Use the Azure Maps Indoor Maps module with custom styles (preview)
Note
Azure Maps Creator retirement
The Azure Maps Creator indoor map service is now deprecated and will be retired on 9/30/25. For more information, see End of Life Announcement of Azure Maps Creator.
The Azure Maps Web SDK includes an Indoor Maps module, enabling you to render indoor maps created in Azure Maps Creator services.
When you create an indoor map using Azure Maps Creator, default styles are applied. Azure Maps Creator now also supports customizing the styles of the different elements of your indoor maps using the Style Rest API, or the visual style editor.
Prerequisites
- Azure Maps account
- Azure Maps Creator resource
- Subscription key
- A map configuration alias or ID. For more information, see map configuration API.
The map configuration alias (or mapConfigurationId) is required to render indoor maps with custom styles via the Azure Maps Indoor Maps module.
Embed the Indoor Maps module
You can install and embed the Azure Maps Indoor module in one of two ways.
To use the globally hosted Azure Content Delivery Network version of the Azure Maps Indoor module, reference the following script and stylesheet references in the <head> element of the HTML file:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/indoor/0.2/atlas-indoor.min.css" type="text/css"/>
<script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/indoor/0.2/atlas-indoor.min.js"></script>
Or, you can download the Azure Maps Indoor module. The Azure Maps Indoor module contains a client library for accessing Azure Maps services. The following steps demonstrate how to install and load the Indoor module into your web application.
Install the latest azure-maps-indoor package.
>npm install azure-maps-indoorImport the Azure Maps Indoor module JavaScript in a source file:
import * as indoor from "azure-maps-indoor";You would also need to embed the CSS Style Sheet for various controls to display correctly. If you're using a JavaScript bundler to bundle the dependencies and package your code, refer to your bundler's documentation on how it's done. For Webpack, it's commonly done via a combination of
style-loaderandcss-loaderwith documentation available at style-loader.To begin, install style-loader and css-loader:
npm install --save-dev style-loader css-loaderInside your source file, import atlas-indoor.min.css:
import "azure-maps-indoor/dist/atlas-indoor.min.css";Then add loaders to the module rules portion of the Webpack config:
module.exports = { module: { rules: [ { test: /\.css$/i, use: ["style-loader", "css-loader"] } ] } };To learn more, see How to use the Azure Maps map control npm package.
Set the domain and instantiate the Map object
Set the map domain with a prefix matching the location of your Creator resource, US or EU, for example:
atlas.setDomain('us.atlas.microsoft.com');
For more information, see Azure Maps service geographic scope.
Next, instantiate a Map object with the map configuration object set to the alias or mapConfigurationId property of your map configuration, then set your styleAPIVersion to 2023-03-01-preview.
The Map object will be used in the next step to instantiate the Indoor Manager object. The following code shows you how to instantiate the Map object with mapConfiguration, styleAPIVersion and map domain set:
const subscriptionKey = "<Your Azure Maps Subscription Key>";
const region = "<Your Creator resource region: us or eu>"
const mapConfiguration = "<map configuration alias or ID>"
atlas.setDomain(`${region}.atlas.microsoft.com`);
const map = new atlas.Map("map-id", {
//use your facility's location
center: [-122.13315, 47.63637],
//or, you can use bounds: [# west, # south, # east, # north] and replace # with your Map bounds
authOptions: {
authType: 'subscriptionKey',
subscriptionKey: subscriptionKey
},
zoom: 19,
mapConfiguration: mapConfiguration,
styleAPIVersion: '2023-03-01-preview'
});
Instantiate the Indoor Manager
To load the indoor map style of the tiles, you must instantiate the Indoor Manager. Instantiate the Indoor Manager by providing the Map object. Your code should look like the following JavaScript code snippet:
const indoorManager = new atlas.indoor.IndoorManager(map, {
});
Indoor level picker control
The Indoor Level Picker control allows you to change the level of the rendered map. You can optionally initialize the Indoor Level Picker control via the Indoor Manager. Here's the code to initialize the level control picker:
const levelControl = new atlas.control.LevelControl({ position: "top-right" });
indoorManager.setOptions({ levelControl });
Indoor events
The Azure Maps Indoor module supports Map object events. The Map object event listeners are invoked when a level or facility has changed. If you want to run code when a level or a facility have changed, place your code inside the event listener. The code below shows how event listeners can be added to the Map object.
