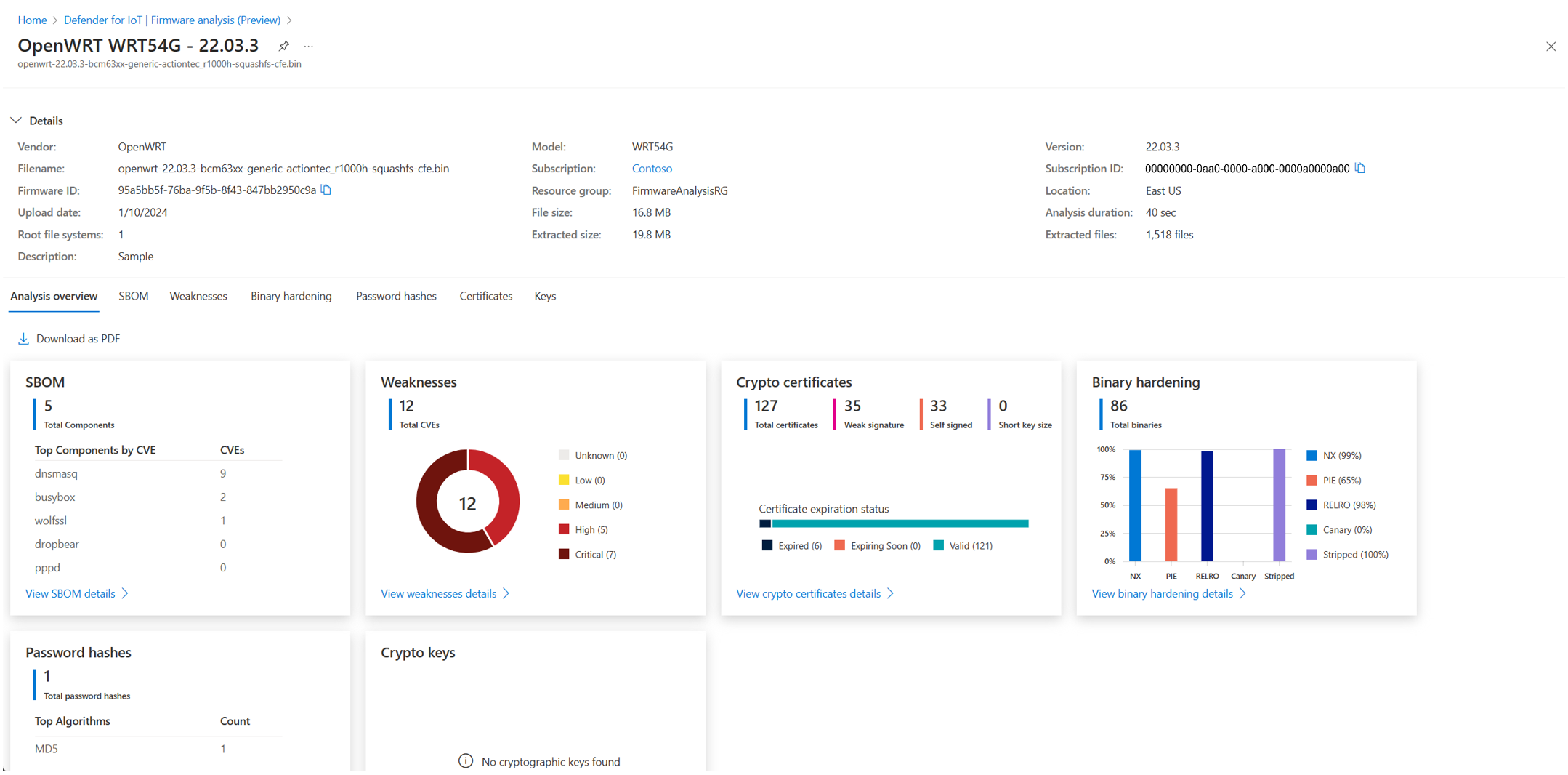
PDF report generator: Addition of a Download as PDF capability on the Overview page that generates and downloads a PDF report of the firmware analysis results.
