Get started with Azure Automation State Configuration
Note
Before you enable Automation State Configuration, we would like you to know that a newer version of DSC is now generally available, managed by a feature of Azure Policy named guest configuration. The guest configuration service combines features of DSC Extension, Azure Automation State Configuration, and the most commonly requested features from customer feedback. Guest configuration also includes hybrid machine support through Arc-enabled servers.
This article provides a step-by-step guide for doing the most common tasks with Azure Automation State Configuration, such as creating, importing, and compiling configurations, enabling machines to manage, and viewing reports. For an overview State Configuration, see State Configuration overview. For Desired State Configuration (DSC) documentation, see Windows PowerShell Desired State Configuration Overview.
If you want a sample environment that is already set up without following the steps described in this article, you can use the Azure Automation Managed Node template. This template sets up a complete State Configuration (DSC) environment, including an Azure VM that is managed by State Configuration (DSC).
Prerequisites
To complete the examples in this article, the following are required:
- An Azure Automation account. To learn more about an Automation account and its requirements, see Automation Account authentication overview.
- An Azure Resource Manager VM (not Classic) running a supported operating system. For instructions on creating a VM, see Create your first Windows virtual machine in the Azure portal
Create a DSC configuration
You create a simple DSC configuration that ensures either the presence or absence of the Web-Server Windows Feature (IIS), depending on how you assign nodes.
Configuration names in Azure Automation must be limited to no more than 100 characters.
Start VSCode (or any text editor).
Type the following text:
configuration TestConfig { Node IsWebServer { WindowsFeature IIS { Ensure = 'Present' Name = 'Web-Server' IncludeAllSubFeature = $true } } Node NotWebServer { WindowsFeature IIS { Ensure = 'Absent' Name = 'Web-Server' } } }Save the file as TestConfig.ps1.
This configuration calls one resource in each node block, the WindowsFeature resource. This resource ensures either the presence or absence of the Web-Server feature.
Import a configuration into Azure Automation
Next, you import the configuration into the Automation account.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, select State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Configurations tab, then click Add.
On the Import Configuration pane, browse to the
TestConfig.ps1file on your computer.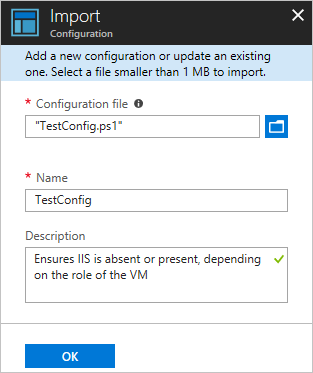
Click OK.
View a configuration in Azure Automation
After you have imported a configuration, you can view it in the Azure portal.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, select State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Configurations tab, then click TestConfig. This is the name of the configuration you imported in the previous procedure.
On the TestConfig Configuration pane, click View configuration source.
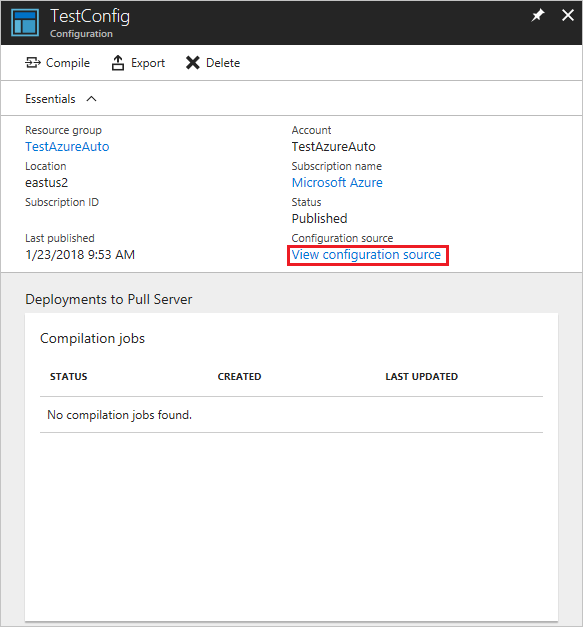
A TestConfig Configuration source pane opens, displaying the PowerShell code for the configuration.
Compile a configuration in Azure Automation
Before you can apply a desired state to a node, a DSC configuration defining that state must be compiled into one or more node configurations (MOF document), and placed on the Automation DSC Pull Server. For a more detailed description of compiling configurations in State Configuration (DSC), see Compile configurations in Azure Automation State Configuration. For more information about compiling configurations, see DSC Configurations.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, click State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Configurations tab, then click TestConfig. This is the name of the previously imported configuration.
On the TestConfig Configuration pane, click Compile, and then click Yes. This starts a compilation job.
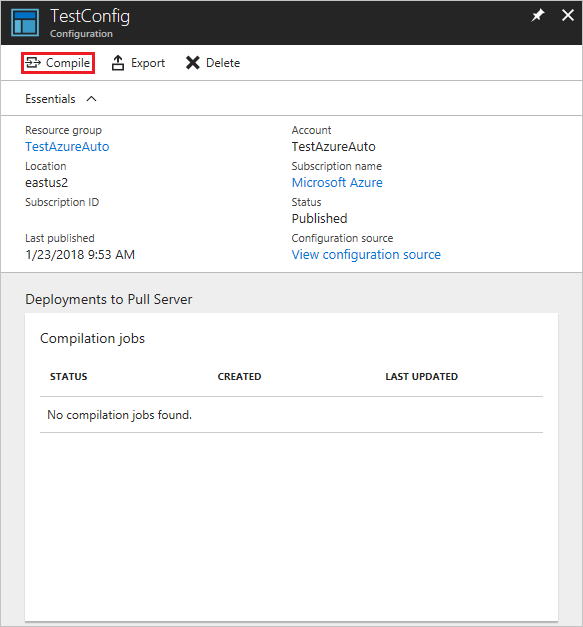
Note
When you compile a configuration in Azure Automation, it automatically deploys any created node configuration MOF files to the pull server.
View a compilation job
After you start a compilation, you can view it in the Compilation Jobs tile on the Configuration page. The Compilation Jobs tile shows currently running, completed, and failed jobs. When you open a compilation job pane, it shows information about that job including any errors or warnings encountered, input parameters used in the configuration, and compilation logs.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, click State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Configurations tab, then click TestConfig. This is the name of the previously imported configuration.
Under Compilation jobs, select the compilation job to view. A Compilation Job pane opens, labeled with the date when the compilation job was started.
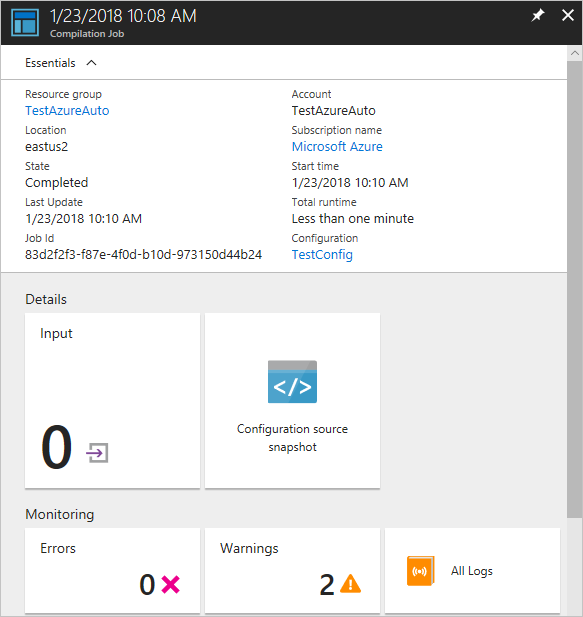
Click on any tile in the Compilation Job pane to see further details about the job.
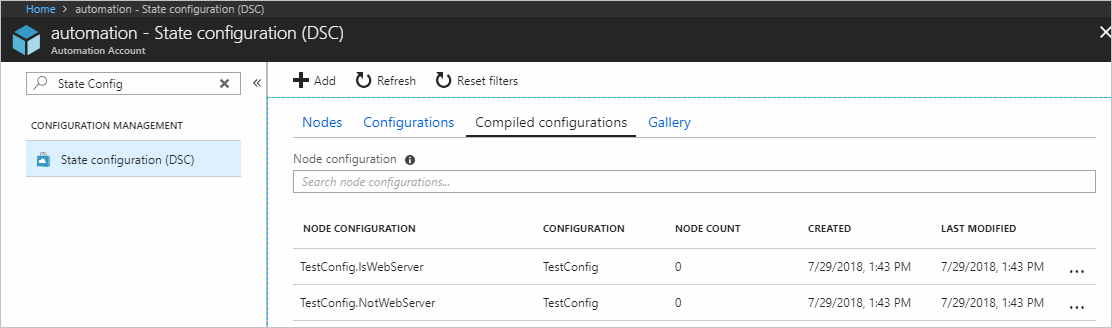
View node configurations
Successful completion of a compilation job creates one or more new node configurations. A node
configuration is a MOF document that is deployed to the pull server and ready to be pulled and
applied by one or more nodes. You can view the node configurations in your Automation account on
the State configuration (DSC) page. A node configuration has a name with the form
ConfigurationName.NodeName.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, click State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Compiled configurations tab.
Enable an Azure Resource Manager VM for management with State Configuration
You can use State Configuration to manage Azure VMs (both classic and Resource Manager), on-premises VMs, Linux machines, AWS VMs, and on-premises physical machines. In this article, you learn how to enable only Azure Resource Manager VMs. For information about enabling other types of machines, see Enable machines for management by Azure Automation State Configuration.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, click State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, select the Nodes tab, then click + Add.
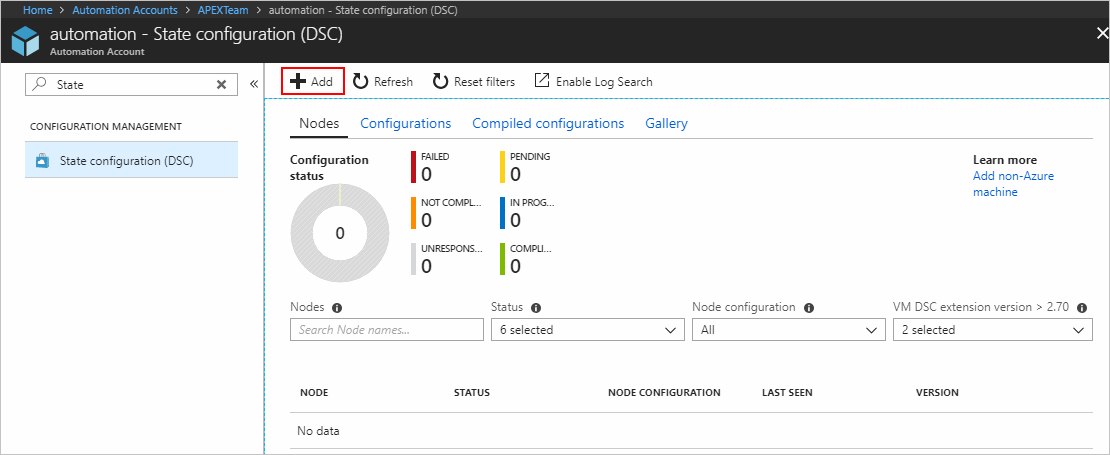
On the Virtual Machines pane, select your VM.
On the Virtual machine detail pane, click + Connect.
Important
The VM must be an Azure Resource Manager VM running a supported operating system.
On the Registration page, select the name of the node configuration to apply to the VM in the Node configuration name field. Providing a name at this point is optional. You can change the assigned node configuration after enabling the node.
Check Reboot Node if Needed, then click OK.
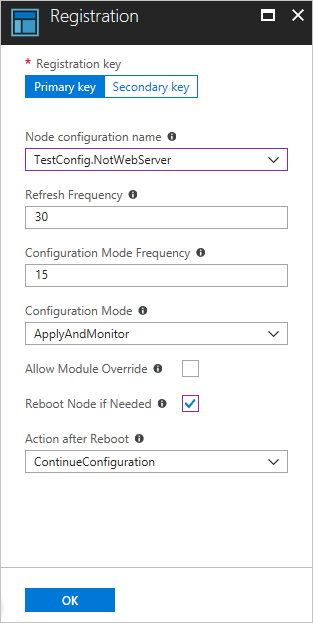
The node configuration you specified is applied to the VM at intervals specified by the value provided for Configuration Mode Frequency. The VM checks for updates to the node configuration at intervals specified by the Refresh Frequency value. For more information about how these values are used, see Configuring the Local Configuration Manager.
