How to validate the Microsoft signature
This article shows you how to validate the Microsoft signature for a submission.
There are a couple cases where you might want to validate the Microsoft signature for a submission:
- You aren’t sure if a driver has been signed by Microsoft or not, and you want to check.
- You have two drivers, and you need to determine which one was signed by attestation and which one was signed after submission of HLK/HCK results to the dashboard.
Step 1: Download signed driver files
In this step, you'll download the signed files you need to validate the Microsoft signature.
Note
The driver submission folder is located in the package files. These files are signed by Microsoft. The partner doesn't have to sign the returned payload. Microsoft always returns a .cat file with an approved submission. If a partner includes its own .cat file. Microsoft discards it and returns its own signed .cat file. In the past, Microsoft only signed the .cat file. Starting with Windows 10, Microsoft now signs all of the portable executables in the returned payload. For example, the .dll file is also signed by Microsoft:
To download the driver signed files:
- Find the hardware submission that contains the drivers that you want to download signed files for.
- Select the Private Product ID to open the driver details.
- On the driver details page, under Packages and signing properties, select More.
- Select Download signed files.
Step 2: Check the Enhanced Key Usage (EKU)
Now you that you've downloaded the signed files, you can validate the Microsoft signature by checking the EKU. The EKU belongs to the certificate that Microsoft uses to sign the submission.
To check the EKU:
Select and hold (or right-click) the .cat file.
Select Properties, and then select the Digital Signatures tab.
Select the name of the certificate, and then select Details.
On the Details tab, select Enhanced Key Usage. There, you will see the EKUs and corresponding OID values for the certificate. In this case, the Windows Hardware Driver Verification OID ends with a 5, which means that driver hasn't been signed by attestation:
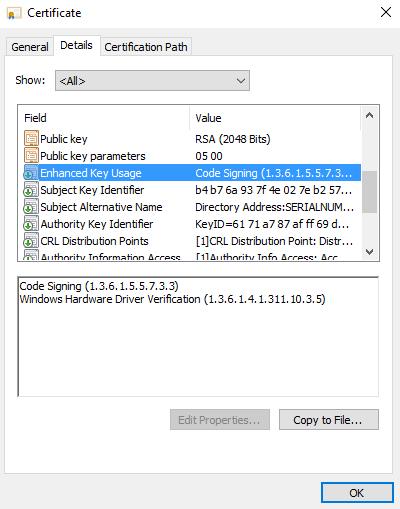
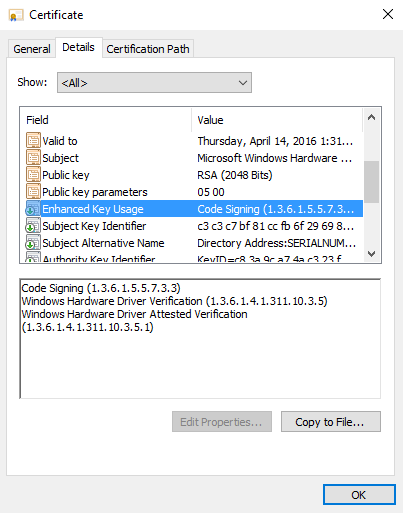
If the driver had been signed by attestation, then the OID would end with a 1:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for