Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn about configuring MQTT clients and client groups.
Clients
Clients can be devices or applications, such as devices or vehicles that send/receive MQTT messages.
For example, consider a fleet management company with hundreds of trucks and other shipment delivery vehicles. You can improve their routing, tracking, driver safety and predictable maintenance capabilities by sending and receiving MQTT messages to/from a cloud service.
In this scenario, vehicles can be configured as clients that publish/subscribe to various topics such as weather information, road conditions, geo location, engine performance and other wear-and-tear aspects of the vehicle. And, while configuring the vehicle as a client, a set of attributes such as vehicle type, year, make & model, max load capacity, etc. can also be included in the client metadata.
Note
- Client name can be 1-128 characters long.
- Client name can include alphanumeric, hyphen(-), colon(:), dot(.), and underscore(_), no spaces. It is case sensitive and needs to be unique per namespace.
Key terms of client metadata
Client Authentication Name: You can provide a unique identifier for the client without Azure Resource Manager naming constraints. It's a mandatory field and if not explicitly provided, it's defaulted to the Client Name.
No two clients can have same authentication name within a Namespace. While authenticating a client, we treat Client authentication name as case insensitive.
We preserve the original case of client authentication name that you configure in the client. We use the original client authentication name (case sensitive) that was provided when client was created, in routing enrichments, topic space matching, etc.
Note
- Client authentication name can be 1-128 characters long, UTf-8 strings, no restrictions
- Client authentication name is case sensitive and needs to be unique per namespace (case is ignored while determining uniqueness)
Client Certificate Authentication Validation Scheme: To use CA certificate for authentication, you can choose from one of following options to specify the location of the client identity in the client certificate. When the client tries to connect to the service, service finds the client identify from this certificate field and matches it with the client authentication name to authenticate the client.
We support five certificate fields:
- Subject Matches Authentication Name
- Dns Matches Authentication Name
- Uri Matches Authentication Name
- IP Matches Authentication Name
- Email Matches Authentication Name
Use the "Thumbprint Match" option while using self-signed certificate to authenticate the client.
Note
- clientCertificateAuthentication is always required with a valid value of validationScheme.
- authenticationName is not required, but after the first create request, authenticationName value defaults to ARM name, and then it can not be updated.
- authenticationName can not be updated.
- If validationScheme is anything other than ThumbprintMatch, then allowedThumbprints list can not be provided.
- allowedThumbprints list can only be provided and must be provided if validationScheme is ThumbprintMatch with at least one thumbprint.
- allowedThumbprints can only hold maximum of 2 thumbprints.
- Allowed validationScheme values are SubjectMatchesAuthenticationName, DnsMatchesAuthenticationName, UriMatchesAuthenticationName, IpMatchesAuthenticationName, EmailMatchesAuthenticationName, ThumbprintMatch
- Using thumbprint with allow reuse of the same certificate across multiple clients. For other types of validation, the authentication name needs to be in the chosen field of the client certificate.
Client attributes
Client attributes are a set of user defined key-value pairs or tags that provide information about the client.
These client attributes can be used to create the client groups. For example, you can group all the vehicles of type semi-trucks into one group and all the vehicles of type pickup-trucks into another.
These attributes are used in the client group queries to filter a set of clients. Attributes could be describing the physical or functional characteristics of the client. Typical attribute could be "type" of the client.
Here's an example:
- Type: Values could be "sensor" or "thermostat" or "vehicle"
Here’s a sample schema for the client with attribute definition:
{
"id": "device123",
"attributes": {
"type": "home-sensors",
"sensors": ["motion", "noise", "light"]
}
}
While configuring the client attributes, consider the topics that the clients publish (subscribe) to. Thinking backwards from topics to clients helps identify the commonalities across client roles easier and defining the client attributes to make the client grouping simpler.
Note
- Client attribute keys must be unique in the client. Keys cannot be repeated.
- Client attribute values can be of
string,integerorarray of stringstypes. - The total size of the client attributes for a client must always be less than 4KB.
- Client attribute name (key) can only contain alphanumeric characters and underscore(_).