Azure starts the process of enabling the VM. When it is complete, the VM shows up in the Nodes tab of the State configuration (DSC) page in the Automation account.
View the list of managed nodes
You can view the list of all machines that have been enabled for management in your Automation account in the Nodes tab of the State configuration (DSC) page.
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
- On the Automation account page, click State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
- On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Nodes tab.
DSC nodes status values
The DSC node can take any of the following six values as follows:
- Failed - This status is displayed when an error occurs while applying one or more configurations on a node.
- Not compliant - This status is displayed when drift occurs on a node and it requires a close review if it is systematic.
- Unresponsive - This status is displayed when a node has not been checked in for more than 24 hours.
- Pending - This status is displayed when a node has a new configuration to apply and the pull server is awaiting node check in.
- In progress - This status is displayed when a node applies configuration, and the pull server is awaiting status.
- Compliant - This status is displayed when a node has a valid configuration, and no drift occurs presently.
Note
- RefreshFrequencyMins - It defines the frequency of node contacting the agent service and can be provided as part of onboarding to DSC. It takes a maximum value of 10080 minutes.
- Node will be marked as Unresponsive if the node does not contact the agent service for 1440 minutes (1 Day). We recommend that you use RefreshFrequencyMins value < 1440 minutes, else the node would show in a false Unresponsive state.
View reports for managed nodes
Each time State Configuration performs a consistency check on a managed node, the node sends a status report back to the pull server. You can view these reports on the page for that node.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, click State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Nodes tab. Here, you can see the overview of Configuration state and the details for each node.
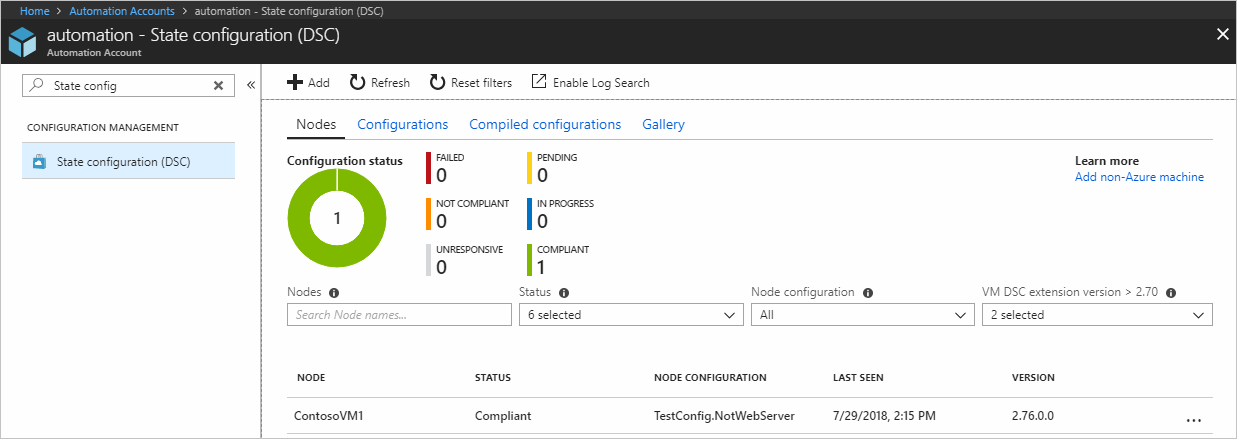
While on the Nodes tab, click the node record to open the reporting. Click the report you want to view additional reporting details.
