GitHub Copilot Chat
GitHub Copilot Chat is an advanced feature of the GitHub Copilot ecosystem, designed to provide developers with an interactive, conversational AI assistant directly within their development environment. It allows developers to have natural language conversations about their code, ask questions, and receive intelligent responses and suggestions in real-time. In this unit, we cover:
- How to generate code using GitHub Copilot Chat.
- Debugging using GitHub Copilot Chat.
- How to get code explanations using GitHub Copilot Chat.
- Using slash commands to perform actions with GitHub Copilot.
- Using custom GitHub Copilot agents to improve prompts.
To access Copilot in your Integrated Development Environment(IDE), click the chat icon on the left navbar.
GitHub Copilot Chat is beneficial in certain scenarios:
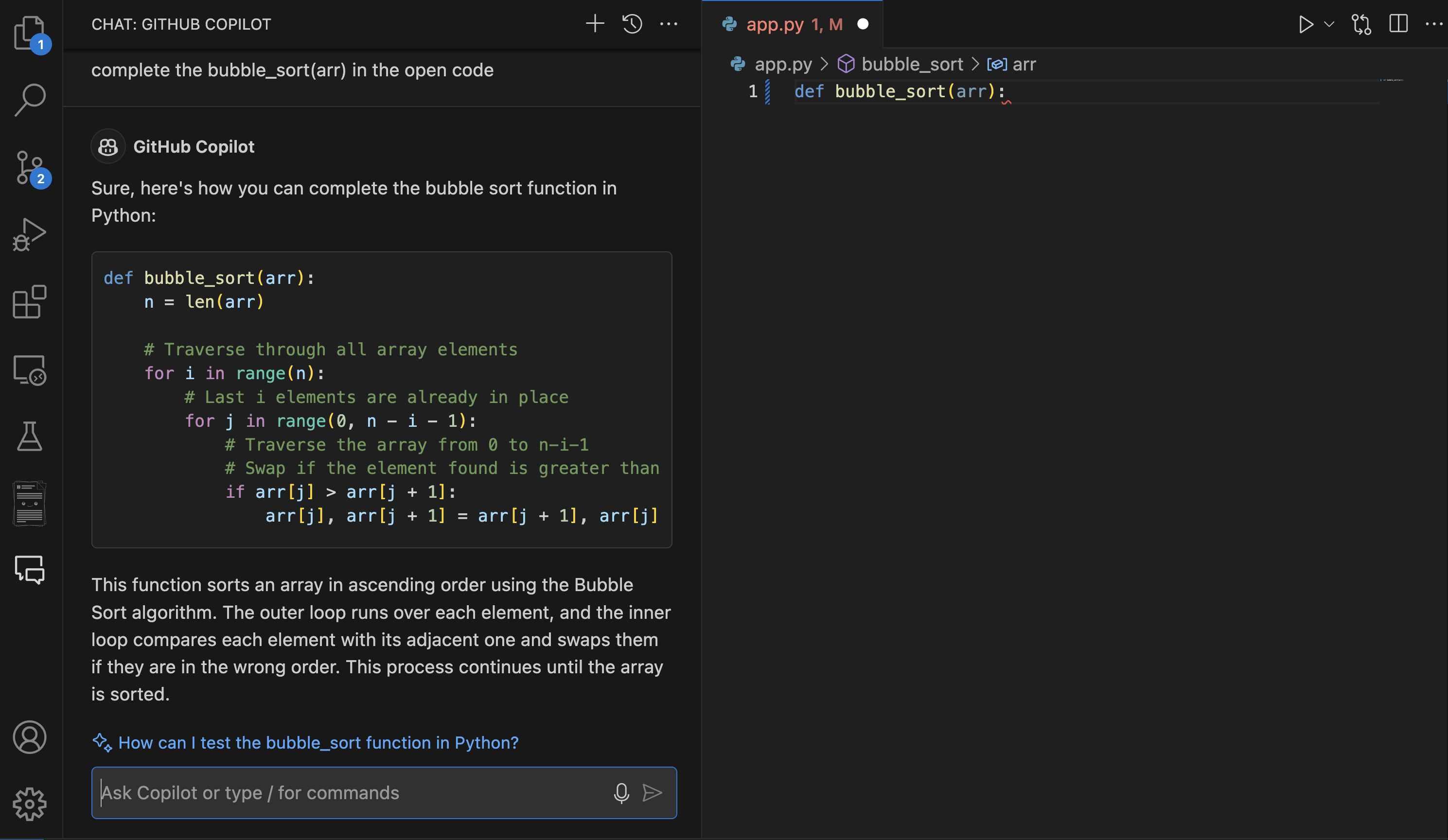
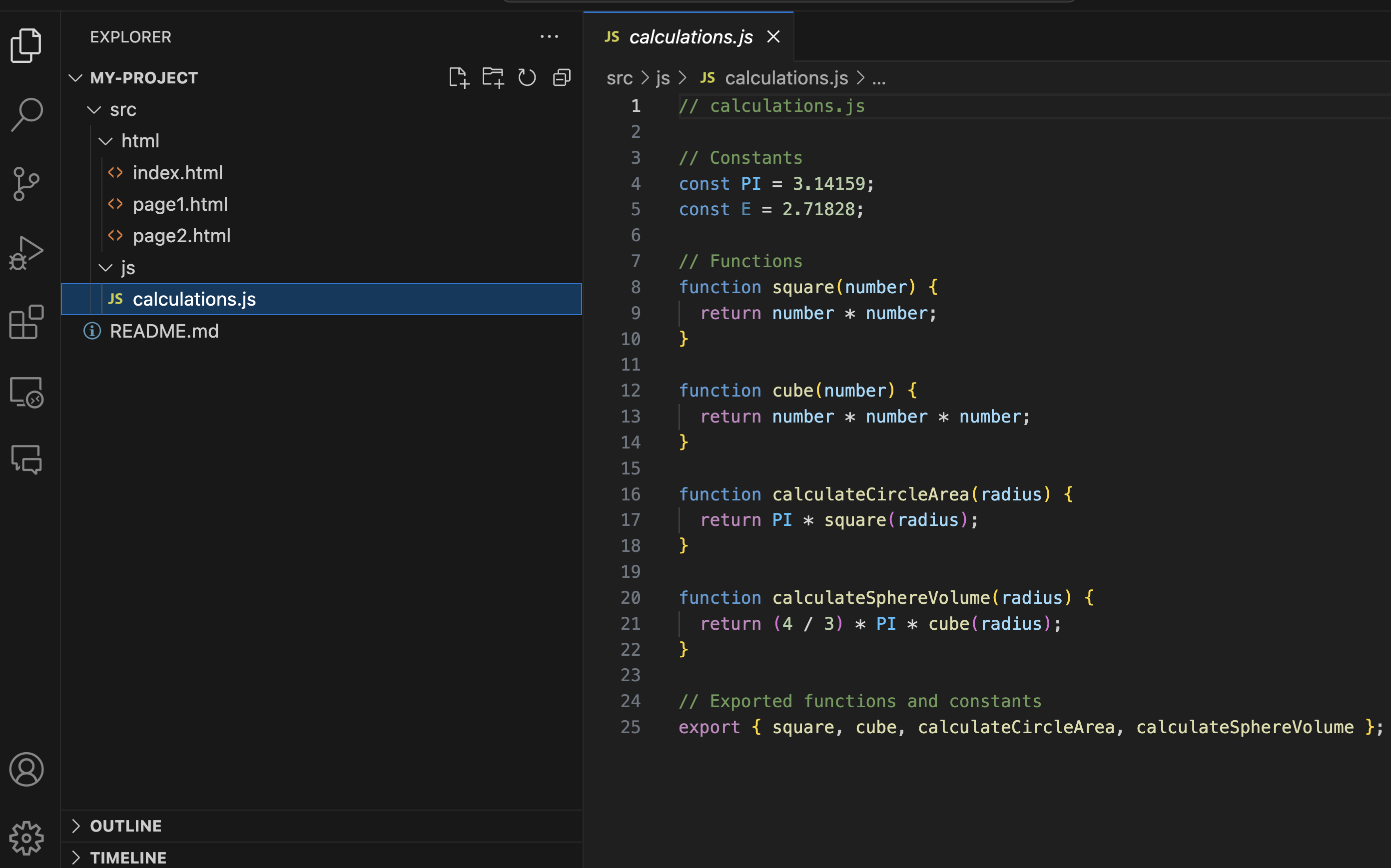
Complex code generation When you need to implement complex algorithms, data structures, or generate boilerplate code for specific design patterns, Copilot Chat can help streamline the process. It can help create intricate regular expressions, construct detailed SQL queries, or develop advanced data structures like a Bubble sort in Python.
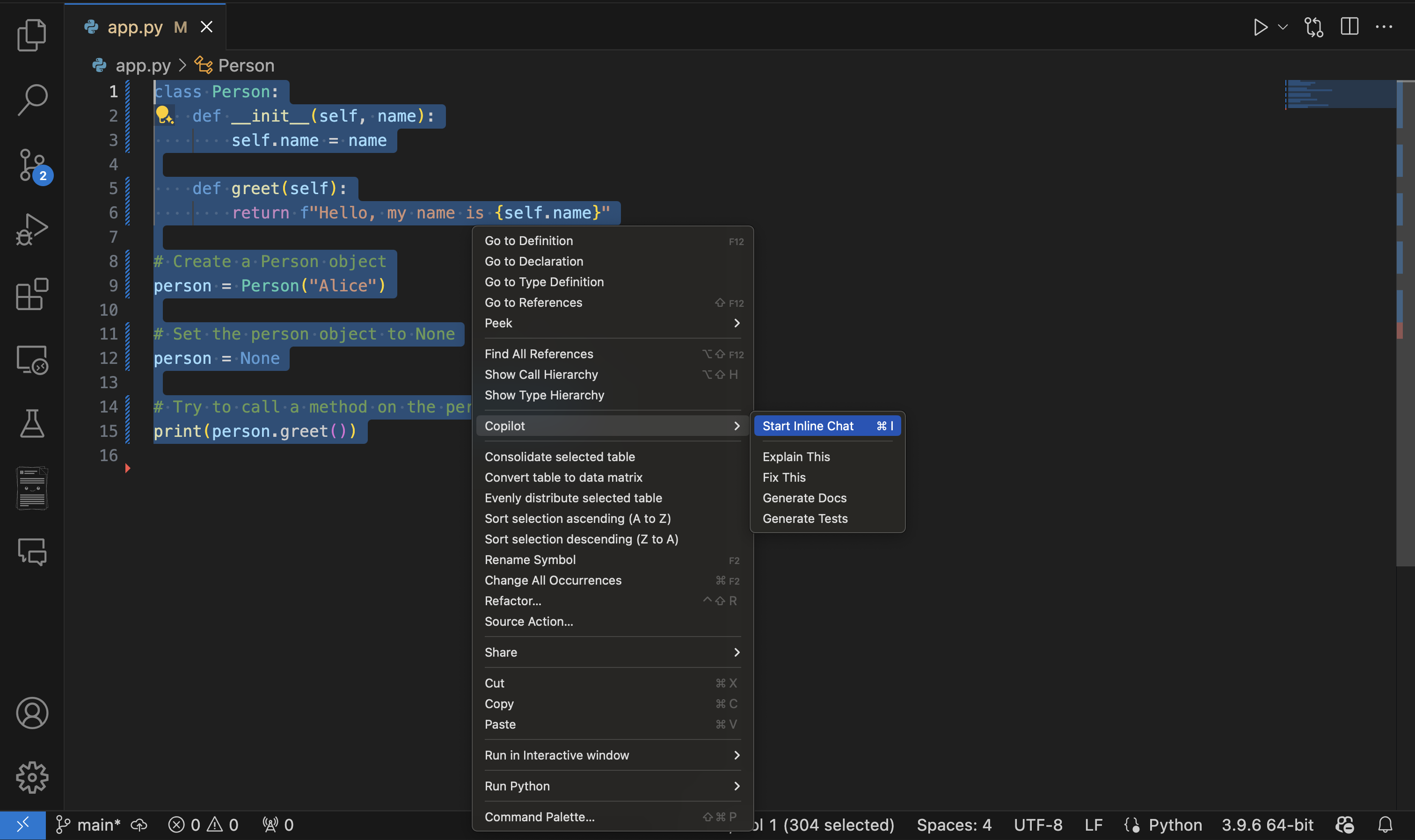
Debugging assistance If you encounter errors in your code, Copilot Chat can be valuable in analyzing error messages and suggesting potential fixes. It can help identify logical errors and provide step-by-step explanations of problematic sections of code. One way to achieve this result is by using Copilot inline-chat by highlighting the piece of code containing the error, right clicking and selecting Copilot, then inline-chat.
For example, you might ask, "I'm getting a
NullReferenceExceptionin this method. Can you help me debug it?"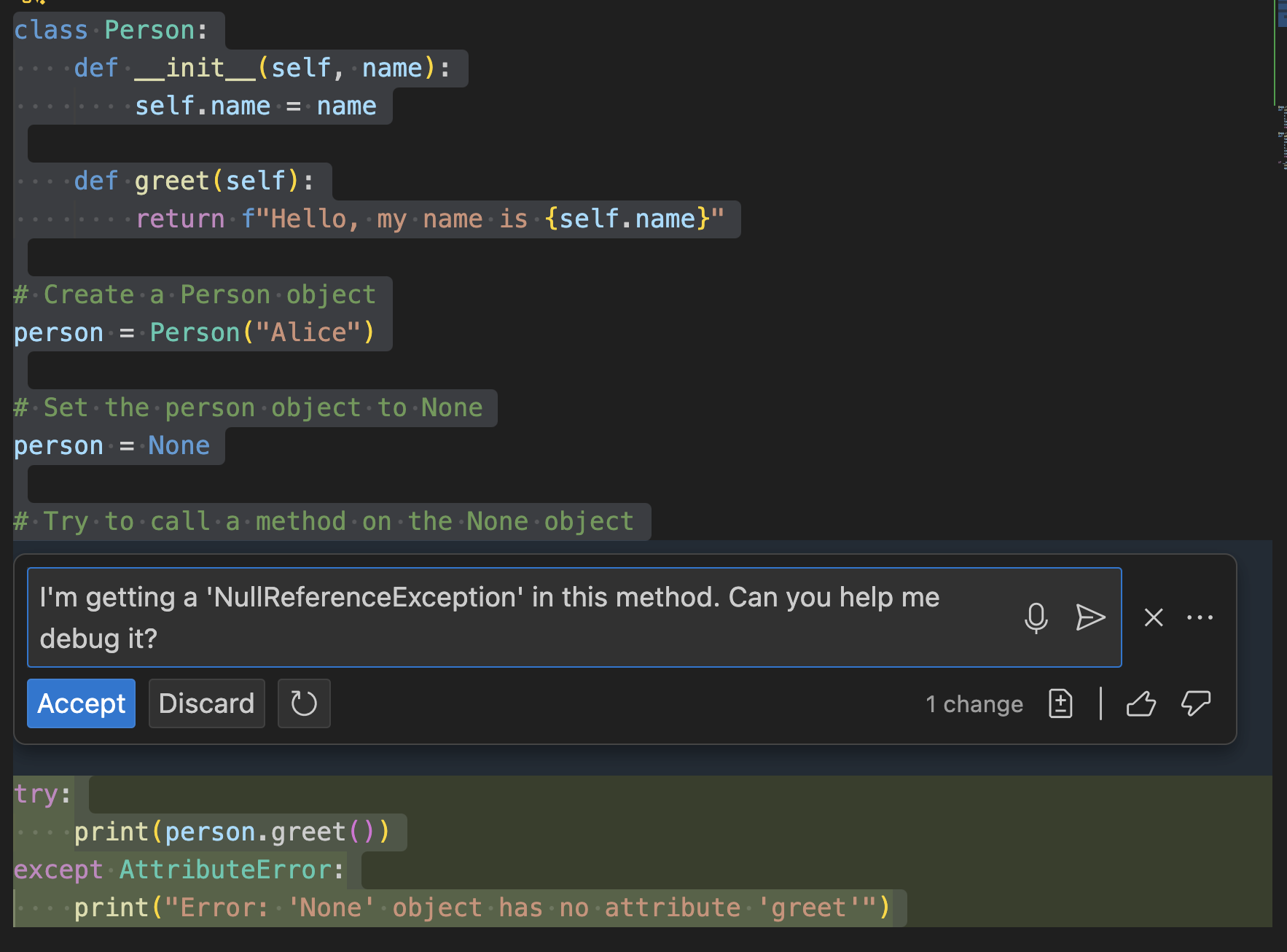
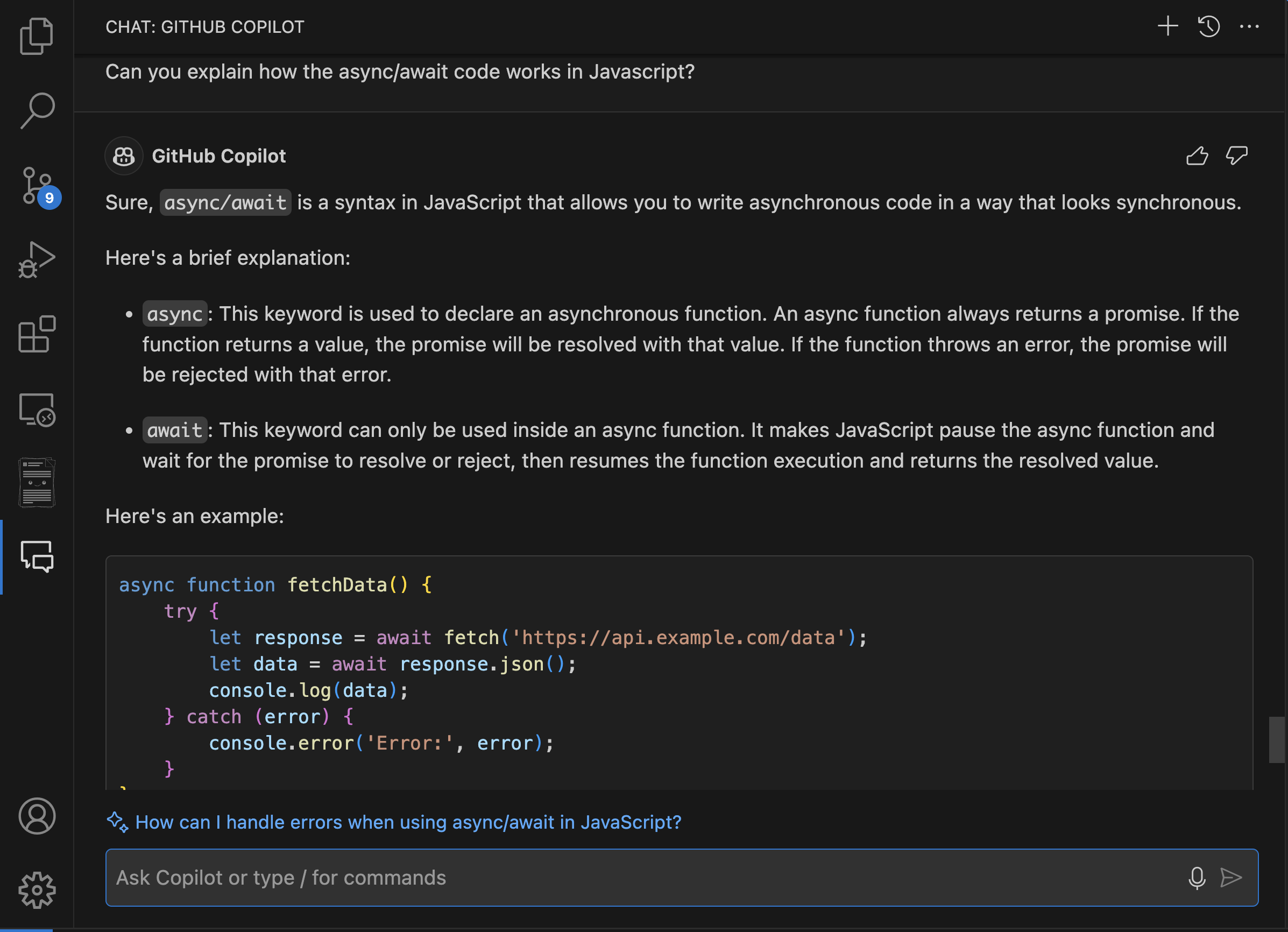
Code explanations Copilot Chat can also be used to better understand complex code snippets. It can break down code into simpler terms, explain the purpose and functionality of unfamiliar code, and offer insights into best practices and potential optimizations. For example, you could ask: - "Can you explain how this async/await code works in Python?"
How to improve GitHub Copilot Chat responses
You can significantly improve the quality and relevance of GitHub Copilot Chat's responses with certain key features. Let's dive into them.
