Configure tempdb settings for Azure SQL Managed Instance
Applies to:
Azure SQL Managed Instance
This article teaches you to configure your tempdb settings for Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Azure SQL Managed Instance allows you to configure the following:
- Number of
tempdbfiles - The growth increment of
tempdbfiles - Maximum
tempdbsize
tempdb settings persist after your instance is restarted, updated, or if there's a failover.
Overview
tempdb is one of the default system databases that comes with Azure SQL Managed Instance. The structure of tempdb is the same as any other user database structure; the difference is that since tempdb used for nondurable storage, transactions are minimally logged.
tempdb can't be dropped, detached, taken offline, renamed, or restored. Attempting any of these operations returns an error. tempdb is regenerated upon every start of the server instance and any objects that may have been created in tempdb during a previous session don't persist when the service restarts, after an instance update management operation or a failover.
The workload in tempdb differs from workloads in other user databases; objects and data are frequently created and destroyed and there's extremely high concurrency. There's only one tempdb for each managed instance. Even if you have multiple databases and applications connecting to the instance, they all use the same tempdb database. Services may experience contention when they try to allocate pages in a heavily used tempdb. Depending on the degree of contention, queries and requests that involve tempdb could become unresponsive. This is why tempdb is critical to the performance of the service.
Number of tempdb files
Increasing the number of tempdb data files creates one or more GAM and SGAM pages for each data file, which helps improve tempdb concurrency and reduces PFC page contention. However, increasing the number of tempdb data files could have other performance implications, so test thoroughly before implementing in production.
By default, Azure SQL Managed Instance creates 12 tempdb data files, and 1 tempdb log file, but it's possible to modify this configuration.
Modifying the number of tempdb files has the following limitations:
- The logical name of the new file is case insensitive, with a maximum of 16 characters and no spaces.
- The maximum number of
tempdbfiles is 128.
Note
You do not have to restart the server after adding new files; however, the emptier files will be filled with higher priority and the round-robin algorithm for allocating pages is lost until the system is rebalanced.
You can use both SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and Transact-SQL (T-SQL) to change the number of files for tempdb in Azure SQL Managed Instance.
You can use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to modify the number of tempdb files. To do so, follow these steps:
Connect to your managed instance in SSMS.
Expand Databases in Object Explorer, and then expand System databases.
Right-click
tempdb, and choose Properties.Select Files under Select a page to view the existing number of
tempdbfiles.To add a file, choose Add and then provide information about the new data file in the row.

To remove a
tempdbfile, choose the file you want to remove from the list of database files, and then select Remove.
Growth increment
tempdb file growth can have a performance impact to queries using tempdb. As such, tempdb data file growth increments that are too small may cause extent fragmentation, while increments that are too large may result in slow growth, or growth failure if there isn't sufficient space for the growth to happen. The optimal value for tempdb file growth increments depends on your workload.
The default growth increments for SQL Managed Instance are 254 MB for tempdb data files, and 64 MB for tempdb log files, but you can configure growth increments to adapt to your workload and tune your performance.
Consider the following:
- The file growth parameter supports the following units for
int_growth_increment: KB, MB, GB, TB, and %. - Growth increments should be the same for all
tempdbdata files as otherwise, the round robin algorithm that allocates pages could be impacted.
You can use both SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and Transact-SQL (T-SQL) to change the growth increment for your tempdb files.
You can use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to modify the growth increment of tempdb files. To do so, follow these steps:
Connect to your managed instance in SSMS.
Expand Databases in Object Explorer, and then expand System databases.
Right-click
tempdb, and choose Properties.Select Files under Select a page to view the existing number of
tempdbfiles.Choose the ellipses (...) next to a data file to open the Change Autogrowth properties dialog window.
Check the box next to Enable Autogrowth and then modify your autogrowth settings by specifying the file growth values, in either percent, or megabytes.