Reduced analysis time: Analysis time has been shortened by 30-80%, depending on image size.
CODESYS libraries detection: Defender for IoT Firmware Analysis now detects the use of CODESYS libraries, which Microsoft recently identified as having high-severity vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited for attacks such as remote code execution (RCE) or denial of service (DoS). For more information, see Multiple high severity vulnerabilities in CODESYS V3 SDK could lead to RCE or DoS.
Enhanced documentation: Addition of documentation addressing the following concepts:
- Azure role-based access control for Defender for IoT Firmware Analysis, which explains roles and permissions needed to upload firmware images and share analysis results, and an explanation of how the FirmwareAnalysisRG resource group works
- Frequently asked questions
Improved filtering for each report: Each subtab report now includes more fine-grained filtering capabilities.
Firmware metadata: Addition of a collapsible tab with firmware metadata that is available on each page.
Improved version detection: Improved version detection of the following libraries:
- pcre
- pcre2
- net-tools
- zebra
- dropbear
- bluetoothd
- WolfSSL
- sqlite3
Added support for file systems: Defender for IoT Firmware Analysis now supports extraction of the following file systems. For more information, see Firmware Analysis FAQs:
- ISO
- RomFS
- Zstandard and non-standard LZMA implementations of SquashFS
July 2023
Firmware Analysis public preview announcement
Microsoft Defender for IoT Firmware Analysis is now available in public preview. Defender for IoT can analyze your device firmware for common weaknesses and vulnerabilities, and provide insight into your firmware security. This analysis is useful whether you build the firmware in-house or receive firmware from your supply chain.
For more information, see Firmware analysis for device builders.
December 2022
Version 4.6.2:
When upgrading the micro agent from version 4.2.* to 4.6.2, you would first need to remove the package and then reinstall it. For more information, see Upgrade the Microsoft Defender for IoT micro agent.
Peripheral collector: Addition of a new collector that detects physical plugins of devices. For more information, see Micro agent event collection - Peripheral events.
File system collector: Addition of a new collector that monitors specified file systems. For more information, see Micro agent event collection - File system events.
Statistics collector: Addition of a new collector that reports for each collection cycle, data regarding the different collectors in the agent. For more information, see Micro agent event collection - Statistics events.
System information collector: System information collector now collects the agent type (Edge/Standalone) and version. For more information, see Micro agent event collection - System information events.
New alerts: Now supporting new peripheral and file system alerts. For more information, see Micro agent security alerts.
DMI decode alternative: Now supporting new alternative to report device information in case device does not support DMI decoder. For more information, see How to configure DMI decoder.
Firmware information: Now supporting device firmware vendor and version collected using DMI decoder or its alternative. For more information, see How to configure DMI decoder.
Device Provisioning Service support: Now you can use DPS to provision your micro agent and devices at scale. For more information, see How to provision the micro agent using DPS.
AMQP protocol over web socket protocol support: Now supporting AMQP over web socket protocol that can be added after installing your micro agent. For more information, see Add AMQP over websocket protocol support.
SBoM collector bug fix: Now supporting collection of all packages instead of first ingested 500. For more information, see Micro agent event collection - SBoM events.
Debian 10 ARM 64 buster support: Now supporting Debian 10 ARM 64 devices. For more information, see Agent portfolio overview and OS support.
22.04 Ubuntu support: Now supporting Ubuntu 22.04 devices. For more information, see Agent portfolio overview and OS support.
September 2022
Micro agent GA announcement
Azure Defender for IoT micro agent is now generally available.
July 2022
Version 4.2.4:
Proxy connection updates: Now you can connect your micro-agent to an IoT Hub via a proxy. For more information, see Connect via a proxy.
Support for TPM-backed certificates: Now you can use OpenSSL certificates backed by TPM. For more information, see Authenticate using a certificate.
AMQP support: Now you can add AMQP support after installing your micro-agent. For more information, see Add AMQP protocol support.
Baseline collector updates: The baseline collector now sends pass and skip checks to the cloud in addition to failed results. For more information, see Baseline (trigger-based collector).
