Events
Power BI DataViz World Championships
14 Feb, 16 - 31 Mar, 16
With 4 chances to enter, you could win a conference package and make it to the LIVE Grand Finale in Las Vegas
Learn moreThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Virtual tables enable integrating data from external data sources by seamlessly representing that data as tables in Microsoft Dataverse, without data replication. Solutions, apps, flows, and more can use virtual tables as if they were native Dataverse tables. Virtual tables allow for full create, read, update, and delete privileges unless the data source they're connecting to specifically forbids it. More information about virtual tables: Create and edit virtual tables that contain data from an external data source.
This document covers the new experience using Power Apps (make.powerapps.com) to create virtual tables using the following virtual connector providers:
Except for the Excel connector provider, all virtual connector providers use a Power Platform connector. More information: Connector reference for virtual connector providers used with virtual tables
You can create a virtual table for Excel using the virtual connector provider by following the legacy process. More information: Create the virtual table for Microsoft Excel
Virtual tables include the following components:
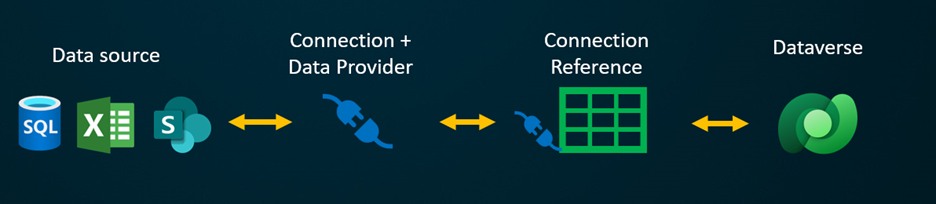
If you were to create a virtual table using a custom data provider, you need to write plugins that define how every Dataverse API would interact with the API on the system where the data is stored. This is a long process that requires knowledge of coding. Virtual connector providers streamline the creation experience by automating some of the creation for you and removing the need to use code to create the virtual tables.
When you establish a remote connection to an external source using a connector data source, the virtual connector provider automatically retrieves a list of all the available tables and lists by retrieving table definitions (metadata) from the external data source. You then select these tables and lists to generate the virtual table.
The underlying data source is key for allowing the provider to establish an authenticated remote connection to the external data. It uses a connection reference that stores pertinent details regarding the external source. The information stored in the connection reference is specific to the connector type and the connection it refers to.
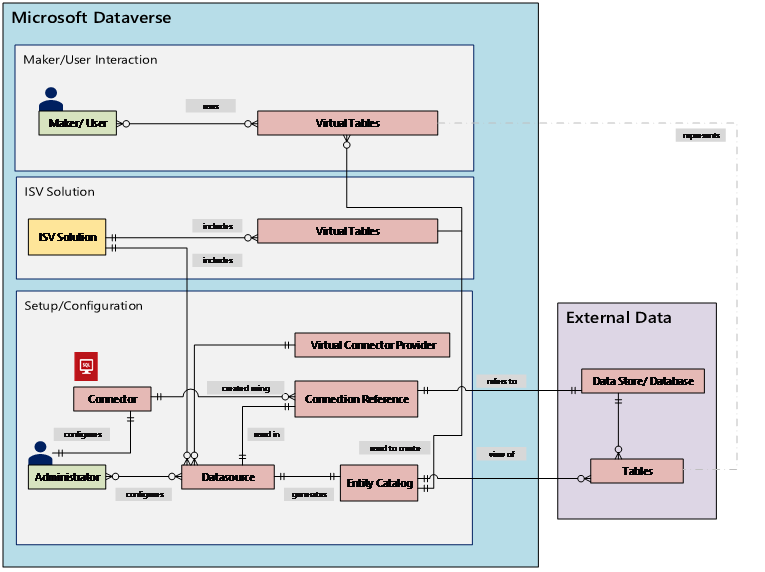
When setting up the connection and connection reference for your data sources, specific information is needed. For example, the SQL Server connector needs server name, database name, the authentication method, username, password, and (optionally) gateway connection details. Each external data source needs a connection reference defined to create the virtual table. When using the Power Apps (make.powerapps.com) experience, the connection reference can be generated automatically for you unless you wish to provide custom naming.
Note
The connector permissions enforce the ability for organizational users to access and operate on the virtual table. The connection can be shared with one user or can be shared with the entire organization. This allows users to access and operate virtual tables using a shared connection. By using security roles, virtual table access can be restricted to a specific set of users within your organization. You can even specify which roles have create, read, update, or delete privileges in this way.
Application lifecycle management (ALM) is supported for virtual tables created using the virtual connector provider. You can even create the virtual tables from directly within a solution when using Power Apps (make.powerapps.com). Virtual tables should be part of a managed solution along with the connection reference to distribute the solution. The solution can have other components, such as a model-driven app that uses virtual tables.
More information about application lifecycle management (ALM) and solutions:
To create a virtual table, you must have a Microsoft Dataverse license through Power Apps or Microsoft Dynamics 365. Microsoft 365 or Teams licenses can't be used to create virtual tables.
Creating a virtual table in Power Apps (make.powerapps.com) using the virtual connector provider includes the following steps:
These steps describe how to create a virtual table from a solution. Use similar steps to create a virtual table by going to Data > Tables.
Watch a short video showing how to create a virtual table with the virtual connector provider.
In the New table from external data wizard you can either select an existing connection if you have one or choose to Add connection.
Important
Connections that are shared with you aren't available for use with this feature. Only connections created by the current user appear in the virtual table wizard.
You're directed to a new tab in your browser. Select your authentication method. Depending on the authentication method selected, you might be asked to provide credential information required to create the connection.
Important
These will be the credentials used for all authentication for the virtual table so use credentials with the correct level of permissions with SQL Server.
Optionally, select Advanced options to use a connection reference and/or environment variable.
When you create a virtual table, a connection reference is automatically created for you with the virtual table. A connection reference is a solution component that contains information about the connector. However, you might want to create you own. To do this, select Manually configure connection reference. More information: Create and select a connection reference (optional)
You can associate a virtual table with its own environment variable. Select Use environment variables to link the environment variable directly to the virtual table provider, offering flexibility to modify data sources when importing the virtual table into a new environment. More information: Environment variable

Select Create.
After the connection is created, go back to your browser tab with the wizard and select Refresh, and then select your connection.
When you create a virtual table, a connection reference is automatically created for you with the virtual table. A connection reference is a solution component that contains information about the connector.
However, you might want to create your own connection reference for the virtual table.
Note
To create a connection reference, when you're creating the connection for the virtual table, follow these steps:
Expand Advanced options and then select the Manually configure connection reference to create a connection reference for the virtual table.
On the Connection Reference page, select or name your connection reference, and then select Next.
Environment variables play a key role in the application lifecycle management (ALM) process, allowing for seamless movement of applications across different Power Platform environments. When creating a virtual table, you can associate it with its own environment variable. To take advantage of this functionality, expand Advanced options, and then select Use environment variables when choosing a connection for your data source during a virtual table create.
If you're creating a SharePoint virtual table, you're asked to enter the URL of your SharePoint site or select from your most recently used SharePoint sites. The most recently used list is populated by gathering information about your recently used sites using Microsoft Graph and your Microsoft Entra credentials. If you're pasting the SharePoint URL, only include the information up to the site name, such as https://microsoft.sharepoint.com/teams/Contoso.
A page is displayed where you can either search your data source for a specific table or list, or select a table or list from the provided list.
Select the check box if you want to configure the table name, column names, and primary field.
Select Next.
When you create a virtual table, by default you can choose to change the suggested table and column names. To do this, follow these steps:
Select Configure table and column names that will be used in Dataverse, accept, or change the following Dataverse table properties:
In the External column area, choose if you would like to rename any of your external columns from the data source. The following fields are provided:
Tip
Instead of entering the information, the Quick format names command provides suggested name changes and can be useful if you have a large number of fields that include prefixed values from your SQL server, such as tablename.column name. For example, Database12.Products would change to Products.
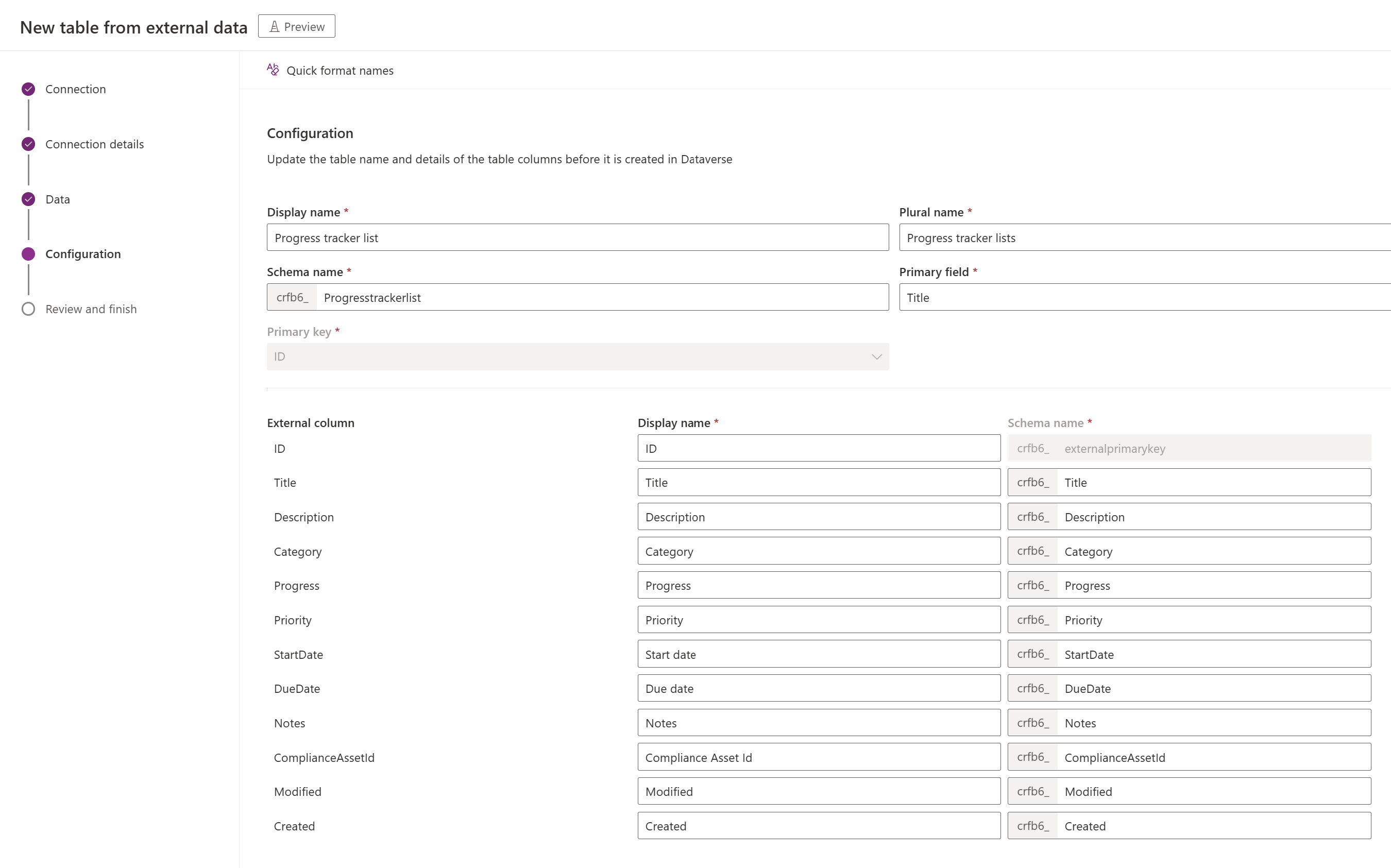
Select Next
Note
Select Choose a different table takes you back to the table selection screen. selecting Edit Configuration of Table takes you to the Configuration screen.
