Connect to dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) in Azure Synapse Analytics with Visual Studio and SSDT
Use Visual Studio to query a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) within Azure Synapse in just a few minutes. This method uses the SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT) extension in Visual Studio 2019.
Prerequisites
To use this tutorial, you need:
- An existing dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW). To create one, see Create a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW).
- SSDT for Visual Studio. If you have Visual Studio, you probably already have SSDT for Visual Studio. For installation instructions and options, see Installing Visual Studio and SSDT.
- The fully qualified SQL server name. To find this information, see Connect to a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW).
1. Connect to your dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW)
Open Visual Studio 2019.
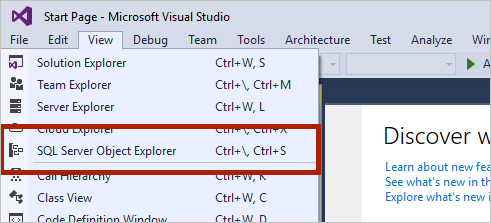
Open SQL Server Object Explorer by selecting View > SQL Server Object Explorer.
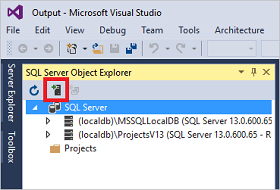
Click the Add SQL Server icon.
Fill in the fields in the Connect to Server window.
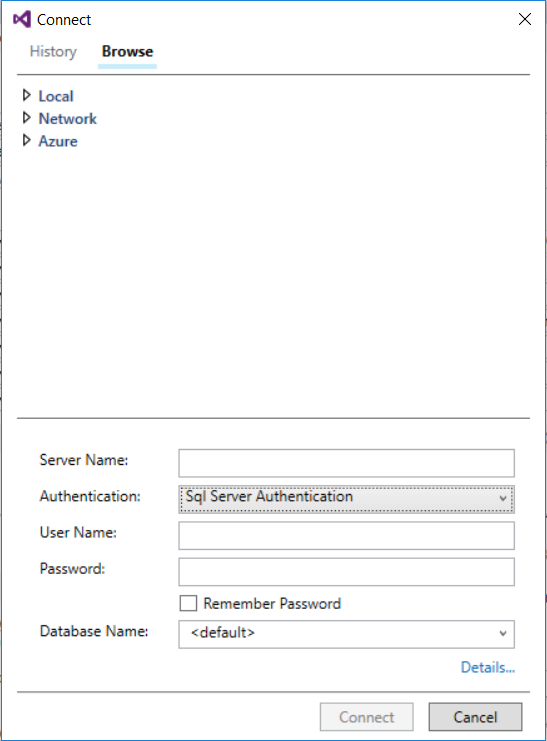
- Server name. Enter the server name previously identified.
- Authentication. Select SQL Server Authentication or Active Directory Integrated Authentication.
- User Name and Password. Enter user name and password if SQL Server Authentication was selected above.
- Click Connect.
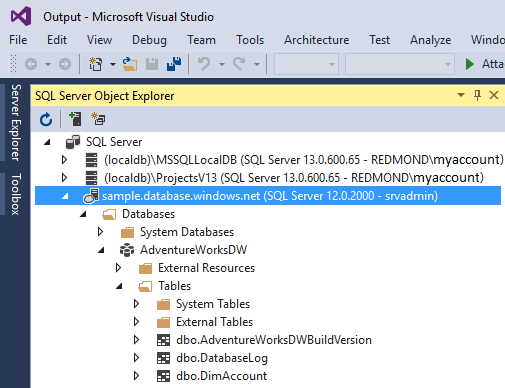
To explore, expand your Azure SQL server. You can view the databases associated with the server. Expand AdventureWorksDW to see the tables in your sample database.
2. Run a sample query
Now that a connection has been established to your database, let's write a query.
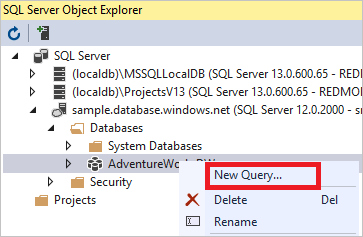
Right-click your database in SQL Server Object Explorer.
Select New Query. A new query window opens.
Copy the following T-SQL query into the query window:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM dbo.FactInternetSales;Run the query by clicking the green arrow or use the following shortcut:
CTRL+SHIFT+E.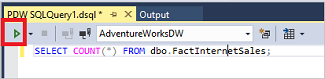
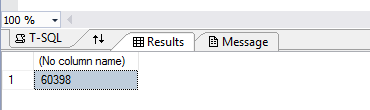
Look at the query results. In this example, the FactInternetSales table has 60398 rows.
Next steps
Now that you can connect and query, try visualizing the data with Power BI.
To configure your environment for Microsoft Entra authentication, see Authenticate to dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW).