Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The components in the Center of Excellence (CoE) Starter Kit are designed for multiple uses. The example process in this article, which uses the starter kit components, is meant to showcase common patterns other organizations have found useful and—hopefully—act as inspiration for defining your own processes.
The app auditing sample process showcases how your CoE department or IT administrators can automate an auditing process on an app-level basis to gather additional information about an app, like business justification and the impact of an outage, from the maker.
Note
Follow the setup compliance components steps to configure this process. More information: Compliance process
Process description
Problem statement: There are many apps in the Contoso tenant. IT doesn't know what all these apps are intended for or how to support individual apps when the helpdesk is called, and it's unclear whether all the apps are being maintained to any standard. They can see details like the description and number of shared users from the Power Apps for Admins connector, but they need to communicate directly with the app owner to fully understand the situation around the apps. Especially in a large organization like Contoso, it's not feasible for the IT team to be responsible for manually reaching out to each app owner individually, and those details can't be stored in email conversations. The Contoso team would like to have a central app catalog for high-quality apps.
Solution: The CoE has decided there should be an auditing process on an app-level basis, using Microsoft Dataverse as a data store for the business justifications. They decide to use apps and flows to facilitate this process.
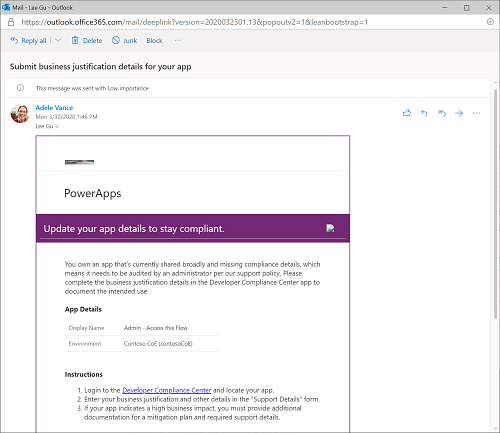
The flow named Admin | Compliance Detail Request is used to iterate through all the apps in the tenant and check whether the apps are compliant. If the owner hasn't submitted a business justification and the app was shared broadly (in this example, with more than 20 users or at least one group), the flow sends the owner an email to notify them that their specific app isn't compliant with Contoso's policy. The email contains a link to the Developer Compliance Center canvas app, where the owner can provide the business justification details in a form submission. The Developer Compliance Center app also contain details about the compliance thresholds and has links to the app settings, so the owner can configure the description and republish if needed.
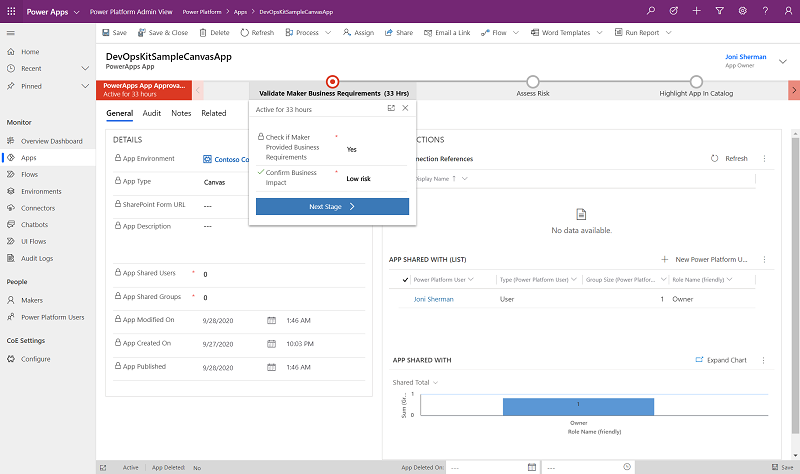
After the maker has proven compliance by adding these details, the admin can review those details and the app itself. A business process flow in the Power Platform Admin View (model-driven app) helps facilitate the auditing process.
When reviewing the app compliance details, the admin can make a decision about whether the app belongs in the app catalog.
The user's view of the process
Here is that process from the point of view of the people involved and the components they interact with.
Maker: The maker gets a notification that they have work to do to bring their app into compliance. The notification includes a deep link to Developer Compliance Center for their app.
Three items are tracked in the system, and the user might have to do all three:
Make a fresh publish, to show it's an active app.
Add a description of the app, to indicate its purpose.
Add supporting details, such as the business justification.
Admin: After an app meets all three of these requirements, it appears in the Compliance - Submitted filter view on the Power Platform Admin View model driven app.
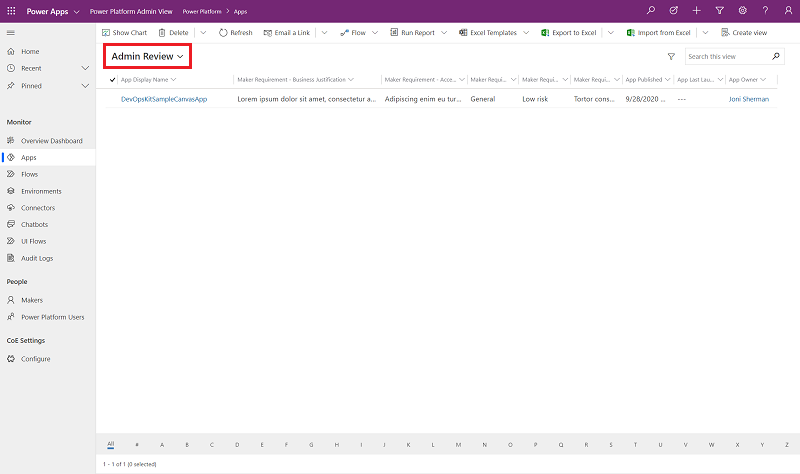
An admin opens Power Platform Admin View > Compliance - Submitted and assesses all the apps due for review by looking at the Audit tab within the app, investigating the work done by the maker, and then marking their assessment in the Compliance - Submitted section.
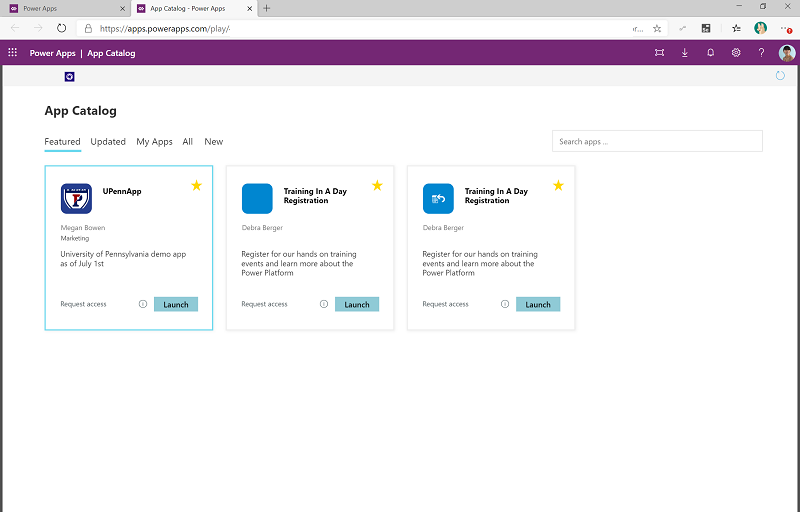
The admin can decide to put an app in the app catalog and mark it as featured or not, depending on whether the app should be highlighted for users.
Users: The maker and users can now see the app in the app catalog.