Once the table is created, you're taken directly to your new virtual table where you can view your data and begin working with it.
Note
When you attempt to create a virtual table that already exists, you receive a message that the table already exists and that you will be re-creating it. You will not be able to change the primary field or schema name if this is the case. Re-creating the table will update any column changes that were made in the data source on the table.
To learn more about supported actions and limitations with each connector, go to:
Download and install the virtual connector. Go to the Microsoft commercial marketplace and search for Virtual Connector or select the link to download the provider: Virtual connectors in Dataverse
Select Get it now. In the sign-in dialog, enter work or school account email. If you agree to the terms and conditions, select Continue. The Power Platform admin center opens automatically.
Select the environment where you want to install the solution. If you agree to the terms and conditions, select Install. Once the installation is complete, you see the Virtual connectors in Dataverse app installed under Environments -> [your environment name] -> Dynamics 365 apps.

You should also see the Virtual Connector Provider solution and other solutions enabled in the Power Platform environment.
Watch a short video showing how to create a virtual table with the Excel virtual connector provider.
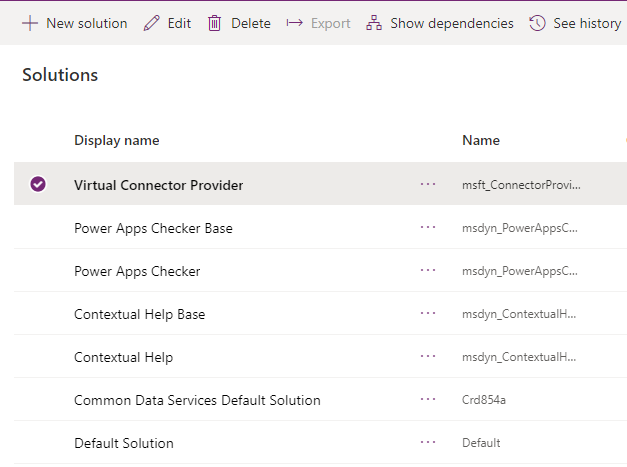
Go to Solutions.
Select the Default Solution or any other existing solution you have in your environment to create the virtual table.
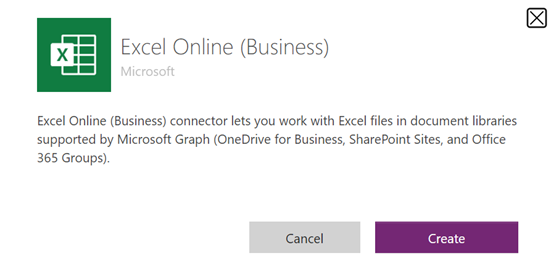
Select New and then select Connection Reference.
Enter Display name, select the connection you created for the Connectors option and then select the data connection that you've created.
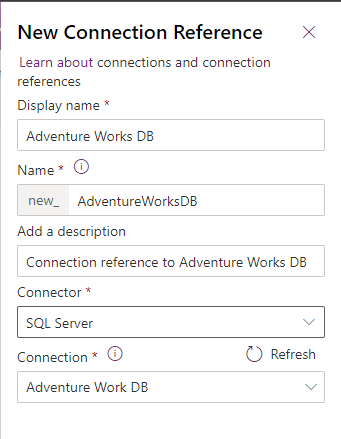
Now create the virtual table data source in Dataverse.
Select the Gear icon -> Advanced Settings.
In the top navigation bar, select Settings and then Administration.

Select Virtual Entity Data Sources.
