Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This tutorial describes how to back up multiple virtual machines by using the Azure portal .
Azure stores backup data in a Recovery Services vault, which is accessible from the Settings menu of most services. This integration simplifies the backup process. However, managing each database or virtual machine separately can be tedious. To streamline backups for multiple virtual machines (for department or location), you can create a backup policy and apply it to the relevant machines.
Sign in to the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Note
The functionality described in the following sections can also be accessed via Backup center. Backup center is a single unified management experience in Azure. It enables enterprises to govern, monitor, operate, and analyze backups at scale. With this solution, you can perform most of the key backup management operations without being limited to the scope of an individual vault.
Create a Recovery Services vault
A Recovery Services vault is a management entity that stores recovery points that are created over time, and it provides an interface to perform backup-related operations. These operations include taking on-demand backups, performing restores, and creating backup policies.
To create a Recovery Services vault:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Search for Business Continuity Center, and then go to the Business Continuity Center dashboard.
On the Vault pane, select +Vault.
Select Recovery Services vault > Continue.
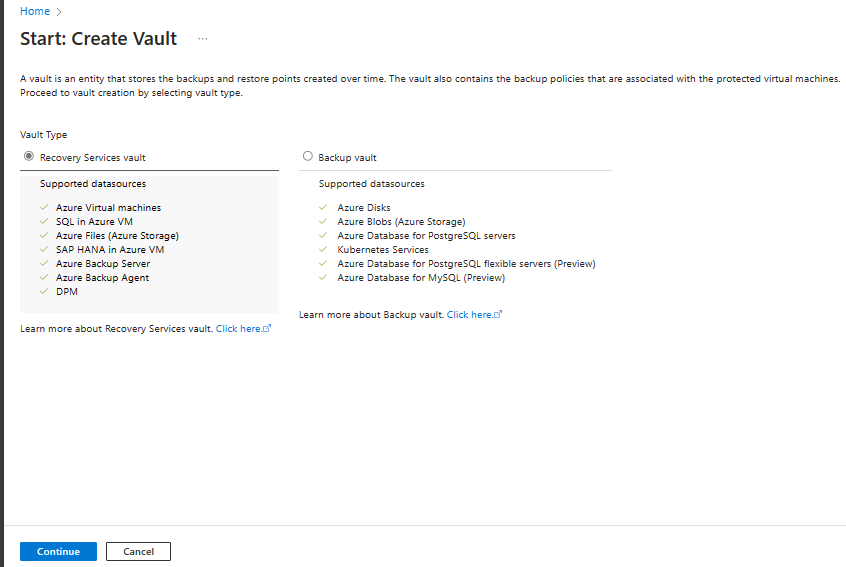
On the Recovery Services vault pane, enter the following values:
Subscription: Select the subscription to use. If you're a member of only one subscription, you'll see that name. If you're not sure which subscription to use, use the default subscription. There are multiple choices only if your work or school account is associated with more than one Azure subscription.
Resource group: Use an existing resource group or create a new one. To view a list of available resource groups in your subscription, select Use existing, and then select a resource in the dropdown list. To create a new resource group, select Create new, and then enter the name. For more information about resource groups, see Azure Resource Manager overview.
Vault name: Enter a friendly name to identify the vault. The name must be unique to the Azure subscription. Specify a name that has at least 2 but not more than 50 characters. The name must start with a letter and consist only of letters, numbers, and hyphens.
Region: Select the geographic region for the vault. For you to create a vault to help protect any data source, the vault must be in the same region as the data source.
Important
If you're not sure of the location of your data source, close the window. Go to the list of your resources in the portal. If you have data sources in multiple regions, create a Recovery Services vault for each region. Create the vault in the first location before you create a vault in another location. There's no need to specify storage accounts to store the backup data. The Recovery Services vault and Azure Backup handle that automatically.
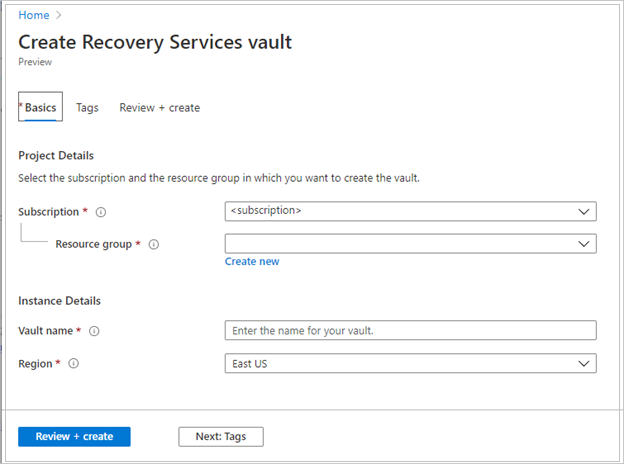
After providing the values, select Review + create.