Login collector via UTMP: The login collector now supports UTMP to catch SSH interactive events, telnet events, and terminal logins, including failed login events. For more information, see Login collector (event-based collector).
SBoM collector known issue: The SBoM collector currently only collects the first 500 packages ingested. For more information, see SBoM (trigger-based collector).
February 2022
Version 4.1.2:
Micro agent for Edge is now in Public Preview: The micro-agent supports IoT Edge devices, with an easy installation and identity provisioning process that uses an automatically provisioned module identity to authenticate Edge devices without the need to perform any manual authentication.
For more information, see Install Defender for IoT micro agent for Edge (Preview).
New directory structure: Now aligned with the standard Linux installation directory structure.
Due to this change, updates to version 4.1.2 require you to reauthenticate the micro agent and save your connection string in the new location. For more information, see Upgrade the Microsoft Defender for IoT micro agent.
SBoM collector: The SBoM collector now collects the packages installed on the device periodically. For more information, see Micro agent event collection (Preview).
CIS benchmarks: The micro agent now supports recommendations based on CIS Distribution Independent Linux Benchmarks, version 2.0.0, and the ability to disable specific CIS Benchmark checks or groups using twin configurations. For more information, see Micro agent configurations (Preview).
Micro agent supported devices list expands: The micro agent now supports Debian 11 AMD64 and ARM32v7 devices, and Ubuntu Server 18.04 ARM32 Linux devices & Ubuntu Server 20.04 ARM32 & ARM64 Linux devices.
For more information, see Agent portfolio overview and OS support (Preview).
DNS hit count: network collector now includes DNS hit count field that can be visible through Log Analytics, which can help indicate if a DNS request was part of an automatic query.
For more information, see Network Activity events (event-based collector).
Login Collector: Now supporting login collector using: SYSLOG collecting SSH login events and PAM collecting SSH, telnet and local login events using the pluggable authentication modules stack. For more information, see Login collector (event-based collector).
November 2021
Version 3.13.1:
DNS network activity on managed devices is now supported. Microsoft threat intelligence security graph can now detect suspicious activity based on DNS traffic.
Leaf device proxying: There's now an enhanced integration with IoT Edge. This integration enhances the connectivity between the agent, and the cloud using leaf device proxying.
October 2021
Version 3.12.2:
More CIS benchmark checks are now supported for Debian 9: These extra checks allow you to make sure your network is compliant with the CIS best practices used to protect against pervasive cyber threats.
Twin configuration: The micro agent’s behavior is configured by a set of module twin properties. You can configure the micro agent to best suit your needs.
September 2021
Version 3.11:
Login collector - The login collectors gather user logins, logouts, and failed login attempts. Such as SSH & telnet.
System information collector - The system information collector gathers information related to the device’s operating system and hardware details.
Event aggregation - The Defender for IoT agent aggregates events such as process, login, network events that reduce the number of messages sent and costs, all while maintaining your device's security.
Twin configuration - The micro agent's behavior is configured by a set of module twin properties. (e.g event sending frequency and Aggregation mode). You can configure the micro agent to best suit your needs.
March 2021
Device builder - new micro agent (Public preview)
A new device builder module is available. The module, referred to as a micro-agent, allows:
Integration with Azure IoT Hub and Defender for IoT - build stronger endpoint security directly into your IoT devices by integrating it with the monitoring option provided by both the Azure IoT Hub and Defender for IoT.
Flexible deployment options with support for standard IoT operating systems - can be deployed either as a binary package or as modifiable source code, with support for standard IoT operating systems like Linux and Eclipse ThreadX.
Minimal resource requirements with no OS kernel dependencies - small footprint, low CPU consumption, and no OS kernel dependencies.
Security posture management – proactively monitor the security posture of your IoT devices.
Continuous, real-time IoT/OT threat detection - detect threats such as botnets, brute force attempts, crypto miners, and suspicious network activity
The deprecated Defender-IoT-micro-agent documentation will be moved to the Agent-based solution for device builders>Legacy folder.
This feature set is available with the current public preview cloud release.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for