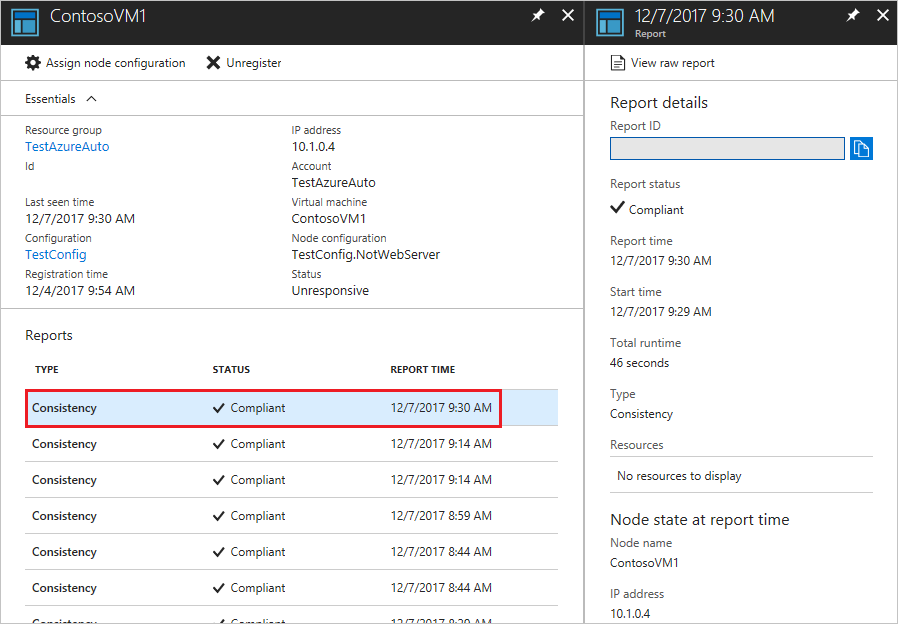
On the blade for an individual report, you can see the following status information for the corresponding consistency check:
- The report status. Possible values are:
- Compliant - the node is compliant with the check.
- Failed - the configuration failed the check.
- Not Compliant - the node is in
ApplyandMonitormode and the machine is not in the desired state.
- The start time for the consistency check.
- The total runtime for the consistency check.
- The type of consistency check.
- Any errors, including the error code and error message.
- Any DSC resources used in the configuration, and the state of each resource (whether the node is in the desired state for that resource). You can click on each resource to get more detailed information for that resource.
- The name, IP address, and configuration mode of the node.
You can also click View raw report to see the actual data that the node sends to the server. For more information about using that data, see Using a DSC report server.
It can take some time after a node is enabled before the first report is available. You might need to wait up to 30 minutes for the first report after you enable a node.
Reassign a node to a different node configuration
You can assign a node to use a different node configuration than the one you initially assigned.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the left, click All resources and then the name of your Automation account.
On the Automation account page, click State configuration (DSC) under Configuration Management.
On the State configuration (DSC) page, click the Nodes tab.
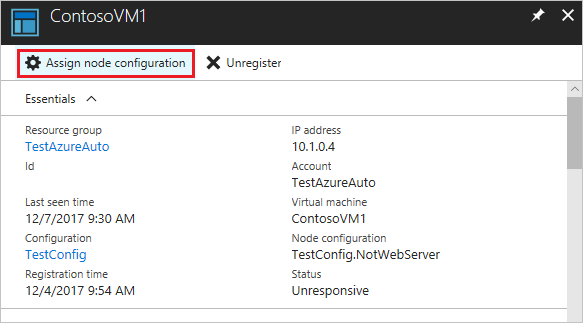
On the Nodes tab, click on the name of the node you want to reassign.
On the page for that node, click Assign node configuration.
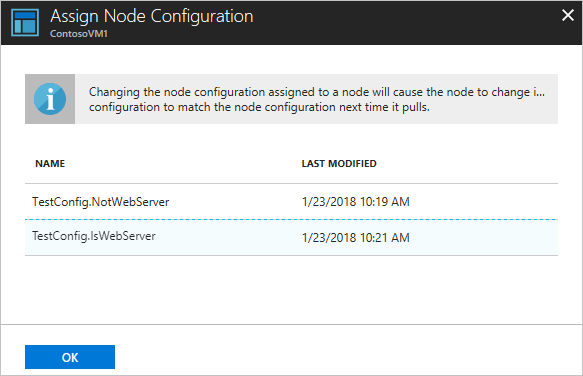
On the Assign Node Configuration page, select the node configuration to which you want to assign the node, and then click OK.
Unregister a node
If you no longer want a node to be managed by State Configuration, you can unregister it. See How to remove a configuration and node from Automation State Configuration.
Next steps
- For an overview, see Azure Automation State Configuration overview.
- To enable the feature for VMs in your environment, see Enable Azure Automation State Configuration.
- To understand PowerShell DSC, see Windows PowerShell Desired State Configuration overview.
- For pricing information, see Azure Automation State Configuration pricing.
- For a PowerShell cmdlet reference, see Az.Automation.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for