map.events.add("levelchanged", indoorManager, (eventData) => {
//code that you want to run after a level has been changed
console.log("The level has changed: ", eventData);
});
map.events.add("facilitychanged", indoorManager, (eventData) => {
//code that you want to run after a facility has been changed
console.log("The facility has changed: ", eventData);
});
The eventData variable holds information about the level or facility that invoked the levelchanged or facilitychanged event, respectively. When a level changes, the eventData object contains the facilityId, the new levelNumber, and other metadata. When a facility changes, the eventData object contains the new facilityId, the new levelNumber, and other metadata.
Example: custom styling: consume map configuration in WebSDK (preview)
When you create an indoor map using Azure Maps Creator, default styles are applied. Azure Maps Creator now also supports customizing your indoor styles. For more information, see Create custom styles for indoor maps. Creator also offers a visual style editor.
Follow the Create custom styles for indoor maps how-to article to create your custom styles. Make a note of the map configuration alias after saving your changes.
Use the Azure Content Delivery Network option to install the Azure Maps Indoor module.
Create a new HTML file
In the HTML header, reference the Azure Maps Indoor module JavaScript and style sheet.
Set the map domain with a prefix matching a location of your Creator resource:
atlas.setDomain('us.atlas.microsoft.com');if your Creator resource has been created in US region, oratlas.setDomain('eu.atlas.microsoft.com');if your Creator resource has been created in EU region.Initialize a Map object. The Map object supports the following options:
Subscription keyis your Azure Maps subscription key.centerdefines a latitude and longitude for your indoor map center location. Provide a value forcenterif you don't want to provide a value forbounds. Format should appear ascenter: [-122.13315, 47.63637].boundsis the smallest rectangular shape that encloses the tileset map data. Set a value forboundsif you don't want to set a value forcenter. You can find your map bounds by calling the Tileset List API. The Tileset List API returns thebbox, which you can parse and assign tobounds. Format should appear asbounds: [# west, # south, # east, # north].mapConfigurationthe ID or alias of the map configuration that defines the custom styles you want to display on the map, use the map configuration ID or alias from step 1.styleallows you to set the initial style from your map configuration that is displayed. If not set, the style matching map configuration's default configuration is used.zoomallows you to specify the min and max zoom levels for your map.styleAPIVersion: pass '2023-03-01-preview' (which is required while Custom Styling is in public preview)
Next, create the Indoor Manager module with Indoor Level Picker control instantiated as part of Indoor Manager options.
Add Map object event listeners.
Tip
The map configuration is referenced using the mapConfigurationId or alias . Each time you edit or change a map configuration, its ID changes but its alias remains the same. It is recommended to reference the map configuration by its alias in your applications. For more information, See map configuration in the concepts article.
Your file should now look similar to the following HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no" />
<title>Indoor Maps App</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.css" type="text/css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/indoor/0.2/atlas-indoor.min.css" type="text/css"/>
<script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/indoor/0.2/atlas-indoor.min.js"></script>
<style>
html,
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
#map-id {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map-id"></div>
<script>
const subscriptionKey = "<Your Azure Maps Subscription Key>";
const mapConfig = "<Your map configuration id or alias>";
const region = "<Your Creator resource region: us or eu>"
atlas.setDomain(`${region}.atlas.microsoft.com`);
const map = new atlas.Map("map-id", {
//use your facility's location
center: [-122.13315, 47.63637],
//or, you can use bounds: [# west, # south, # east, # north] and replace # with your Map bounds
authOptions: {
authType: 'subscriptionKey',
subscriptionKey: subscriptionKey
},
zoom: 19,
mapConfiguration: mapConfig,
styleAPIVersion: '2023-03-01-preview'
});
const levelControl = new atlas.control.LevelControl({
position: "top-right",
});
const indoorManager = new atlas.indoor.IndoorManager(map, {
levelControl: levelControl, //level picker
});
map.events.add("levelchanged", indoorManager, (eventData) => {
//put code that runs after a level has been changed
console.log("The level has changed:", eventData);
});
map.events.add("facilitychanged", indoorManager, (eventData) => {
//put code that runs after a facility has been changed
console.log("The facility has changed:", eventData);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
To see your indoor map, load it into a web browser. It should appear like the following image. If you select the stairwell feature, the level picker appears in the upper right-hand corner.
