Manage access key authentication for an Azure App Configuration instance
Every request to an Azure App Configuration resource must be authenticated. By default, requests can be authenticated with either Microsoft Entra credentials, or by using an access key. Of these two types of authentication schemes, Microsoft Entra ID provides superior security and ease of use over access keys, and is recommended by Microsoft. To require clients to use Microsoft Entra ID to authenticate requests, you can disable the usage of access keys for an Azure App Configuration resource. If you want to use access keys to authenticate the request, it's recommended to rotate access keys every 90 days to enhance security.
Enable access key authentication
Access key is enabled by default, you can use access keys in your code to authenticate requests.
Warning
If any clients are currently accessing data in your Azure App Configuration resource with access keys, then Microsoft recommends that you migrate those clients to Microsoft Entra ID before disabling access key authentication.
To allow/disallow access key authentication for an Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Navigate to your Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal.
Locate the Access settings setting under Settings.
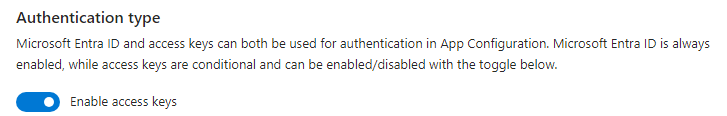
Set the Enable access keys toggle to Enabled.
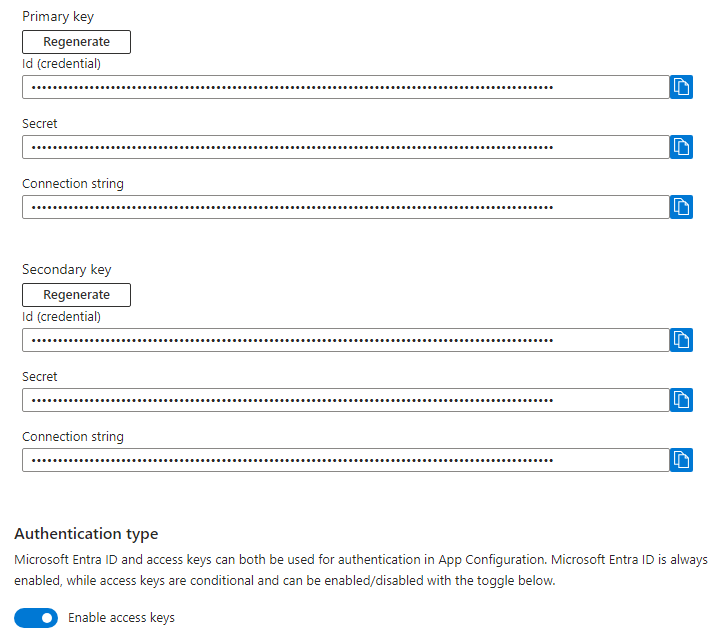
Verify that access key authentication is enabled
To verify if access key authentication is enabled, check if you're able to get a list of read and read-write access keys. This list will only exist if access key authentication is enabled.
To check if access key authentication is enabled for an Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Navigate to your Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal.
Locate the Access settings setting under Settings.

Check if there are access keys displayed and if the toggled state of Enable access keys is enabled.
Disable access key authentication
Disabling access key authentication will delete all access keys. If any running applications are using access keys for authentication, they will begin to fail once access key authentication is disabled. Only requests that are authenticated using Microsoft Entra ID will succeed. For more information about using Microsoft Entra ID, see Authorize access to Azure App Configuration using Microsoft Entra ID. Enabling access key authentication again will generate a new set of access keys and any applications attempting to use the old access keys will still fail.
To disallow access key authentication for an Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Navigate to your Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal.
Locate the Access settings setting under Settings.

Set the Enable access keys toggle to Disabled.
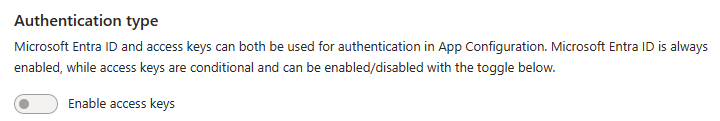
Verify that access key authentication is disabled
To verify that access key authentication is no longer permitted, a request can be made to list the access keys for the Azure App Configuration resource. If access key authentication is disabled, there will be no access keys, and the list operation will return an empty list.
To verify access key authentication is disabled for an Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Navigate to your Azure App Configuration resource in the Azure portal.
Locate the Access settings setting under Settings.

Check that there are no access keys displayed and the toggled state of Enable access keys is off.

Permissions for allowing or disallowing access key authentication
To modify the state of access key authentication for an Azure App Configuration resource, a user must have permissions to create and manage Azure App Configuration resources. Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) roles that provide these permissions include the Microsoft.AppConfiguration/configurationStores/write or Microsoft.AppConfiguration/configurationStores/* action. Built-in roles with this action include:
- The Azure Resource Manager Owner role
- The Azure Resource Manager Contributor role
These roles do not provide access to data in an Azure App Configuration resource via Microsoft Entra ID. However, they include the Microsoft.AppConfiguration/configurationStores/listKeys/action action permission, which grants access to the resource's access keys. With this permission, a user can use the access keys to access all the data in the resource.
Role assignments must be scoped to the level of the Azure App Configuration resource or higher to permit a user to allow or disallow access key authentication for the resource. For more information about role scope, see Understand scope for Azure RBAC.
Be careful to restrict assignment of these roles only to those users who require the ability to create an App Configuration resource or update its properties. Use the principle of least privilege to ensure that users have the fewest permissions that they need to accomplish their tasks. For more information about managing access with Azure RBAC, see Best practices for Azure RBAC.
Note
The classic subscription administrator roles Service Administrator and Co-Administrator include the equivalent of the Azure Resource Manager Owner role. The Owner role includes all actions, so a user with one of these administrative roles can also create and manage App Configuration resources. For more information, see Azure roles, Microsoft Entra roles, and classic subscription administrator roles.
Note
When access key authentication is disabled and ARM authentication mode of App Configuration store is local, the capability to read/write key-values in an ARM template will be disabled as well. This is because access to the Microsoft.AppConfiguration/configurationStores/keyValues resource used in ARM templates requires access key authentication with local ARM authentication mode. It's recommended to use pass-through ARM authentication mode. For more information, see Deployment overview.
Rotate access key
Microsoft recommends that you rotate your access keys periodically to help keep your resource secure. If possible, use Azure Key Vault to manage your access keys. If you are not using Key Vault, you will need to rotate your keys manually.
Each Azure App Configuration resource has two access keys to enable secret rotation. This is a security precaution that lets you regularly change the keys that can access your service, protecting the privacy of your resource if a key gets leaked. The recommended rotation cycle is 90 days.
You can rotate keys using the following procedure:
If you're using both keys in production, change your code so that only one access key is in use. In this example, let's say you decide to keep using your store's primary key. You must have only one key in your code, because when you regenerate your secondary key, the older version of that key will stop working immediately, causing clients using the older key to get 401 access denied errors.
Once the primary key is the only key in use, you can regenerate the secondary key. Go to your resource's page on the Azure portal, open the Settings > Access settings menu, and select Regenerate under Secondary key.
Next, update your code to use the newly generated secondary key. It helps to have logs or availability to check that users of the key have successfully swapped from using the primary key to the secondary key before you proceed.
Now you can regenerate the primary key using the same process.
Finally, update your code to use the new primary key.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for