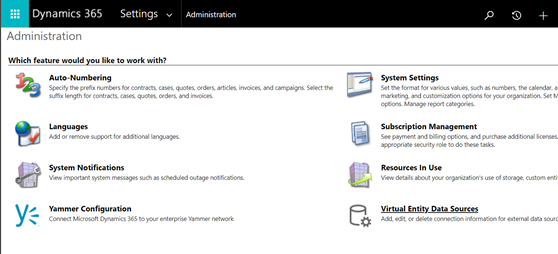
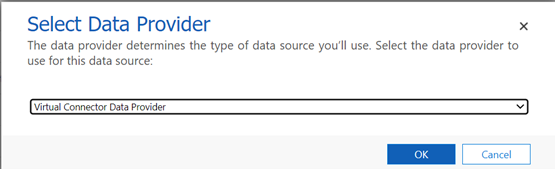
Select New. In the pop-up dialog, select the Virtual Connector Data Provider.

Name your Data Source and select the Connection Reference you created in the drop-down list.
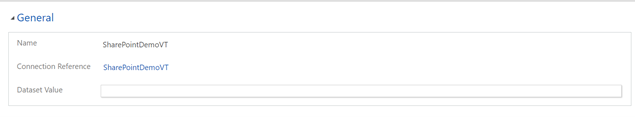
Add your Dataset Value
Paste in the file name including extension into the Dataset Value. Remember the file must be in the OneDrive that was used for the Connection setup. (for example: SampleData.xlsx)
Select Save.
With the connection reference and the virtual table data source setup, an Entity Catalog is automatically generated. The Entity Catalog is specific to the data source and will list all the tables that are in the respective data source.
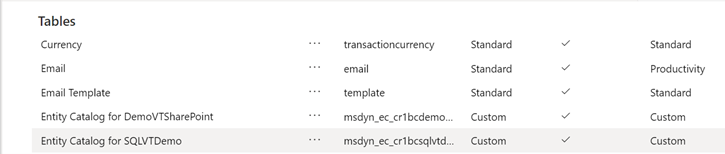
Note
Tip
Select Data > Tables, and then select the entity catalog that was created.
Select Advanced Find and use the Look for: column. The catalog includes a prefix Entity Catalog for followed by the connection reference (example: Entity Catalog for Adventure Works). Find the entity catalog for your respective data connection and select Results to display all the external data source tables.

Note
Bulk creation of virtual tables is not supported currently. Even though the entity catalog allows you to select multiple tables, you will have to select one table at a time to create virtual tables.
To create a virtual table, a model driven app must be built for the entity catalog. Select the entity catalog table.
Select Create an app in the top navigation.
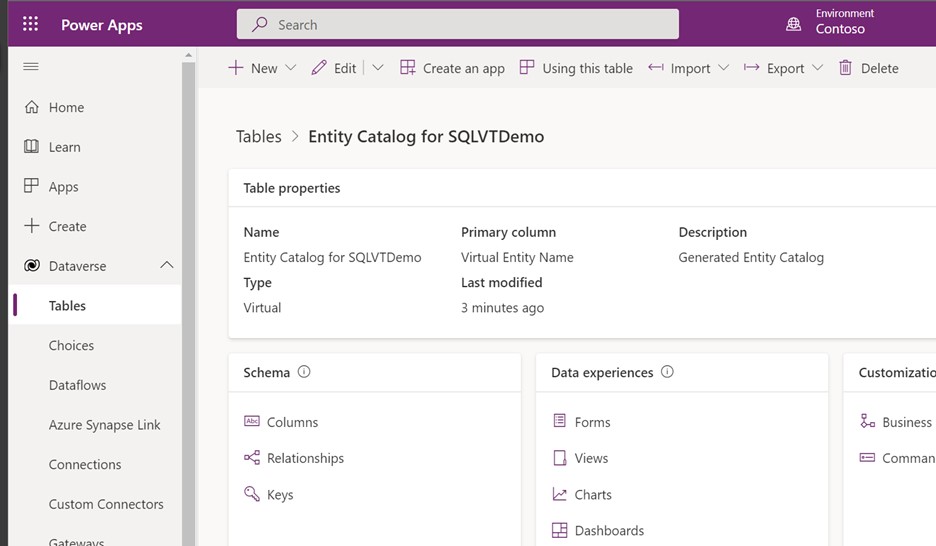
Name the app, and then select Create.