To finish creating the Recovery Services vault, select Create.
It can take a while to create the Recovery Services vault. Monitor the status notifications in the Notifications area at the upper right. After the vault is created, it appears in the list of Recovery Services vaults. If the vault doesn't appear, select Refresh.
Note
Azure Backup now supports immutable vaults that help you ensure that recovery points once created can't be deleted before their expiry as per the backup policy. You can make the immutability irreversible for maximum protection to your backup data from various threats, including ransomware attacks and malicious actors. Learn more.
When you create a Recovery Services vault, by default the vault has geo-redundant storage. To provide data resiliency, geo-redundant storage replicates the data multiple times across two Azure regions.
Set backup policy to protect VMs
After the Recovery Services vault creation is complete, configure the vault for the data type backup and set the backup policy. The policy defines the schedule for recovery points and their retention period. In this tutorial, let's assume you have a business (a sports complex with a hotel, stadium, and restaurants) that requires virtual machine data protection.
To set a backup policy to your Azure VMs, follow these steps:
Go to Backup center and click +Backup from the Overview tab.
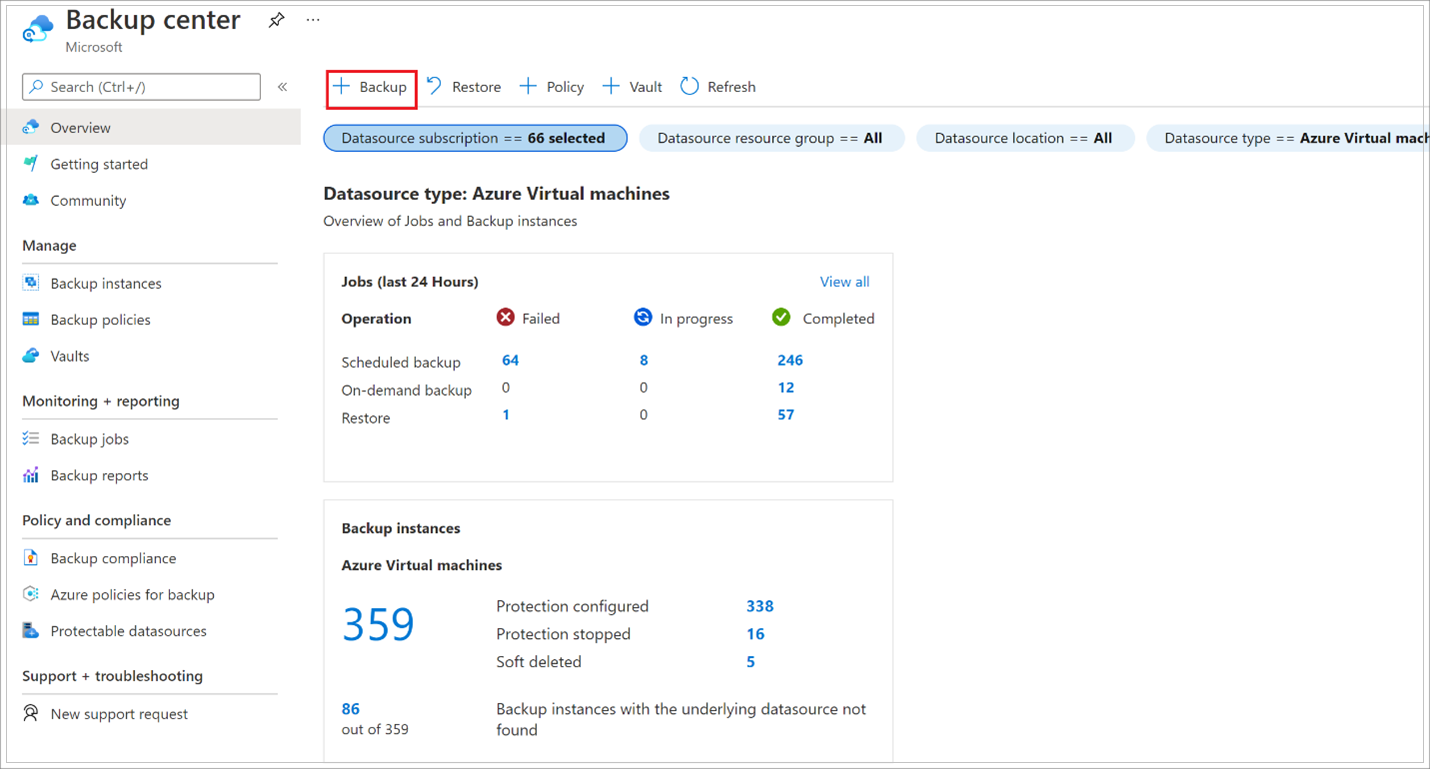
On the Start: Configure Backup blade, select Azure Virtual machines, as the Datasource type, and then select the vault you have created. Then click Continue.
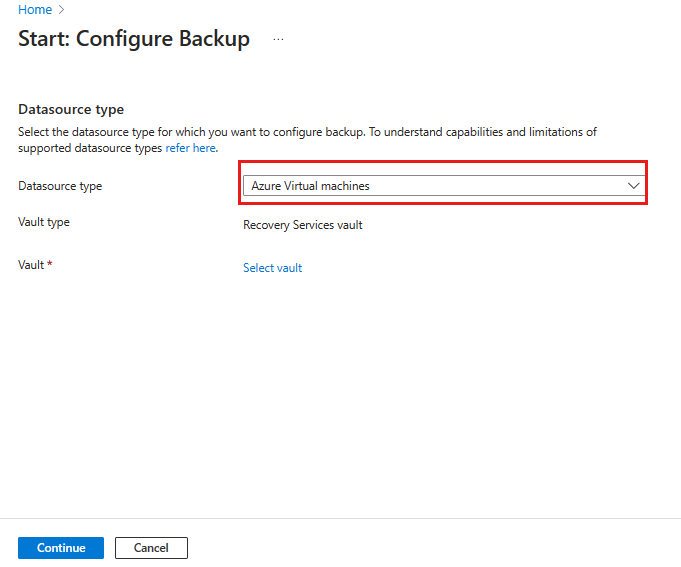
Assign a Backup policy.
The default policy backs up the VM once a day. The daily backups are retained for 30 days. Instant recovery snapshots are retained for two days.
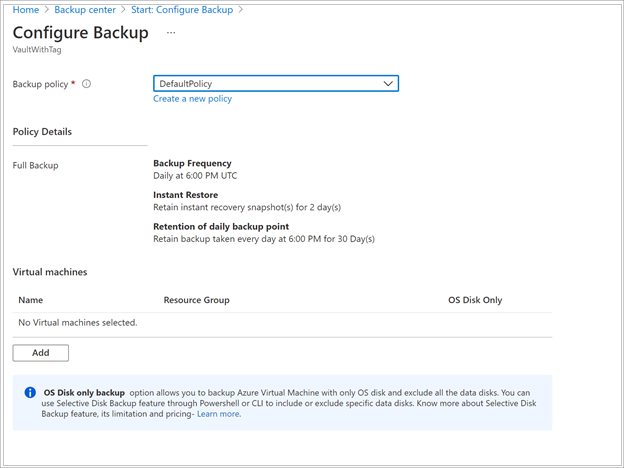
If you don't want to use the default policy, select Create New, and create a custom policy as described in the next procedure.
Under Virtual Machines, select Add.

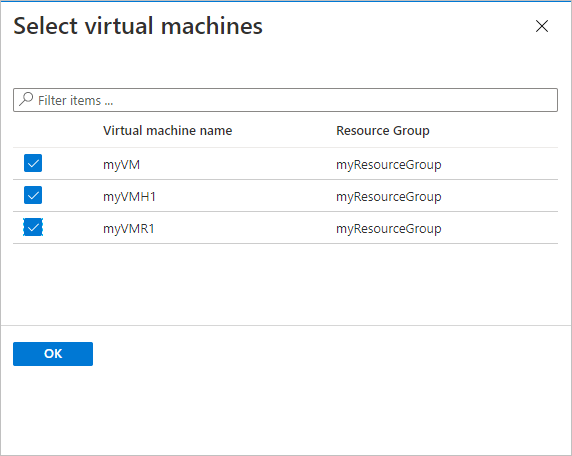
The Select virtual machines blade will open. Select the VMs you want to back up using the policy. Then select OK.
