Use external tables with Synapse SQL
An external table points to data located in Hadoop, Azure Storage blob, or Azure Data Lake Storage. You can use external tables to read data from files or write data to files in Azure Storage.
With Synapse SQL, you can use external tables to read external data using dedicated SQL pool or serverless SQL pool.
Depending on the type of the external data source, you can use two types of external tables:
- Hadoop external tables that you can use to read and export data in various data formats such as CSV, Parquet, and ORC. Hadoop external tables are available in dedicated SQL pools, but they aren't available in serverless SQL pools.
- Native external tables that you can use to read and export data in various data formats such as CSV and Parquet. Native external tables are available in serverless SQL pools, and they are in public preview in dedicated SQL pools. Writing/exporting data using CETAS and the native external tables is available only in the serverless SQL pool, but not in the dedicated SQL pools.
The key differences between Hadoop and native external tables:
| External table type | Hadoop | Native |
|---|---|---|
| Dedicated SQL pool | Available | Only Parquet tables are available in public preview. |
| Serverless SQL pool | Not available | Available |
| Supported formats | Delimited/CSV, Parquet, ORC, Hive RC, and RC | Serverless SQL pool: Delimited/CSV, Parquet, and Delta Lake Dedicated SQL pool: Parquet (preview) |
| Folder partition elimination | No | Partition elimination is available only in the partitioned tables created on Parquet or CSV formats that are synchronized from Apache Spark pools. You might create external tables on Parquet partitioned folders, but the partitioning columns are inaccessible and ignored, while the partition elimination won't be applied. Don't create external tables on Delta Lake folders because they aren't supported. Use Delta partitioned views if you need to query partitioned Delta Lake data. |
| File elimination (predicate pushdown) | No | Yes in serverless SQL pool. For the string pushdown, you need to use Latin1_General_100_BIN2_UTF8 collation on the VARCHAR columns to enable pushdown. For more information on collations, refer to Collation types supported for Synapse SQL. |
| Custom format for location | No | Yes, using wildcards like /year=*/month=*/day=* for Parquet or CSV formats. Custom folder paths are not available in Delta Lake. In the serverless SQL pool, you can also use recursive wildcards /logs/** to reference Parquet or CSV files in any sub-folder beneath the referenced folder. |
| Recursive folder scan | Yes | Yes. In serverless SQL pools must be specified /** at the end of the location path. In Dedicated pool the folders are always scanned recursively. |
| Storage authentication | Storage Access Key(SAK), Microsoft Entra passthrough, Managed identity, custom application Microsoft Entra identity | Shared Access Signature(SAS), Microsoft Entra passthrough, Managed identity, Custom application Microsoft Entra identity. |
| Column mapping | Ordinal - the columns in the external table definition are mapped to the columns in the underlying Parquet files by position. | Serverless pool: by name. The columns in the external table definition are mapped to the columns in the underlying Parquet files by column name matching. Dedicated pool: ordinal matching. The columns in the external table definition are mapped to the columns in the underlying Parquet files by position. |
| CETAS (exporting/transformation) | Yes | CETAS with the native tables as a target works only in the serverless SQL pool. You cannot use the dedicated SQL pools to export data using native tables. |
Note
The native external tables are the recommended solution in the pools where they are generally available. If you need to access external data, always use the native tables in serverless pools. In dedicated pools, you should switch to the native tables for reading Parquet files once they are in GA. Use the Hadoop tables only if you need to access some types that are not supported in native external tables (for example - ORC, RC), or if the native version is not available.
External tables in dedicated SQL pool and serverless SQL pool
You can use external tables to:
- Query Azure Blob Storage and Azure Data Lake Gen2 with Transact-SQL statements.
- Store query results to files in Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage using CETAS.
- Import data from Azure Blob Storage and Azure Data Lake Storage and store it in a dedicated SQL pool (only Hadoop tables in dedicated pool).
Note
When used in conjunction with the CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement, selecting from an external table imports data into a table within the dedicated SQL pool.
If performance of Hadoop external tables in the dedicated pools do not satisfy your performance goals, consider loading external data into the Datawarehouse tables using the COPY statement.
For a loading tutorial, see Use PolyBase to load data from Azure Blob Storage.
You can create external tables in Synapse SQL pools via the following steps:
- CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE to reference an external Azure storage and specify the credential that should be used to access the storage.
- CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT to describe format of CSV or Parquet files.
- CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE on top of the files placed on the data source with the same file format.
Folder partition elimination
The native external tables in Synapse pools are able to ignore the files placed in the folders that are not relevant for the queries. If your files are stored in a folder hierarchy (for example - /year=2020/month=03/day=16) and the values for year, month, and day are exposed as the columns, the queries that contain filters like year=2020 will read the files only from the subfolders placed within the year=2020 folder. The files and folders placed in other folders (year=2021 or year=2022) will be ignored in this query. This elimination is known as partition elimination.
The folder partition elimination is available in the native external tables that are synchronized from the Synapse Spark pools. If you have partitioned data set and you would like to leverage the partition elimination with the external tables that you create, use the partitioned views instead of the external tables.
File elimination
Some data formats such as Parquet and Delta contain file statistics for each column (for example, min/max values for each column). The queries that filter data will not read the files where the required column values do not exist. The query will first explore min/max values for the columns used in the query predicate to find the files that do not contain the required data. These files will be ignored and eliminated from the query plan.
This technique is also known as filter predicate pushdown and it can improve the performance of your queries. Filter pushdown is available in the serverless SQL pools on Parquet and Delta formats. To leverage filter pushdown for the string types, use the VARCHAR type with the Latin1_General_100_BIN2_UTF8 collation. For more information on collations, refer to Collation types supported for Synapse SQL.
Security
User must have SELECT permission on an external table to read the data.
External tables access underlying Azure storage using the database scoped credential defined in data source using the following rules:
- Data source without credential enables external tables to access publicly available files on Azure storage.
- Data source can have a credential that enables external tables to access only the files on Azure storage using SAS token or workspace Managed Identity - For examples, see the Develop storage files storage access control article.
Example for CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE
The following example creates a Hadoop external data source in dedicated SQL pool for Azure Data Lake Gen2 pointing to the New York data set:
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL [ADLS_credential]
WITH IDENTITY='SHARED ACCESS SIGNATURE',
SECRET = 'sv=2018-03-28&ss=bf&srt=sco&sp=rl&st=2019-10-14T12%3A10%3A25Z&se=2061-12-31T12%3A10%3A00Z&sig=KlSU2ullCscyTS0An0nozEpo4tO5JAgGBvw%2FJX2lguw%3D'
GO
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE AzureDataLakeStore
WITH
-- Please note the abfss endpoint when your account has secure transfer enabled
( LOCATION = 'abfss://data@newyorktaxidataset.dfs.core.windows.net' ,
CREDENTIAL = ADLS_credential ,
TYPE = HADOOP
) ;
The following example creates an external data source for Azure Data Lake Gen2 pointing to the publicly available New York data set:
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE YellowTaxi
WITH ( LOCATION = 'https://azureopendatastorage.blob.core.windows.net/nyctlc/yellow/',
TYPE = HADOOP)
Example for CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT
The following example creates an external file format for census files:
CREATE EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT census_file_format
WITH
(
FORMAT_TYPE = PARQUET,
DATA_COMPRESSION = 'org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec'
)
Example CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE
The following example creates an external table. It returns the first row:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE census_external_table
(
decennialTime varchar(20),
stateName varchar(100),
countyName varchar(100),
population int,
race varchar(50),
sex varchar(10),
minAge int,
maxAge int
)
WITH (
LOCATION = '/parquet/',
DATA_SOURCE = population_ds,
FILE_FORMAT = census_file_format
)
GO
SELECT TOP 1 * FROM census_external_table
Create and query external tables from a file in Azure Data Lake
Using Data Lake exploration capabilities of Synapse Studio you can now create and query an external table using Synapse SQL pool with a simple right-click on the file. The one-click gesture to create external tables from the ADLS Gen2 storage account is only supported for Parquet files.
Prerequisites
You must have access to the workspace with at least the
Storage Blob Data Contributoraccess role to the ADLS Gen2 account or Access Control Lists (ACL) that enable you to query the files.You must have at least permissions to create an external table and query external tables on the Synapse SQL pool (dedicated or serverless).
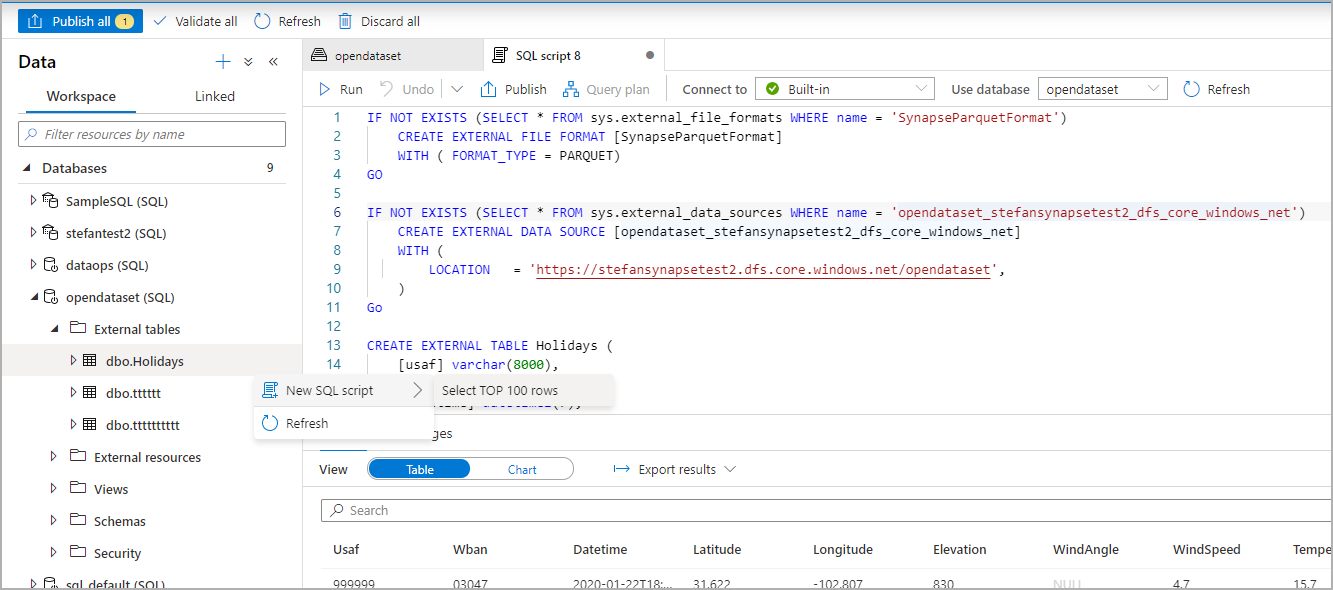
From the Data panel, select the file that you would like to create the external table from:
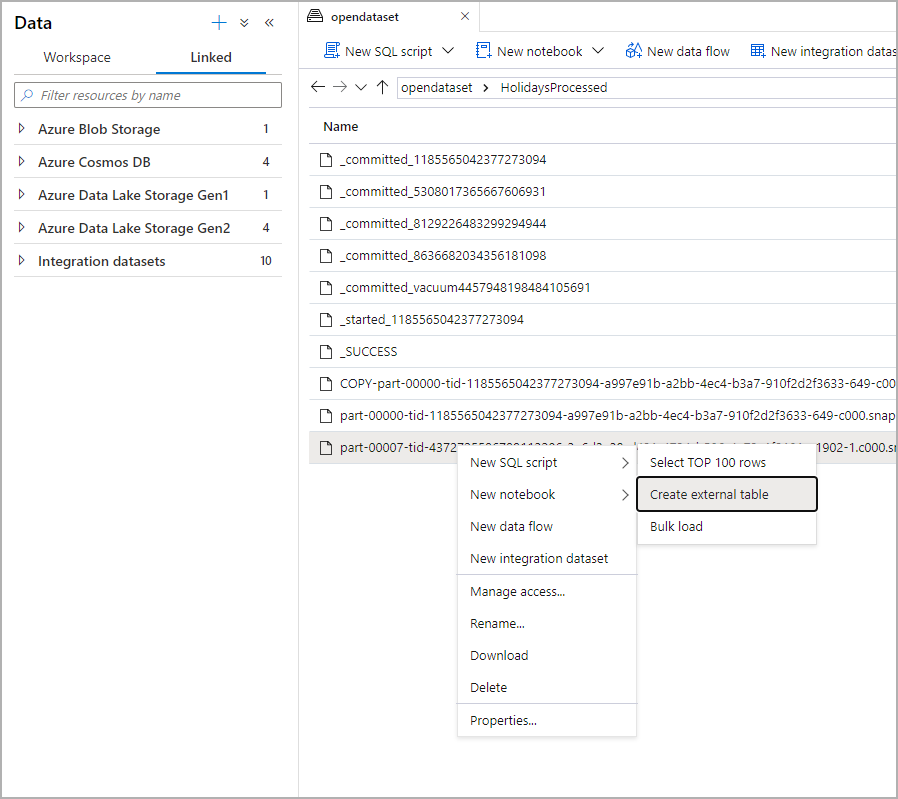
A dialog window will open. Select dedicated SQL pool or serverless SQL pool, give a name to the table and select open script:
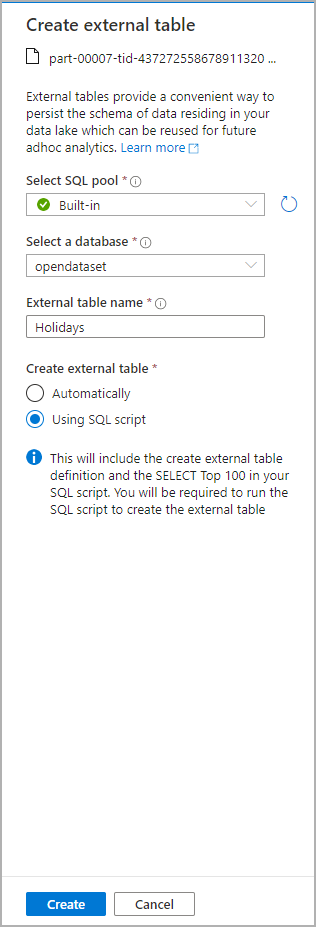
The SQL Script is autogenerated inferring the schema from the file:
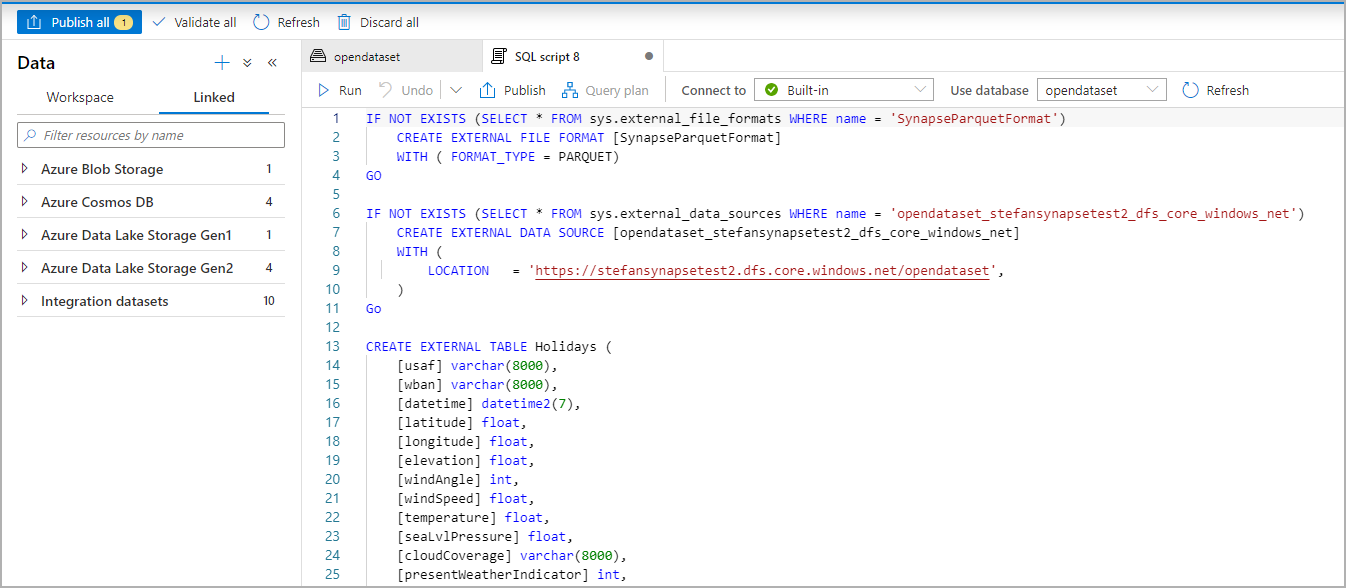
Run the script. The script will automatically run a Select Top 100 *.:
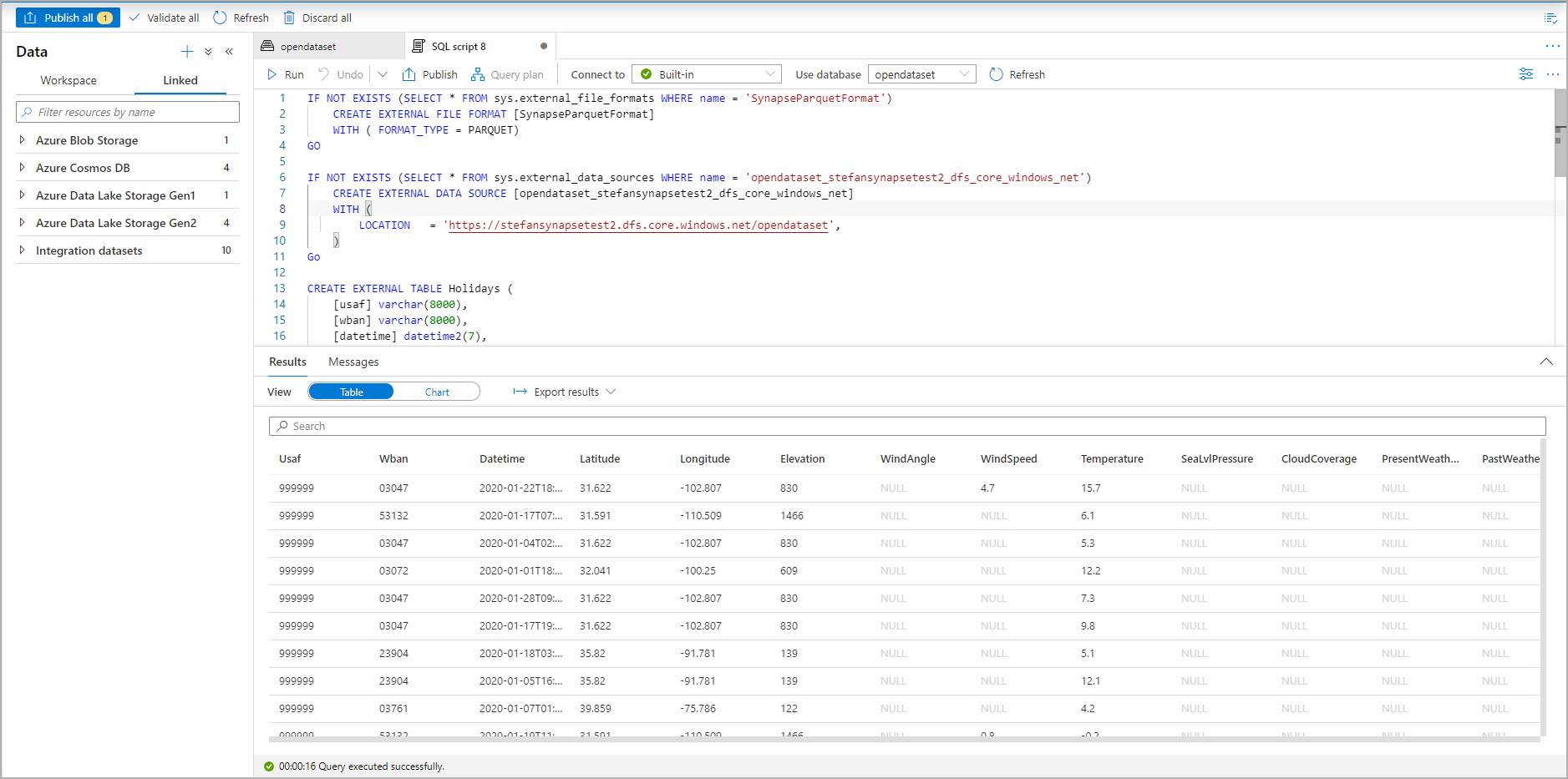
The external table is now created, for future exploration of the content of this external table the user can query it directly from the Data pane:
Next steps
See the CETAS article for how to save query results to an external table in Azure Storage. Or you can start querying Apache Spark for Azure Synapse external tables.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for