Scope referencing
To enhance the accuracy and relevance of the responses provided by GitHub Copilot Chat, it’s important to properly scope your questions using references. Here’s how you can do that:
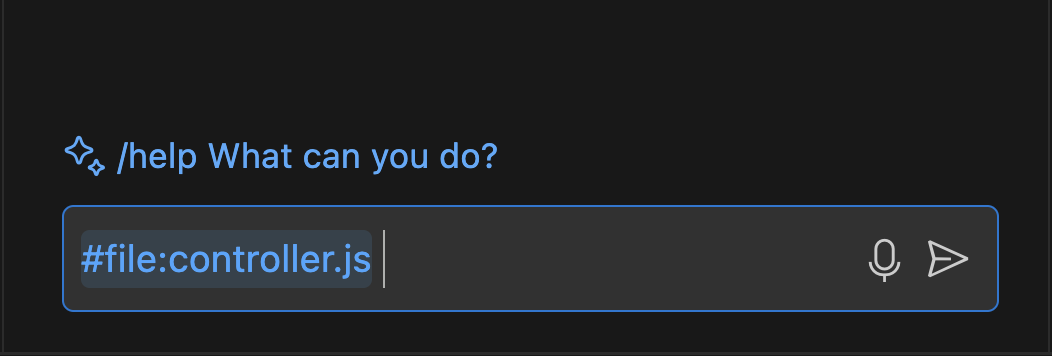
File references: You can specify a particular file in your question by adding a
#file:before the file name.For example, if you’re working with a file named
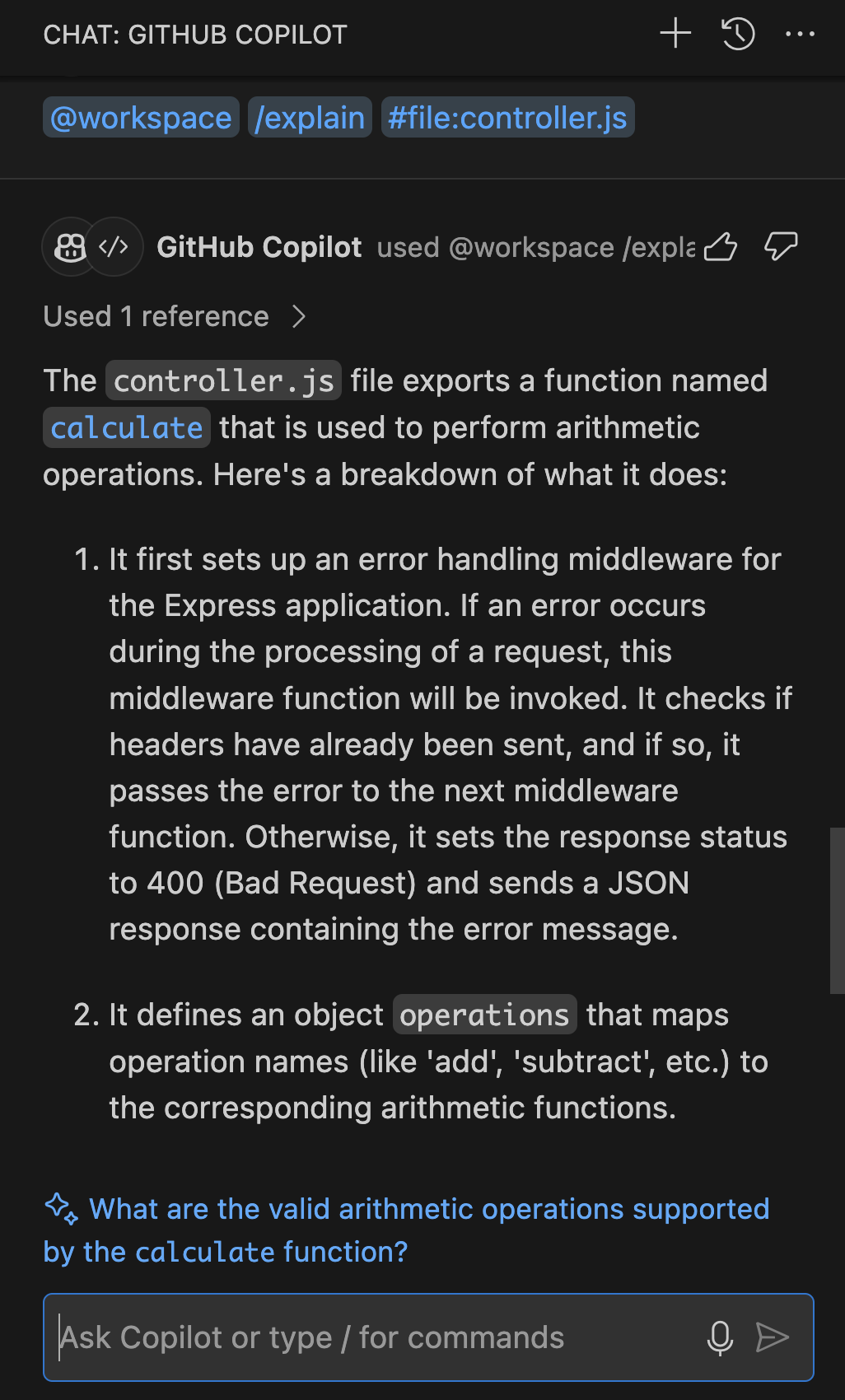
controller.js, you can use the #file command to select it and reference it directly in your question as#file:controller.js. This feature tells Copilot Chat to focus on the contents of that file when generating a response.Environment References: You can reference the entire solution or workspace by using
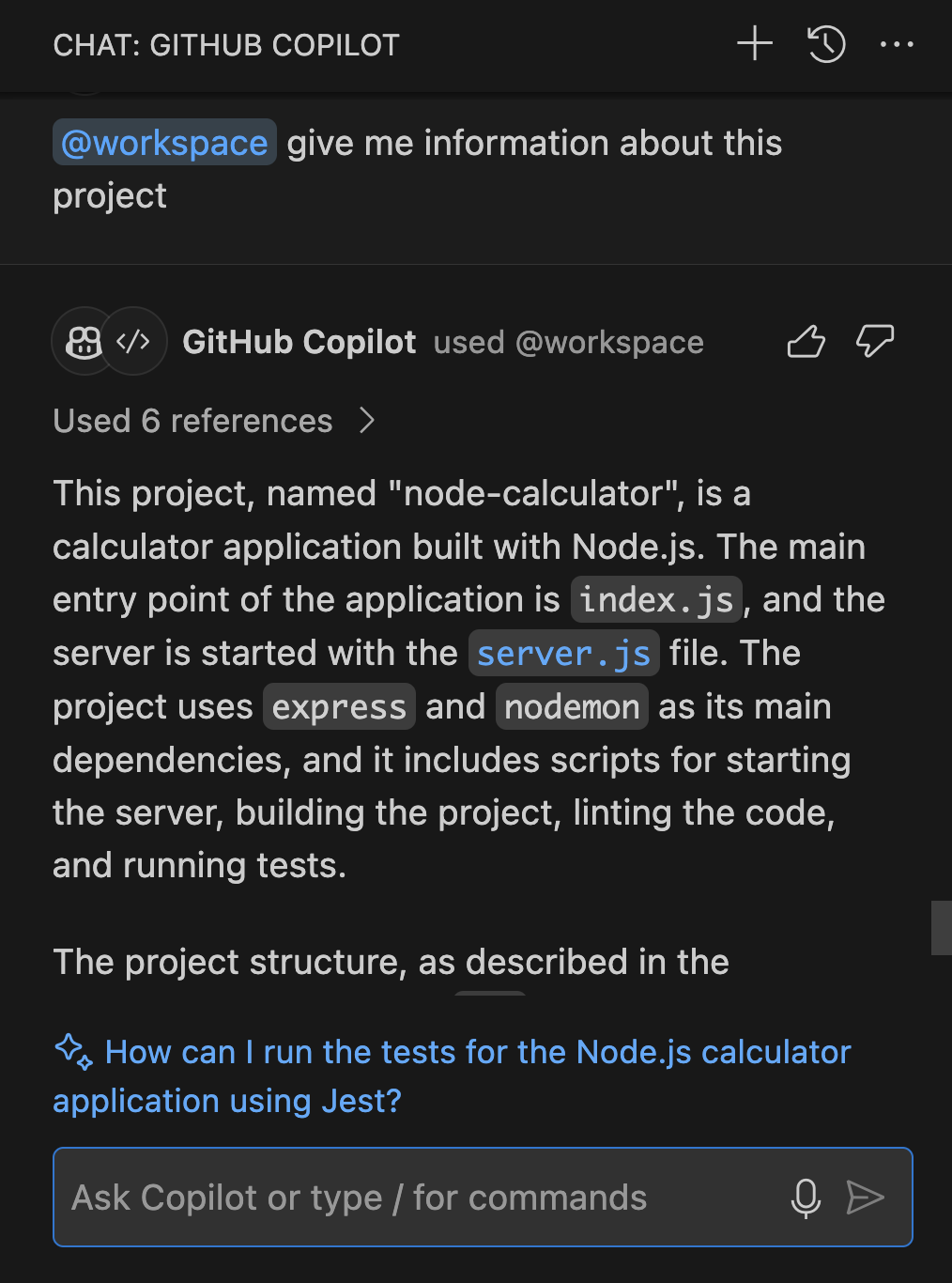
@workspace. This feature allows Copilot Chat to consider the broader context of the projects and configurations that are currently open in your Visual Studio IDE. For instance, asking "@workspace where is the calculate function?" prompts Copilot to consider the entire solution to find the most relevant information.
Slash commands
Slash commands in GitHub Copilot Chat allow you to quickly specify the intent of your query. This can significantly improve the quality of the responses you receive by making your requests more focused. Here are some commonly used slash commands:
/doc: Adds comments to the specified or selected code. For example, you can type
/docfollowed by the code you want to document, and Copilot generates appropriate comments./explain: Provides explanations for selected code. This command is useful when you need to understand what a particular piece of code does. For example,
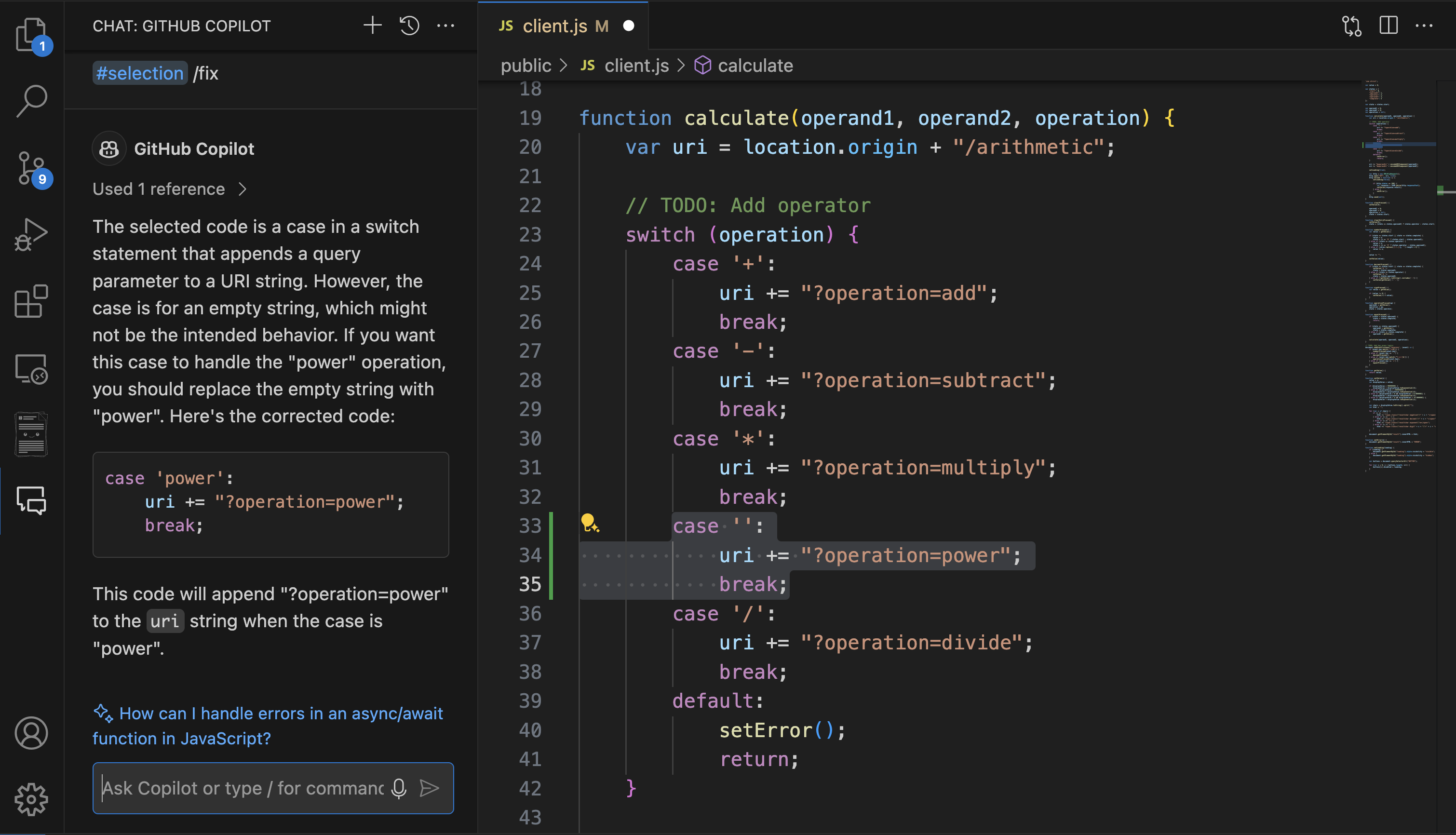
/explain the #file:controller.jsgives you a detailed explanation of that file./fix: Proposes fixes for problems in the selected code. If you're facing issues, you can highlight the problematic section and use
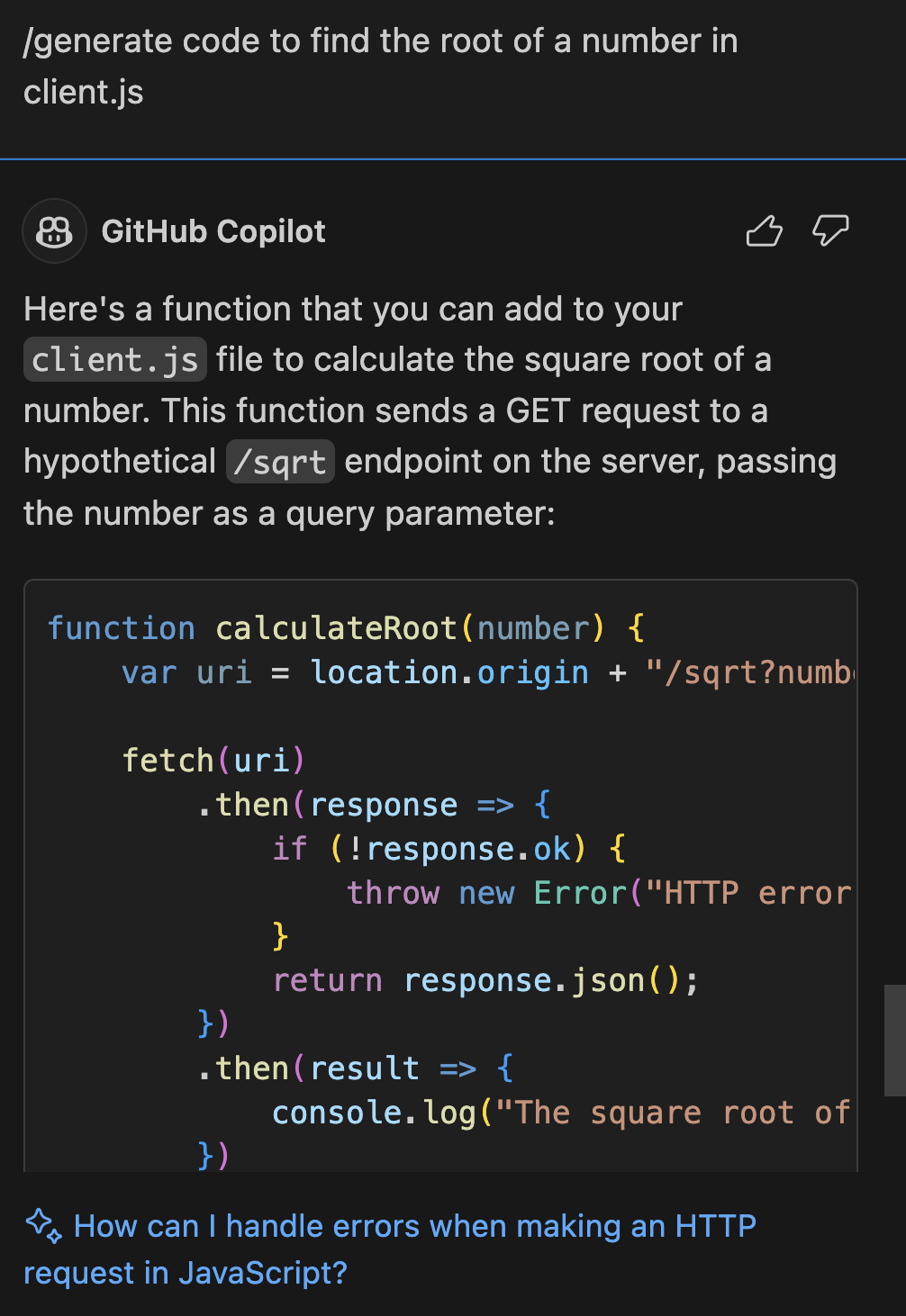
/fixto receive suggestions for resolving the issue./generate: Helps in generating new code based on your requirements. For example,
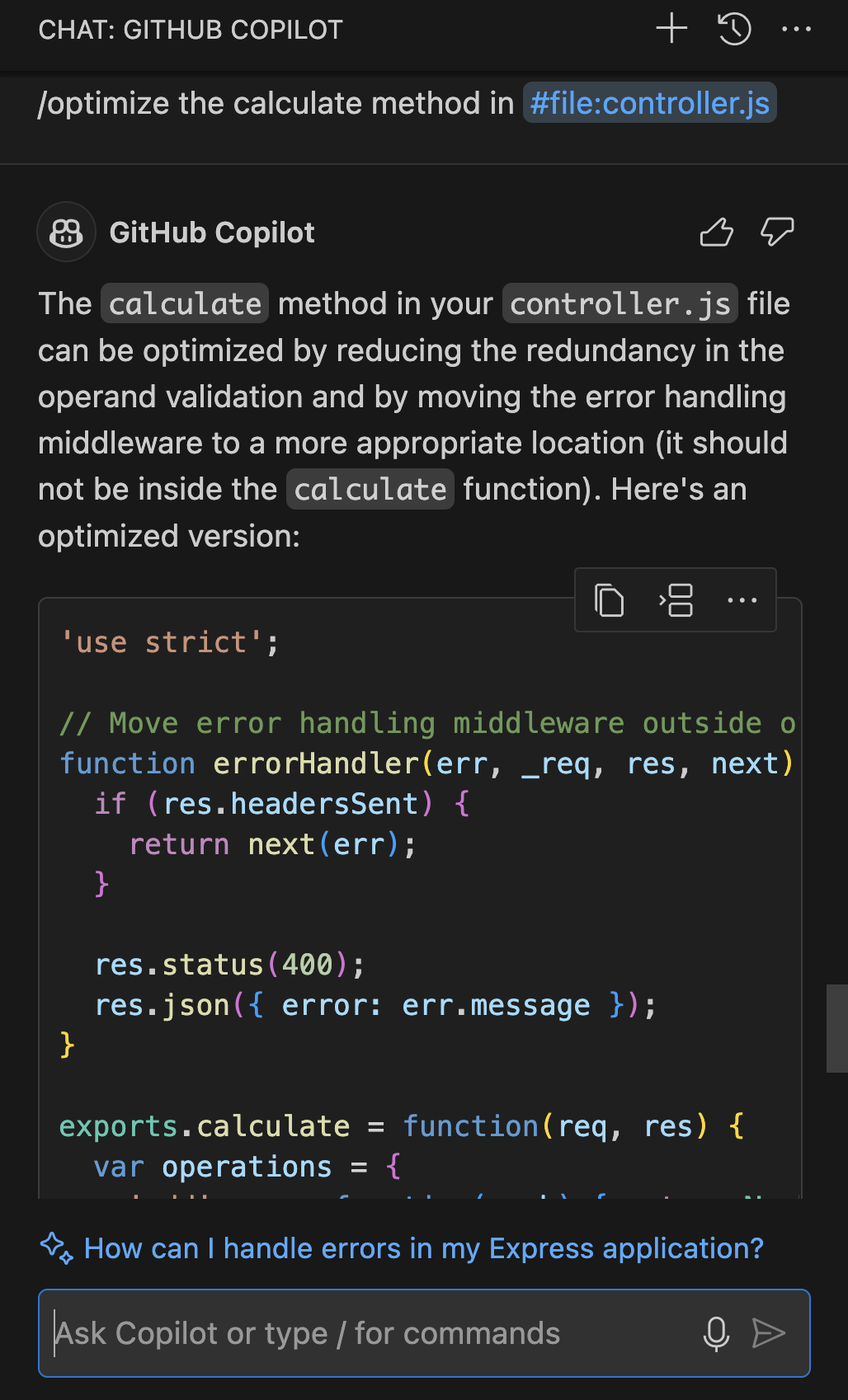
/generate code to find the root of a number in client.jscreates a function to perform the task./optimize: Analyzes and suggests improvements to the running time or efficiency of the selected code. For instance,