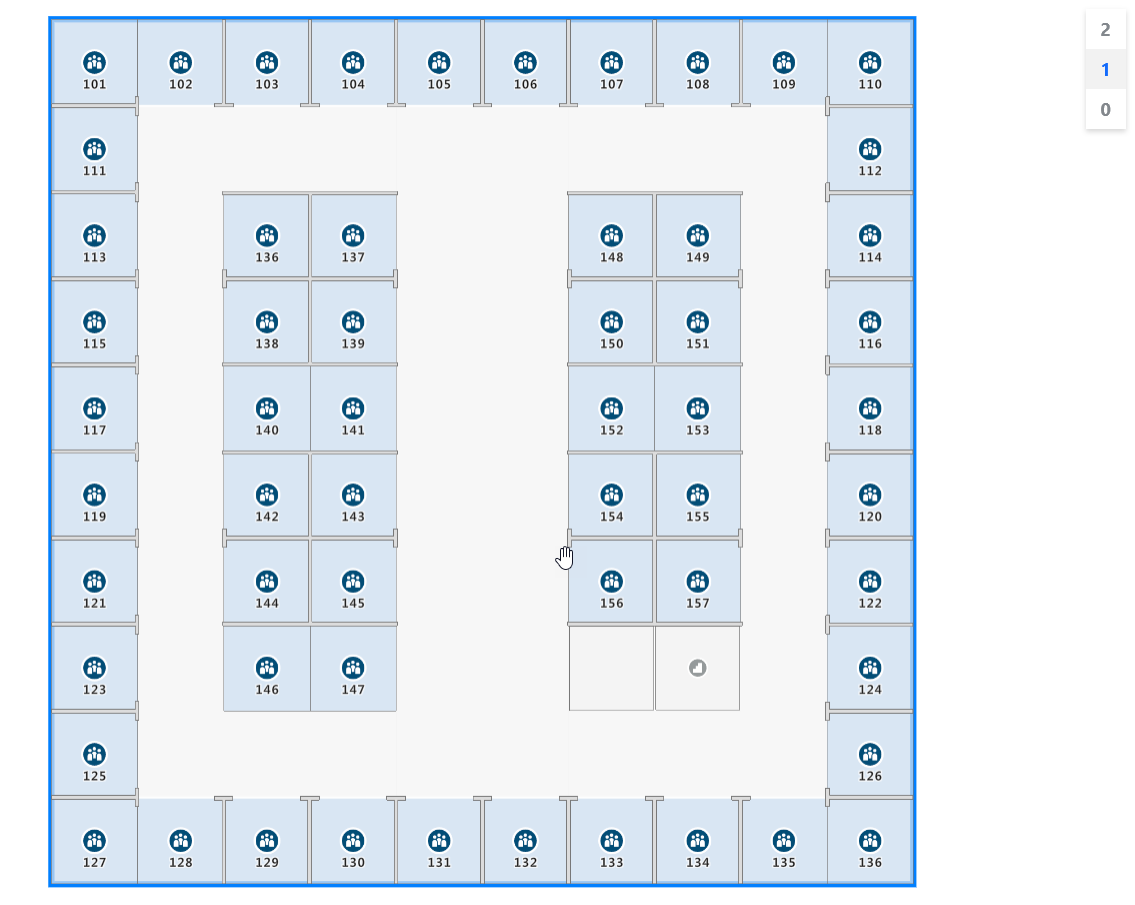
For a live demo of an indoor map with available source code, see Creator Indoor Maps in the [Azure Maps Samples].
Next steps
Read about the APIs that are related to the Azure Maps Indoor module:
Learn more about how to add more data to your map: