Navigate Speaker Progress for dynamic presentations
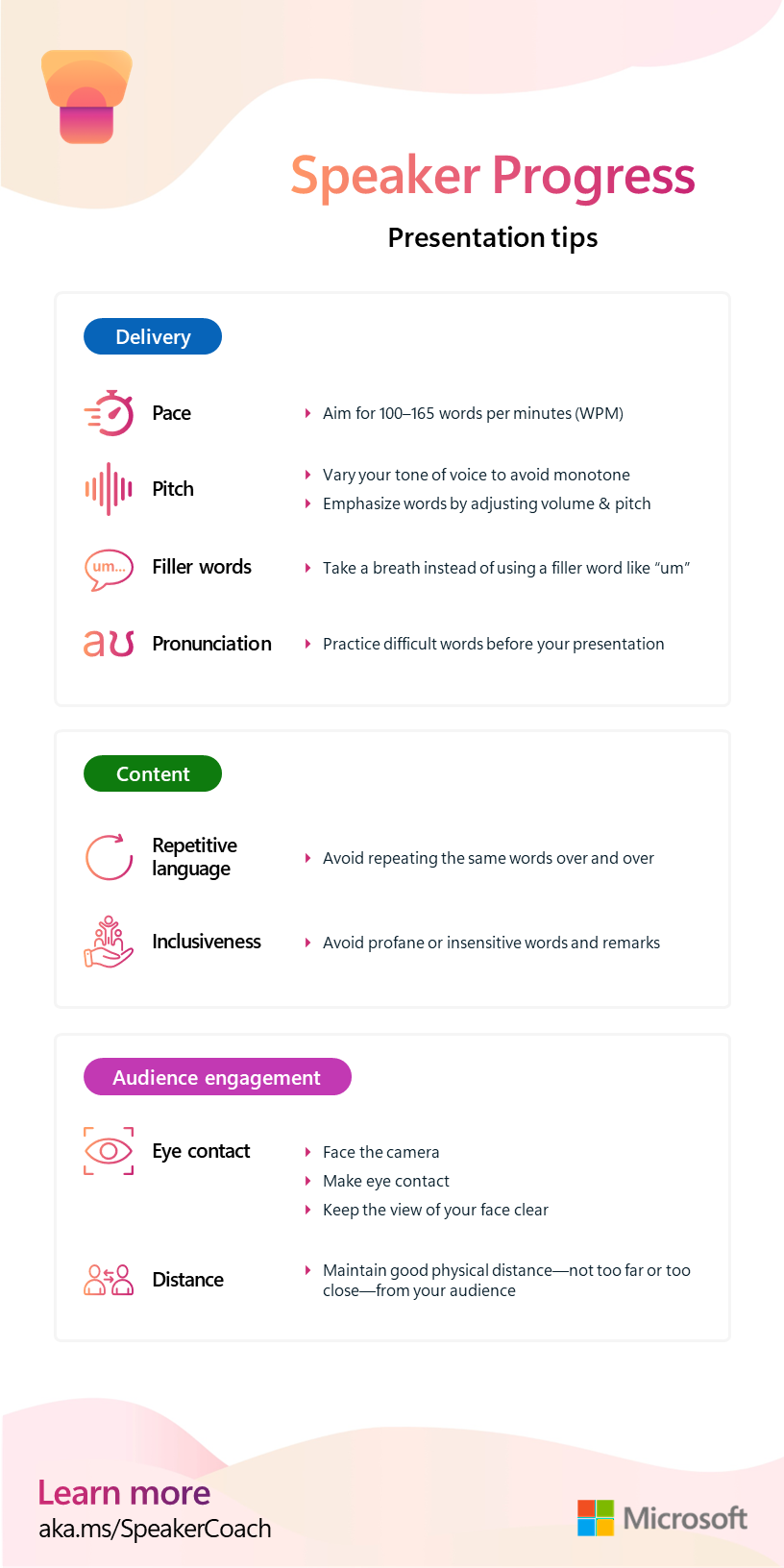
Speaker Progress helps learners gain confidence in their presentation skills by offering feedback in three categories:
- Delivery
- Content
- Audience engagement
Speaker Coach delivery feedback
Speaker Coach delivery feedback helps learners improve their speaking skills and performance.
Pace
The ideal range for a presentation is between 100 and 165 words per minute. During the rehearsal, Speaker Coach shows learners their pace based on their last few seconds of speaking.
Pace feedback helps learners understand if they should speed up or slow down.
Pitch
If a speaker has a monotone delivery, their audience can lose interest. To keep the audience's attention, learners should emphasize key words and phrases by adjusting their volume and pitch. Learners must avoid simply reading from a script, which can lead to more monotone and less natural speech patterns.
Pitch feedback lets learners know when they should vary their tone of voice to engage their audience.
Filler words
Although filler words are a normal part of speaking, they can become distracting or detrimental to the message if learners use too many. Research indicates that a presenter who frequently uses filler words is perceived as less confident, which in turn makes the audience less confident in the speaker's message.
Filler words feedback helps learners adjust if they're relying too much on common filler words.
Pronunciation
Mispronouncing words can cause an audience to misunderstand the speaker, which might then cause them to become disengaged. Learners need to be clear and precise in how they pronounce their words.
Pronunciation feedback identifies mispronounced words and encourages learners to practice difficult words.
Speaker Coach content feedback
Speaker Coach content feedback helps learners refine and improve the content of their presentation.
Repetitive language
Reusing the same words too many times can be distracting to an audience. Repetitive language isn't the same as filler words, which are words or sounds used to fill space between sentences. Repetitive language, on the other hand, is words or phrases that recur frequently in the content.
Speaker Coach has a database of about 200 common words and phrases. It counts the number of times a learner uses words or phrases from the database. Some words are checked for whether they occur at the beginning of a sentence (for example, basically, nevertheless, or technically.) Other words are checked for whether they occur at the end of a sentence (for example, right.)
Repetitive language feedback suggests alternative words when learners are using a word too often.
Inclusiveness
Profane or insensitive language can also distract from the speaker's main message. Speaker Coach helps learners to be inclusive by listening for culturally sensitive phrases in the following areas:
- Disability
- Age
- Gender
- Race
- Sexual orientation
- Mental health
- Geopolitically sensitive topics
- Profanity
Inclusiveness feedback lets learners know when they accidentally make a profane or insensitive remark and offers alternatives.
Note
Speaker Coach transcribes learners' speech to text, then evaluates the text. Transcription mistakes can sometimes occur. Speaker Coach might sometimes miss non-inclusive language and mistakenly flag some language as non-inclusive.
Speaker Coach audience engagement feedback
Audience engagement feedback helps learners improve their body language to better engage with their audience.
Eye contact
Eye contact can help enhance audience engagement and help a speaker's voice carry better. Body language feedback reminds learners to make eye contact, face the camera, and keep the view of their face clear.
Physical distance
If a presenter is too close or too far from their audience, it can be hard to see them and engage with what they're saying. Body language feedback helps learners know if they're a good distance from their audience.
Note
Speaker Coach body language critiques are designed for a stationary, seated audience receiving a visual presentation.
Speaker Progress & Speaker Coach presentation tips infographic accessible PDF version