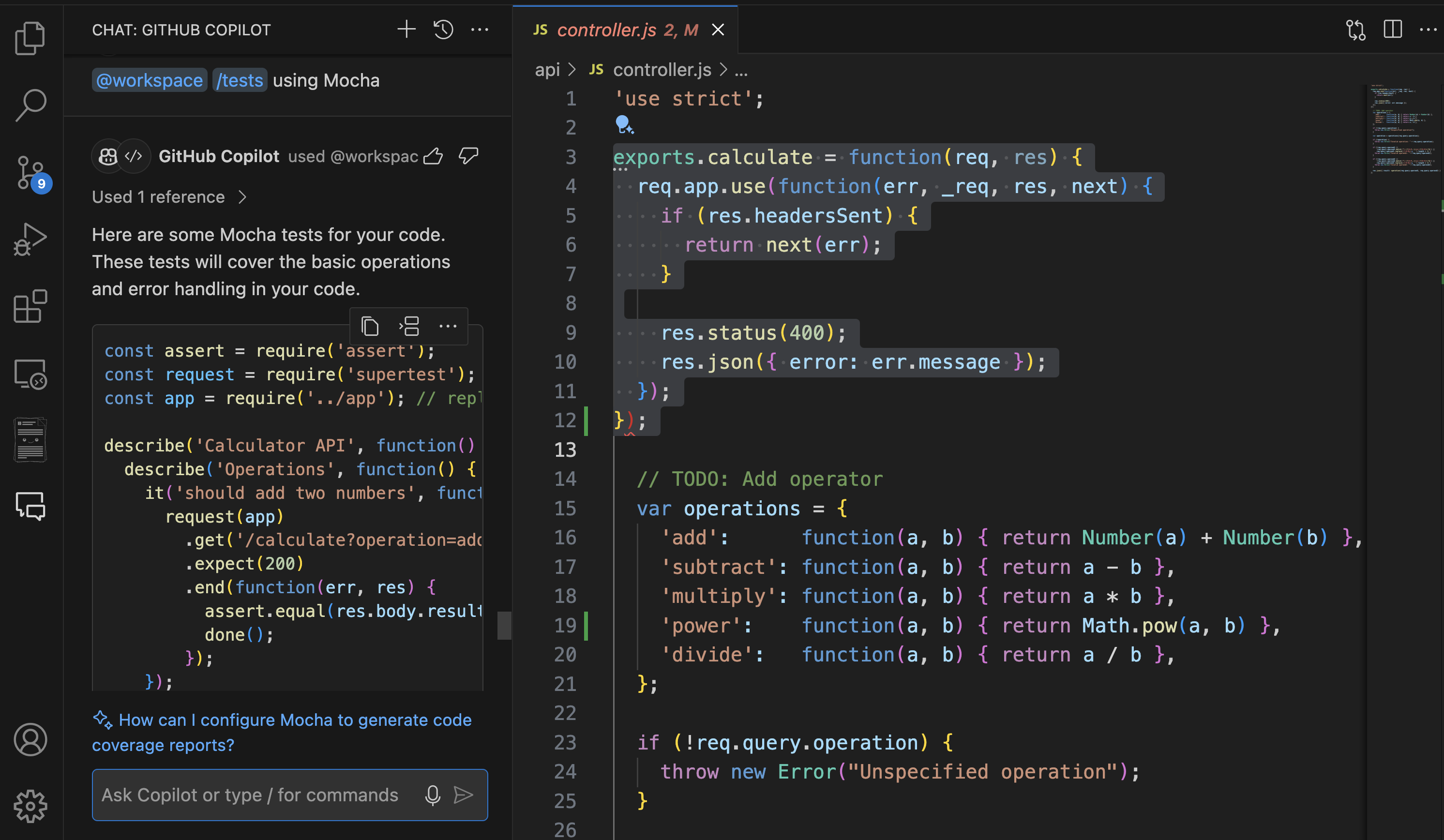
/optimize thecalculatemethod in controller.jsfocuses on enhancing the performance of that specific method./tests: Automatically creates unit tests for the selected code. You can simply highlight the code and use
/tests using Mochato generate tests.
Model selection and premium features
GitHub Copilot Chat offers different AI models to optimize your development workflow. Some environments provide model selection options that let you choose between different capability levels based on your specific needs:
Standard models (GPT-4o):
- Provide fast, reliable responses for most development tasks
- Consume 1 PRU per request
- Ideal for routine coding assistance, code explanations, and basic debugging
- Examples: Simple function generation, syntax help, basic refactoring suggestions
Premium models (o1-preview, o1-mini):
- Offer enhanced reasoning capabilities for complex problems
- Consume 2 PRUs per request (double the standard rate)
- Better suited for sophisticated analysis, complex algorithms, and architectural decisions
- Examples: Advanced debugging of multi-threaded code, complex algorithm design, security analysis
When working on challenging problems that require deep reasoning, premium models can provide more thorough analysis and comprehensive solutions. However, consider your PRU usage when selecting models for different types of tasks.
Note
Using premium models (o1-preview, o1-mini) consumes 2 PRUs instead of 1 for the same request. Monitor your monthly allowances and choose the appropriate model based on task complexity. For current details on PRU consumption and limits, refer to the Requests in GitHub Copilot documentation.
Copilot agents
GitHub Copilot agents are custom tools that you can build and integrate with GitHub Copilot Chat to provide additional functionalities tailored to your specific needs. In addition to slash commands, you can use specific agents within Copilot Chat in your IDE to handle different tasks:
@workspace: This agent allows you to extend the context of whatever questions you ask Copilot to the whole project. It is useful for getting code generated that would fit in your project right away, using information from your whole project. It can also be utilized for getting answers about your whole codebase.