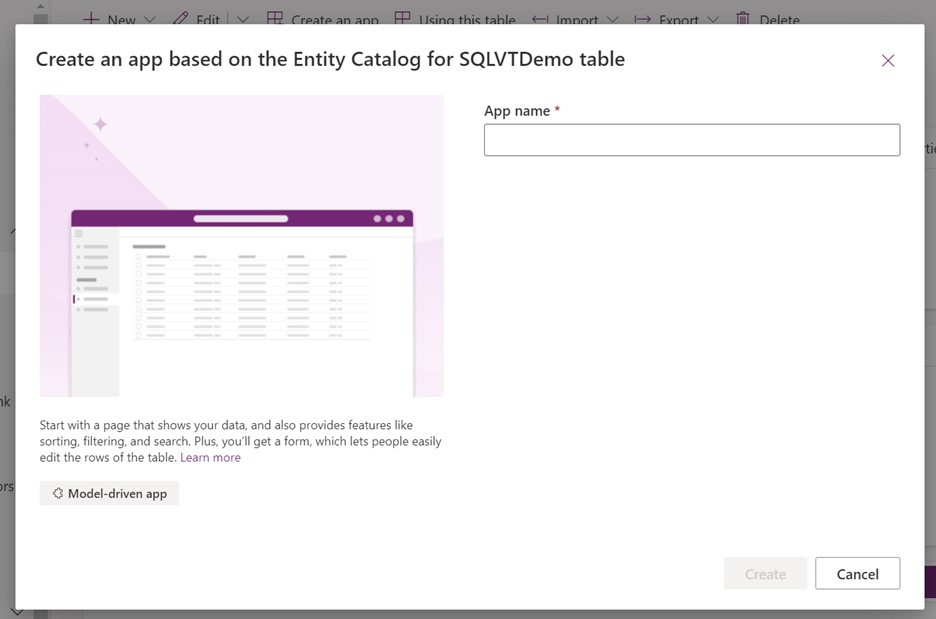
The app is automatically generated using the entity catalog table.
Once the app is completed, you can select Publish to complete the app and use it later, or you can select Play to create your virtual table now without publishing the app.
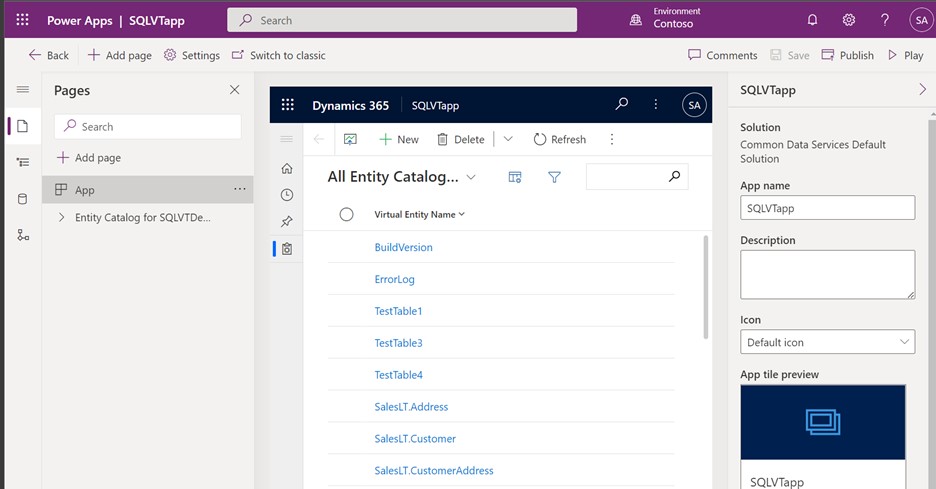
All tables from your Excel file will be provided in the app view.
