Use packages from Google Maven Repository
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
With Azure Artifacts, developers can enable upstream sources to consume packages from different public registries such as Google Maven Repository. Once enabled, Azure Artifacts will automatically save a copy of any package installed from the upstream. Additionally, Azure Artifacts supports other Maven upstream sources such as Maven Central, Gradle Plugins, and JitPack. In this article, you'll learn how to:
- Add Google Maven Repository as an upstream source
- Consume a package from upstream
- Find saved packages in your feed
Prerequisites
An Azure DevOps organization and a project. Create an organization or a project if you haven't already.
An Azure Artifacts feed.
Enable upstream sources
If you don't have a feed already, follow the instructions below to create a new feed, and make sure to check the upstream sources checkbox to enable them. If you already have a feed, jump to the next step to add Google Maven Repository as an upstream source:
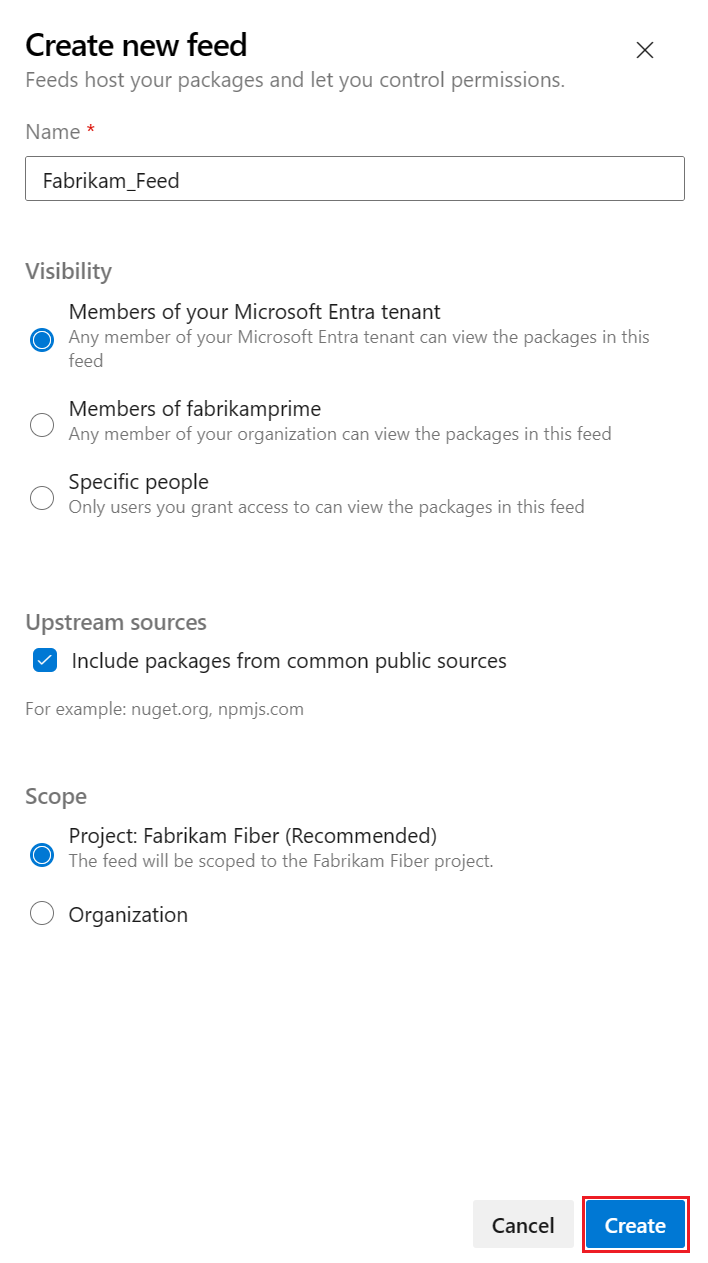
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization, and then navigate to your project.