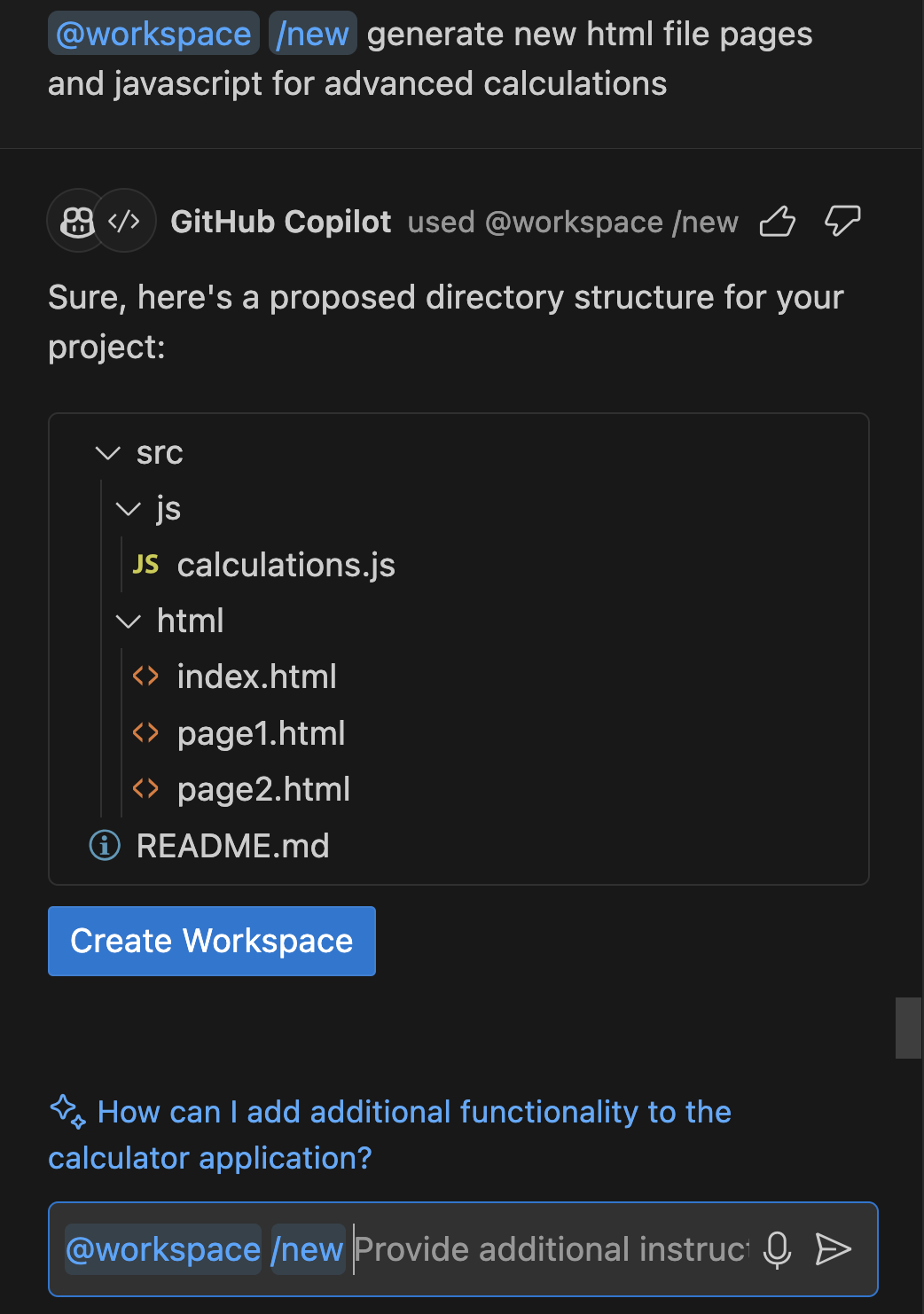
You can also use the “@workspace /new” smart action, which allows you to generate a completely new project from scratch based on your requirements. For example, “@workspace /new generate new html file pages and JavaScript for advanced calculations“
Click on “Create Workspace” to proceed with code generation and just like that you have your new project with the code you requested.
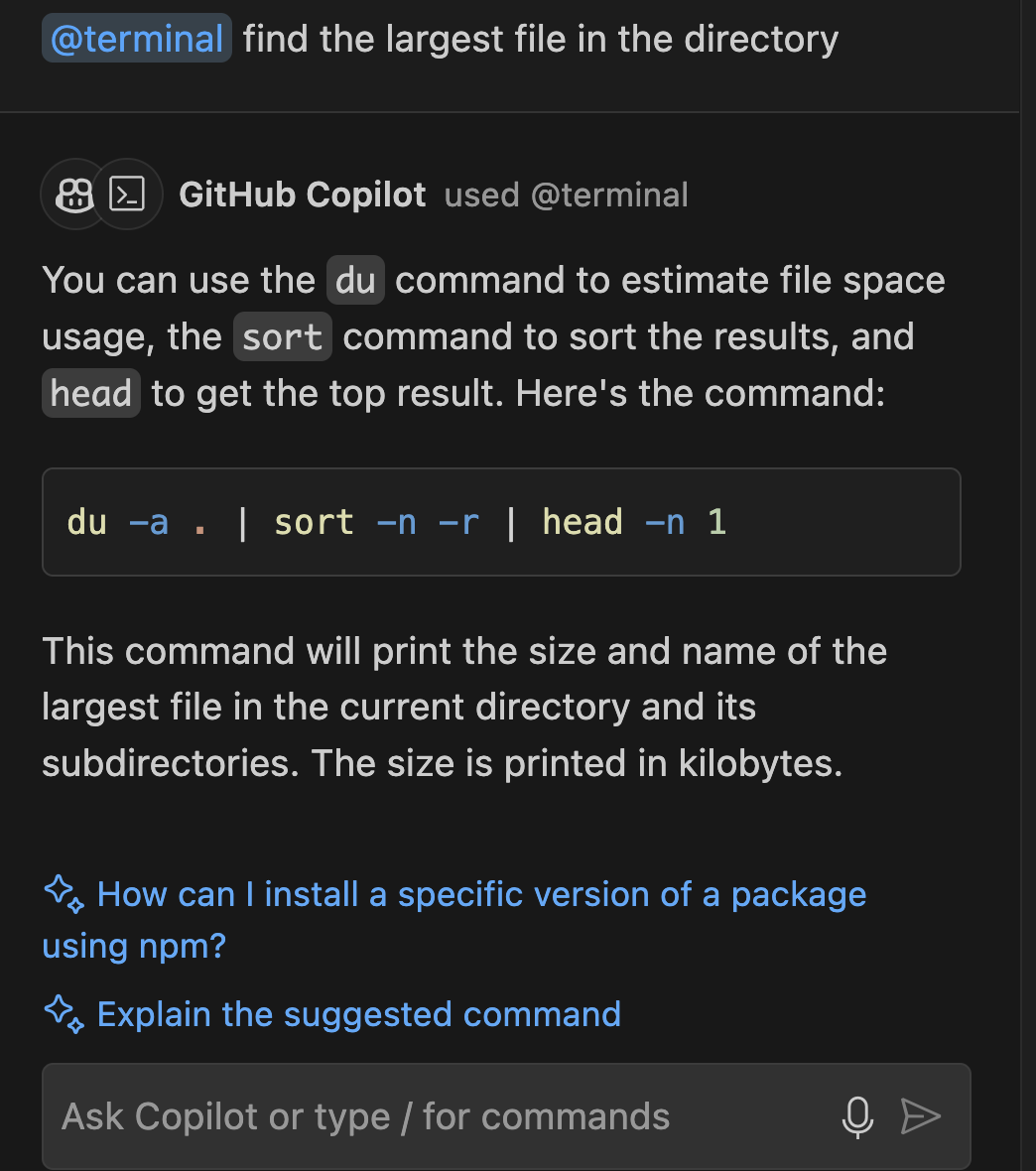
@terminal: This agent is useful for command-line related questions. For example, you could ask it to find the largest file in a directory or explain the last command you ran.
@vscode: Use this agent to ask questions related to Visual Studio Code, such as how to debug or change settings within the IDE.
By effectively utilizing these tools and techniques, you can significantly improve the quality of responses you receive from GitHub Copilot Chat, making your coding experience more efficient and productive.
Note
Advanced agents like @workspace and complex operations may consume more Premium Request Units (PRUs). Simple queries typically use 1 PRU, while complex workspace analysis or project generation can use 2-5 PRUs. For current details on PRU consumption, monthly allowances, and rate limits, refer to the Requests in GitHub Copilot documentation.
Sharing feedback on GitHub Copilot Chat
Most IDEs with Copilot Chat integration have built-in feedback mechanisms. For example, in Visual Studio Code, you can find feedback options at the beginning of GitHub Copilot Chat's suggestions. Hover over a suggestion, and you should see "thumbs up" and "thumbs down" buttons.
Click on the thumbs up to rate a suggestion as helpful.
Click on thumbs down to rate an unhelpful one.