Select OK to save your settings.
Maximum size
tempdb size is the sum size of all tempdb files. tempdb file size is an allocated (zeroed) space for that tempdb file. The initial file size for all tempdb files is 16 MB, which is the size of all tempdb files when the instance restarts, or fails over. Once a tempdb data file's used space reaches the file size, all tempdb data files automatically grow by their configured growth increments.
tempdb used space is the sum of the used space of all tempdb files. tempdb file used space is equal to the part of that tempdb file size that is occupied with nonzero information. The sum of tempdb used space and tempdb free space is equal to the tempdb size.
You can use T-SQL to determine the current used and free space for your tempdb files.
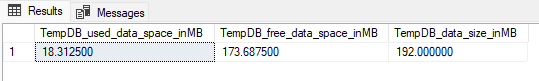
To get used space, free space, and size of your tempdb data files, run this command:
USE tempdb
SELECT SUM((allocated_extent_page_count)*1.0/128) AS TempDB_used_data_space_inMB,
SUM((unallocated_extent_page_count)*1.0/128) AS TempDB_free_data_space_inMB,
SUM(total_page_count*1.0/128) AS TempDB_data_size_inMB
FROM sys.dm_db_file_space_usage
The following screenshot shows an example output:
To get the used space, free space, and size of your tempdb log files, run this command:
USE tempdb
SELECT used_log_space_in_bytes*1.0/1024/1024 AS TempDB_used_log_space_inMB,
(total_log_size_in_bytes- used_log_space_in_bytes)*1.0/1024/1024 AS TempDB_free_log_space_inMB,
total_log_size_in_bytes*1.0/1024/1024 AS TempDB_log_size_inMB
FROM sys.dm_db_log_space_usage
The following screenshot shows an example output:

tempdb max size is the limit after which your tempdb can't grow further.
tempdb max size in SQL Managed Instance has the following limitations:
- In the General Purpose service tier, the maximum size for
tempdbis limited to 24 GB/vCore (96-1920 GB), and the log file is 120 GB. - In the Business Critical service tier,
tempdbcompetes with other databases for resources, so the reserved storage is shared betweentempdband other databases. The max size of thetempdblog file is 2 TB.
tempdb files grow until they reach either the maximum limit allowed by the service tier, or by the manually configured max tempdb file size.
You can use both SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and Transact-SQL (T-SQL) to change the maximum size for your tempdb files.
To determine your current tempdb max size in SSMS, follow these steps:
- Connect to your managed instance in SSMS.
- Expand Databases in Object Explorer, and then expand System databases.
- Right-click
tempdb, and choose Properties. - On the General page, check the Size value under Database to determine your max tempdb size. A value of
-1indicates tempdb max size is unlimited.

To change your current tempdb max size in SSMS, follow these steps:
- Connect to your managed instance in SSMS.
- Expand Databases in Object Explorer, and then expand System databases.
- Right-click
tempdb, and choose Properties. - Select Files under Select a page to view the existing number of
tempdbfiles. - Choose the ellipses (...) next to a data file to open the Change Autogrowth properties dialog window.
- Modify your
tempdbmax size settings by changing the values under Maximum file size. - Select OK to save your settings.

tempdb limits
The following table defines limits for various tempdb configuration settings:
| Configuration setting | Values |
|---|---|
Logical names of tempdb files |
16 characters maximum |
Number of tempdb files |
128 files maximum |
Default number of tempdb files |
13 (1 log file + 12 data files) |
Initial size of tempdb data files |
16 MB |
Default growth increment of tempdb data files |
256 MB |
Initial size of tempdb log files |
16 MB |
Default growth increment of tempdb log files |
64 MB |
Initial max tempdbsize |
-1 (unlimited) |
Max size of tempdb |
Up to the storage size |
Next steps
- To learn how to create your first managed instance, see Quickstart guide.
- For a features and comparison list, see SQL common features.
- For more information about VNet configuration, see SQL Managed Instance VNet configuration.
- For a quickstart that creates a managed instance and restores a database from a backup file, see Create a managed instance.
- For a tutorial about using Azure Database Migration Service for migration, see SQL Managed Instance migration using Database Migration Service.
- For advanced monitoring of SQL Managed Instance, see database watcher.
- For pricing information, see SQL Database pricing.