Select the data set you wish to use from the entity catalog, and then select Edit in the navigation bar.
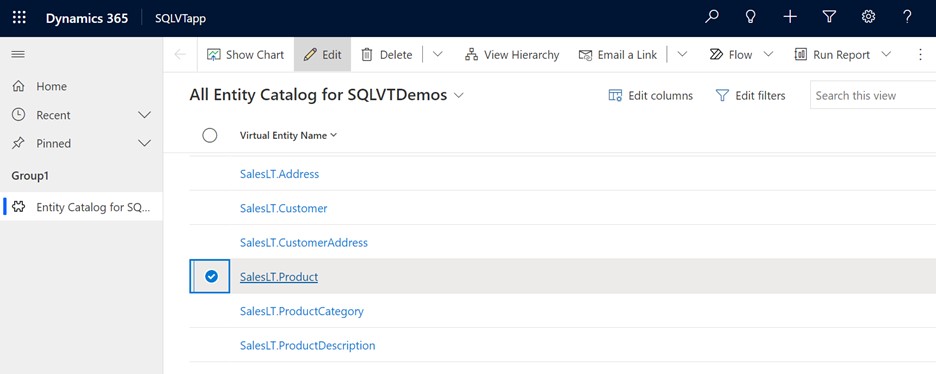
Wait for the form to fully load before editing. When loaded the form appears like this:
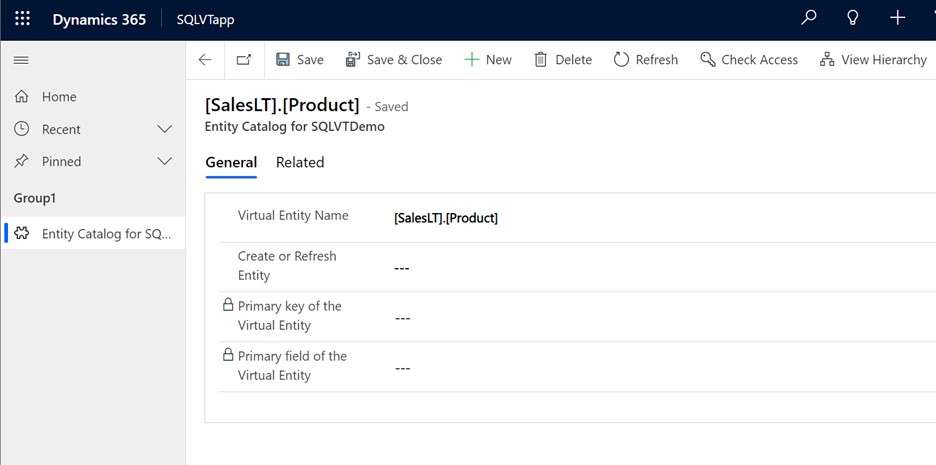
In the provided form set the Create or Refresh Entity column to Yes.
Select the Primary Key and Primary Field of the virtual entity by using the dropdown lists to find the columns you want to use.