Select Artifacts, and then select Create Feed to create a new feed.
Enter a descriptive Name for your feed and define its Visibility (indicating who can view packages within the feed). Specify the Scope of your feed, and if you wish to include packages from public sources, mark the Upstream sources checkbox.
Select Create when you're done.
Note
By default, newly created feeds have their project's Build Service set to Feed and Upstream Reader (Collaborator).
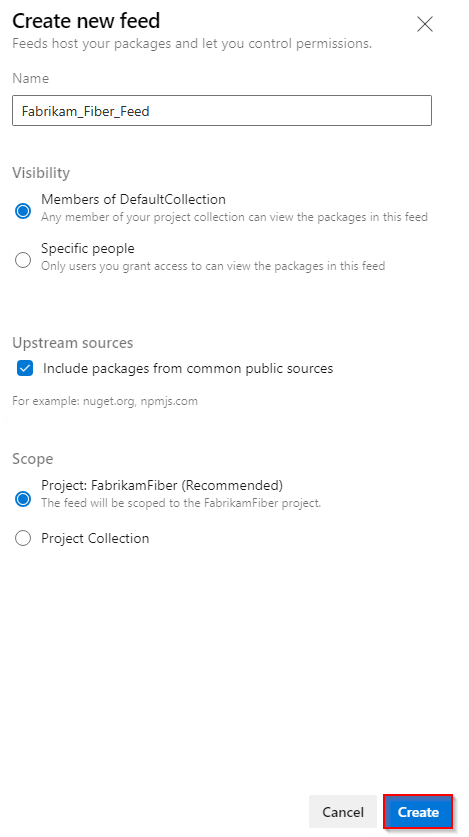
Sign in to your Azure DevOps server, and then navigate to your project.
Select Artifacts, and then select Create Feed to create a new feed.
Enter a descriptive Name for your feed and define its Visibility (indicating who can view packages within the feed). Specify the Scope of your feed, and if you wish to include packages from public sources, mark the Upstream sources checkbox.
Select Create when you're done.
Note
By default, newly created feeds have their project's Build Service set to Feed and Upstream Reader (Collaborator).
Select Create when you're done.
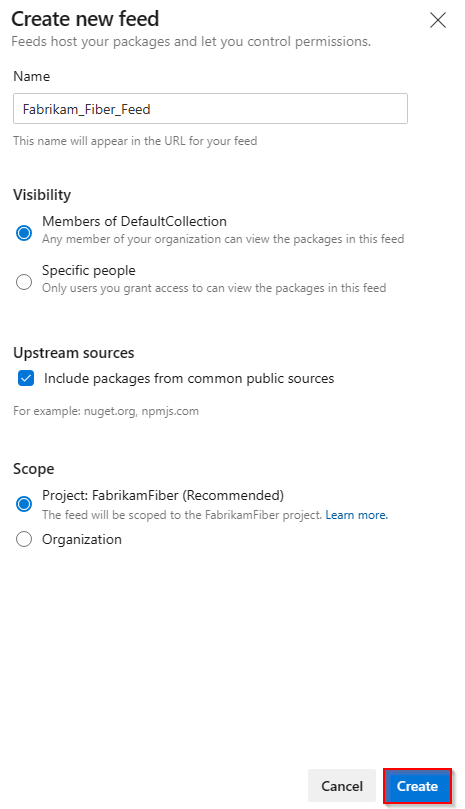
Note
By default, newly created feeds have their project's Build Service set to Feed and Upstream Reader (Collaborator).