Sample contracts
Example for certificate chain based client authentication
{
"properties": {
"authenticationName": "127.0.0.1",
"state": "Enabled",
"clientCertificateAuthentication": {
"validationScheme": "IpMatchesAuthenticationName"
},
"attributes": {
"room": "345",
"floor": 3,
"bldg": "17"
},
"description": "Description of the client"
}
}
Example for self-signed certificate thumbprint based client authentication
{
"properties": {
"authenticationName": "abcd@domain.com-1",
"state": "Enabled",
"clientCertificateAuthentication": {
"validationScheme": "ThumbprintMatch",
"allowedThumbprints": ["primary", "secondary"]
},
"attributes": {
"room": "345",
"floor": "3",
"bldg": 17
},
"description": "Description of the client"
}
}
Azure portal configuration
Use the following steps to create a client:
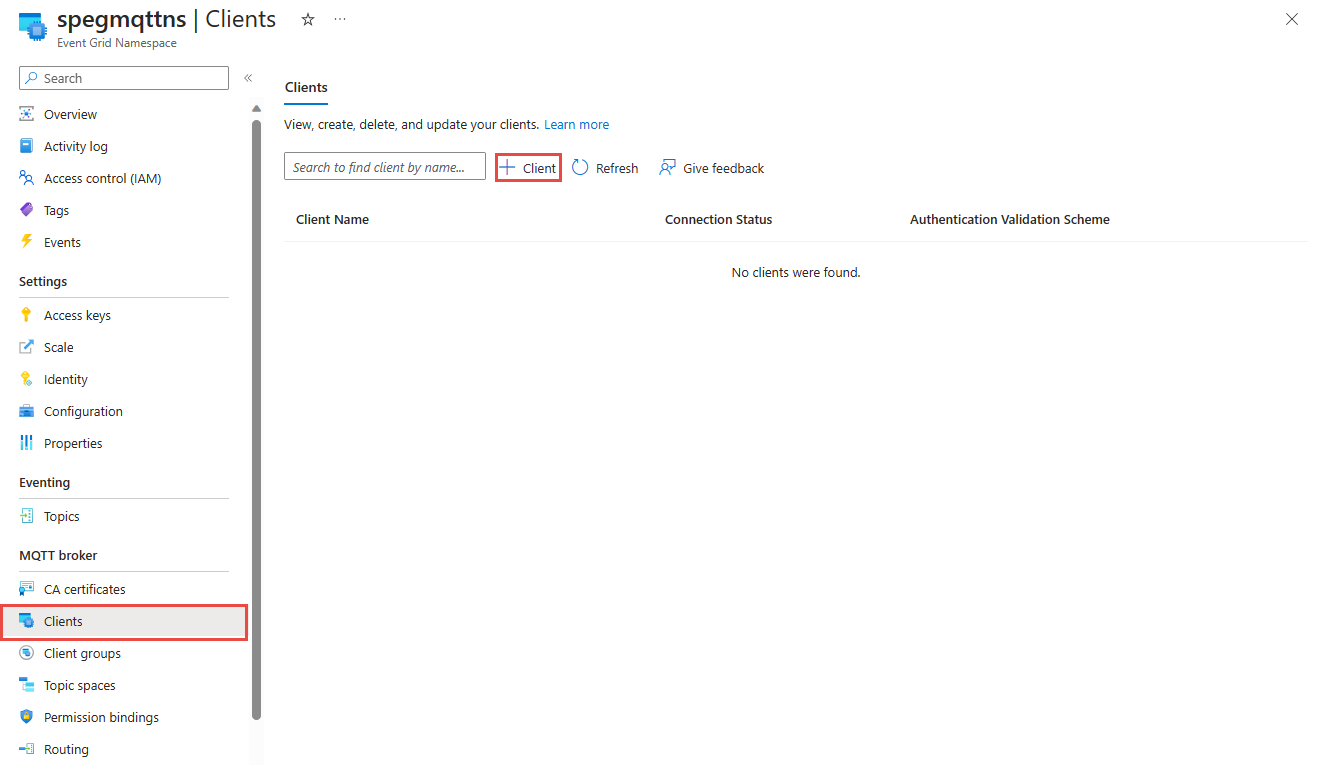
Go to your namespace in the Azure portal
Under Clients, select + Client.
Choose the client certificate authentication validation scheme. For more information about client authentication configuration, see client authentication article.
Add client attributes.
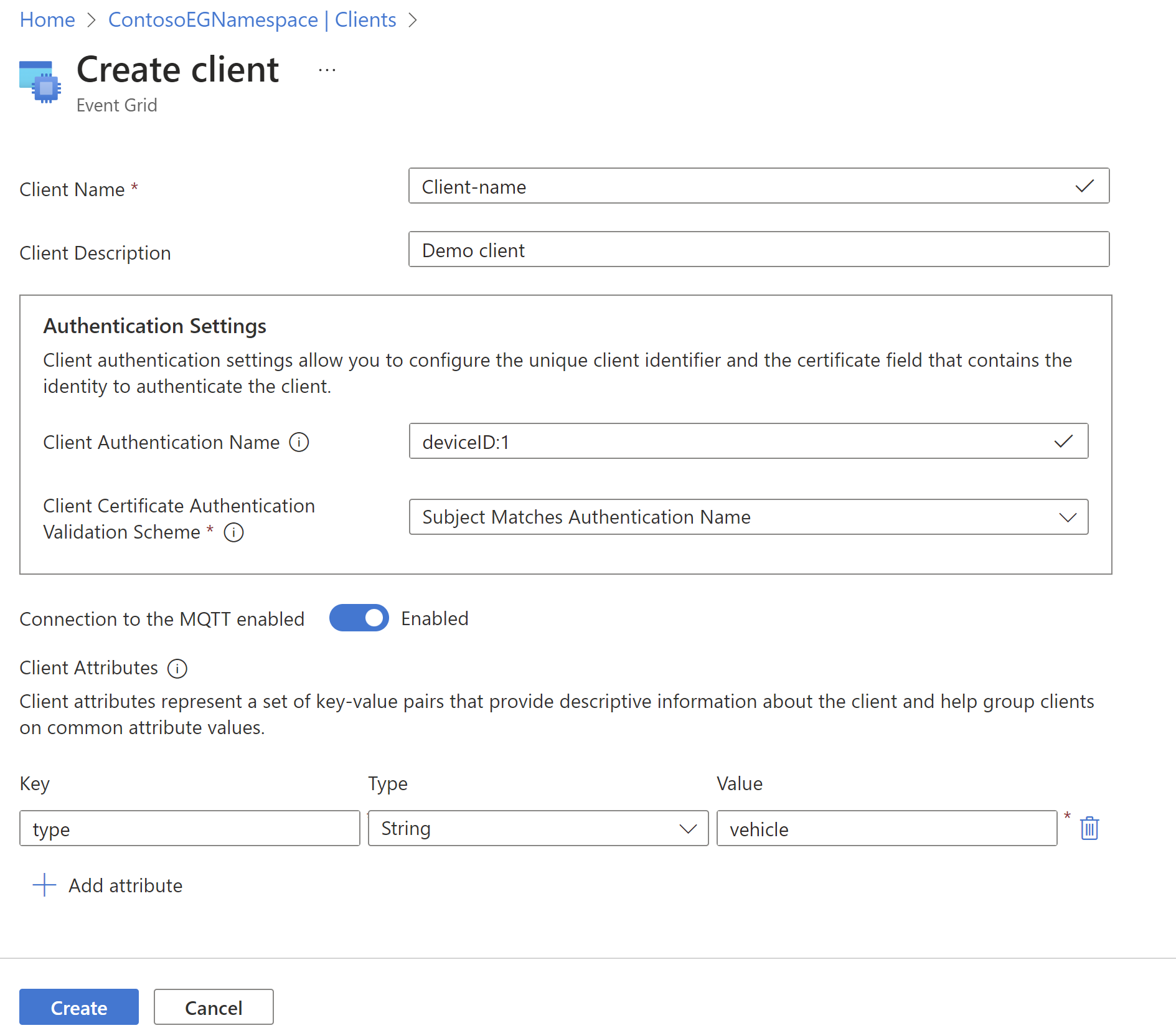
- Select Create
Azure CLI configuration
Use the following commands to create/show/delete a client
Create client
az eventgrid namespace client create -g myRG --namespace-name myNS -n myClient
Get client
az eventgrid namespace client show -g myRG --namespace-name myNS -n myClient
Delete client
az eventgrid namespace client delete -g myRG --namespace-name myNS -n myClient
Next steps
- Learn about client authentication