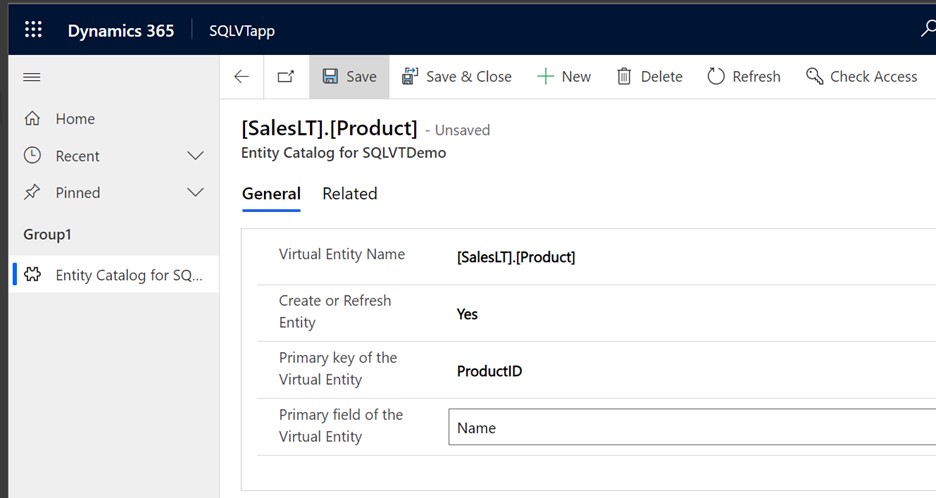
Save the record to create the virtual table.
Note
After the save completes, the form will "reset" with all fields shown as blank, this is normal.
Return to the Power Apps home page and select Data. Your virtual table is now created with a "Custom Entity" prefix. It might take a few moments for the creation to complete.
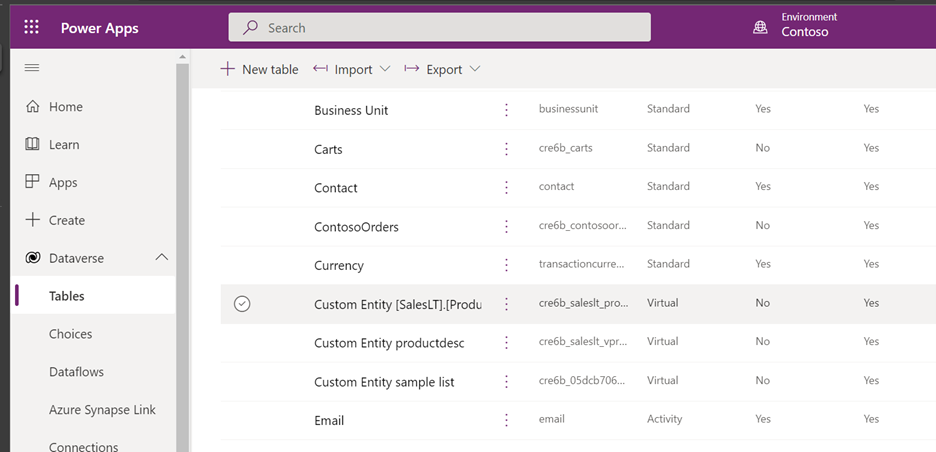
Important
Once you've created a virtual table, you can work with it much the same way as any other table. You can start defining the relationships with other tables, in the environment and use them in your Power Apps and Power Automate flows.
Setting up a virtual table relationship
Known limitations and troubleshooting with virtual tables
Developers Guide: Get started with virtual tables (entities)
Events
Power BI DataViz World Championships
14 Feb, 16 - 31 Mar, 16
With 4 chances to enter, you could win a conference package and make it to the LIVE Grand Finale in Las Vegas
Learn moreTraining
Module
Create tables in Microsoft Dataverse - Training
Explore secure data management with Dataverse, learning how to create tables and import data into a cloud-based storage system.
Certification
Microsoft Certified: Power Platform Functional Consultant Associate - Certifications
Demonstrate the use of Microsoft Power Platform solutions to simplify, automate, and empower business processes for organizations in the role of a Functional Consultant.
Documentation
Create and edit virtual tables with Microsoft Dataverse - Power Apps
Learn how to create virtual tables
Limitations and troubleshooting virtual tables with Power Apps - Power Apps
Understand the limitations and how to troubleshoot virtual tables.
Get started with virtual tables (entities) (Microsoft Dataverse) - Power Apps
Virtual tables enable integration of data residing in external systems with Microsoft Dataverse.