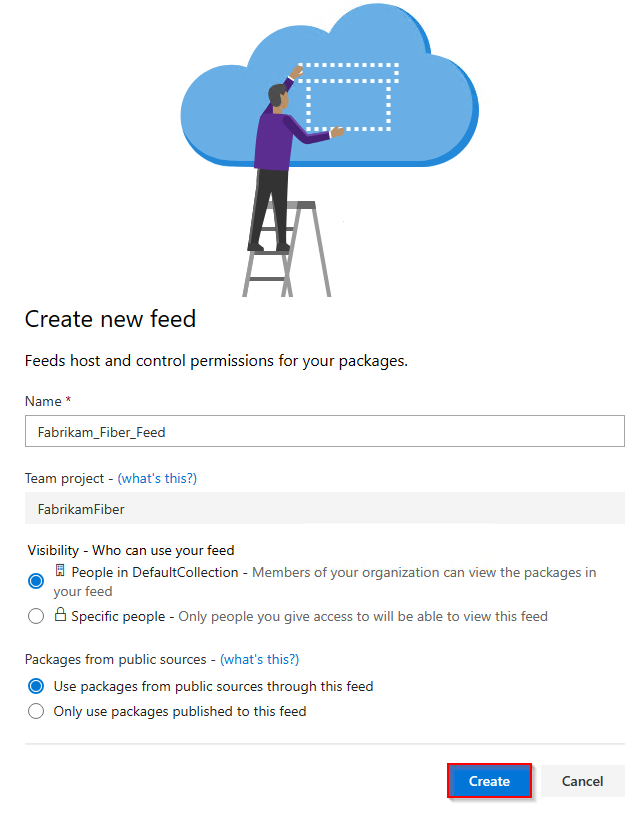
Sign in to your Azure DevOps server, and then navigate to your project.
Select Artifacts, and then select New feed.
Enter a descriptive Name for your feed and define its Visibility (indicating who can view packages within the feed). If you wish to include packages from public sources, select the Use packages from public sources through this feed option.
Select Create when you're done.
Note
By default, newly created feeds have their project's Build Service set to Feed and Upstream Reader (Collaborator).
Add Google Maven Repository upstream
If you checked the upstream sources checkbox when creating your feed, Google Maven Repository should already be added as an upstream source. If not, you can add it manually using the following steps:
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization, and then navigate to your project.
Select Artifacts, and then select the gear icon
 in the top right corner to navigate to your Feed Settings.
in the top right corner to navigate to your Feed Settings.Select Upstream sources, and then select Add Upstream.
Select Public source, and then select Google Maven Repository (https://maven.google.com/web/index.html) from the dropdown menu.
Select Save when you're done, and then select Save again in the top right corner to save your changes.
Note
Maven snapshots are not supported with Maven upstream sources.
Save packages from Google Maven Repository
Before saving packages from Google Maven Repository, make sure you have set up your project to connect to your feed. If you haven't done so already, follow the instruction in the project setup to set up your Maven project and connect to your feed.
In this example, we will save the Zipflinger Library from Google Maven Repository.
Navigate to Google Maven Repository at
https://mvnrepository.com/.Search for the Zipflinger library. Select the Zipflinger package, and then select the version you wish to install.
Copy the
<dependency>snippet from the Maven tab.<dependency> <groupId>com.android</groupId> <artifactId>zipflinger</artifactId> <version>8.3.0-alpha13</version> </dependency>Open your pom.xml file and paste the snippet inside your
<dependencies>tag, and then save your file.Run the following command from the same path as your pom.xml file to install your dependencies:
mvn install
Note
To save packages from upstreams, you must have the Feed and Upstream Reader (Collaborator) role or higher. See Manage Permissions for more details.
View saved packages
To view the packages you installed from upstream, select the Google Maven Repository source from the dropdown menu.
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization, and then navigate to your project.
Select Artifacts, and then select your feed from the dropdown menu.
Select the Google Maven Repository source from the dropdown menu to find packages from this upstream.
The Zipflinger package that we saved in the previous step is now available in our feed, as Azure Artifacts automatically saved a copy when we executed the mvn install command.
Tip
If Maven is not downloading all your dependencies, run the following command from the project directory to regenerate your project's files:
mvn eclipse:eclipse -DdownloadSources=true -DdownloadJavadocs=true
Related articles
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