The selected VMs are validated.
You can only select VMs in the same region as the vault.
VMs can only be backed up in a single vault.
Note
All the VMs in the same region and subscription as that of the vault are available to configure backup. When configuring backup, you can browse to the virtual machine name and its resource group, even though you don’t have the required permission on those VMs. If your VM is in soft deleted state, then it won't be visible in this list. If you need to re-protect the VM, then you need to wait for the soft delete period to expire or undelete the VM from the soft deleted list. For more information, see the soft delete for VMs article.
In Backup, select Enable backup. This deploys the policy to the vault and to the VMs, and installs the backup extension on the VM agent running on the Azure VM.
After enabling backup:
- The Backup service installs the backup extension whether or not the VM is running.
- An initial backup will run in accordance with your backup schedule.
- When backups run, note that:
- A VM that's running has the greatest chance for capturing an application-consistent recovery point.
- However, even if the VM is turned off, it's backed up. Such a VM is known as an offline VM. In this case, the recovery point will be crash-consistent.
- Explicit outbound connectivity isn't required to allow backup of Azure VMs.
Note
You can also set Enhanced policy to back up Azure VMs multiple times a day. Learn about Enhanced policy.
Initial backup
You've enabled backup for the Recovery Services vaults, but an initial backup hasn't been created. It's a disaster recovery best practice to trigger the first backup, so that your data is protected.
The initial backup will run in accordance with the schedule, but you can run it immediately as follows:
- Go to Backup center and select the Backup Instances menu item.
- Select Azure Virtual machines as the Datasource type. Then search for the VM that you have configured for backup.
- Right-click the relevant row or select the more icon (…), and then click Backup Now.
- In Backup Now, use the calendar control to select the last day that the recovery point should be retained. Then select OK.
- Monitor the portal notifications. To monitor the job progress, go to Backup center > Backup Jobs and filter the list for In progress jobs. Depending on the size of your VM, creating the initial backup may take a while.
Clean up resources
If you plan to continue on to work with subsequent tutorials, don't clean up the resources created in this tutorial. If you don't plan to continue, then delete all resources created by this tutorial in the Azure portal by following these steps:
On the myRecoveryServicesVault dashboard, select 3 under Backup Items to open the Backup Items menu.
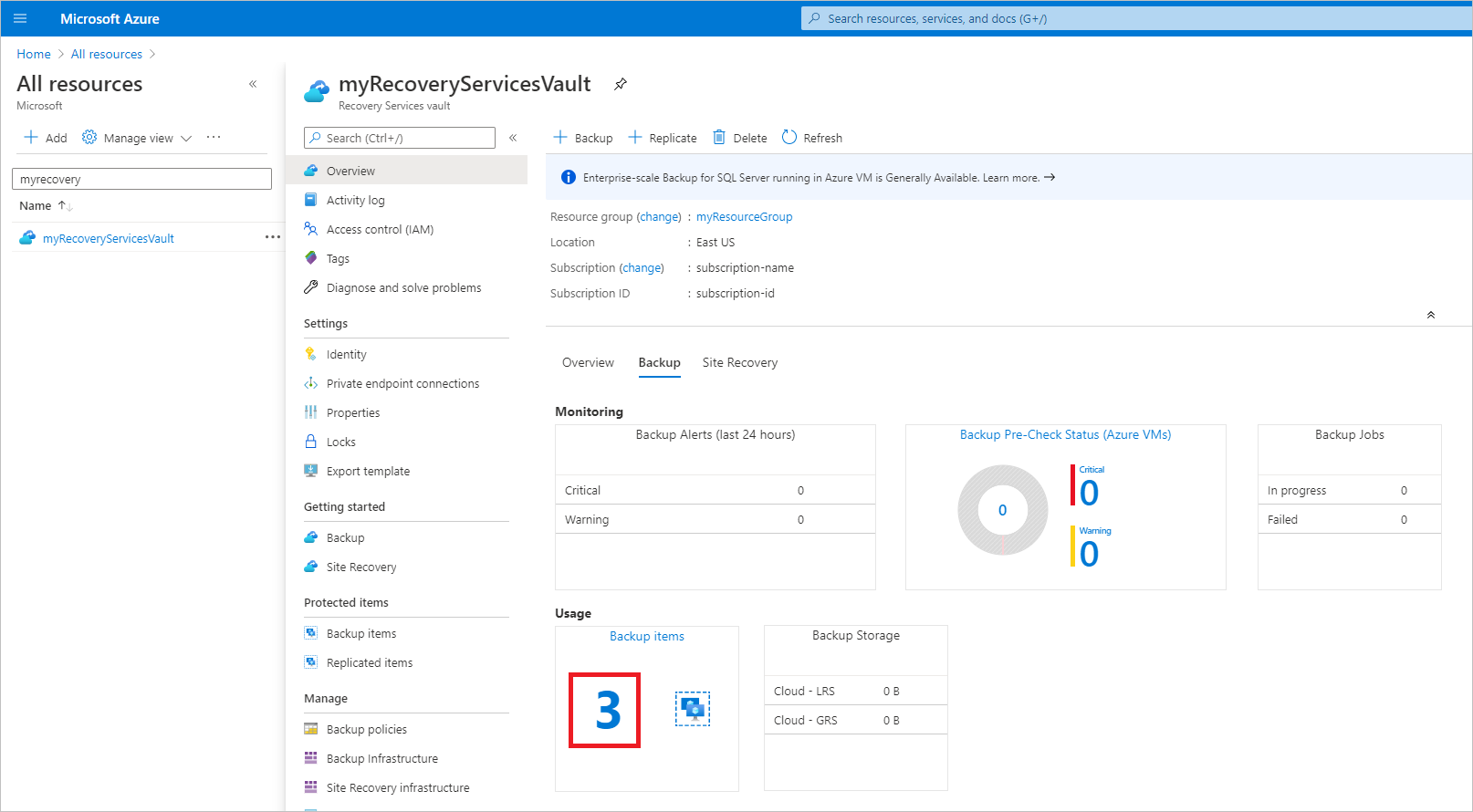
On the Backup Items menu, select Azure Virtual Machine to open the list of virtual machines associated with the vault.
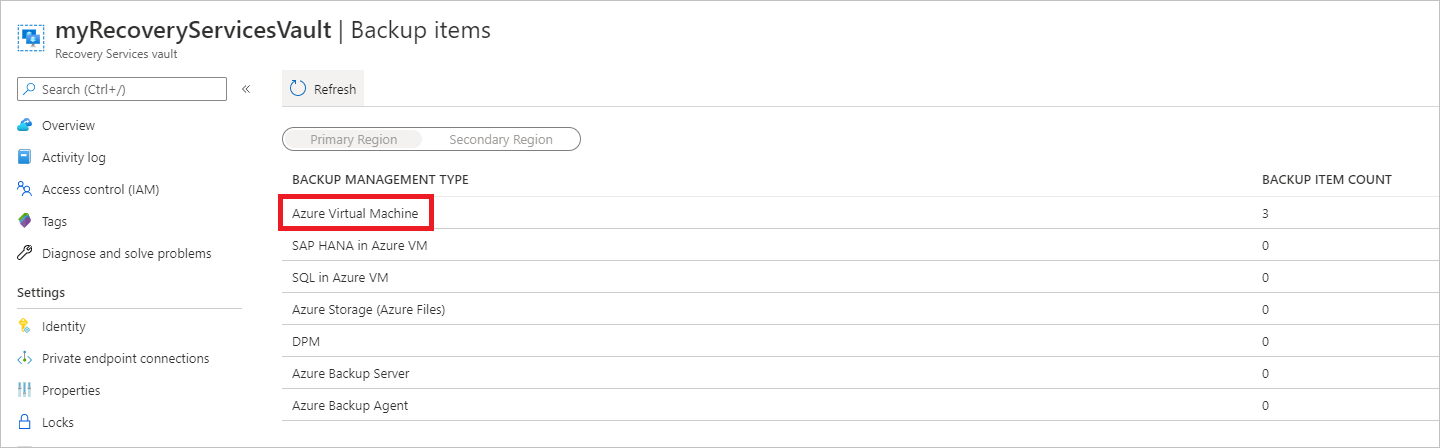
The Backup Items list opens.
In the Backup Items menu, select the ellipsis to open the Context menu.
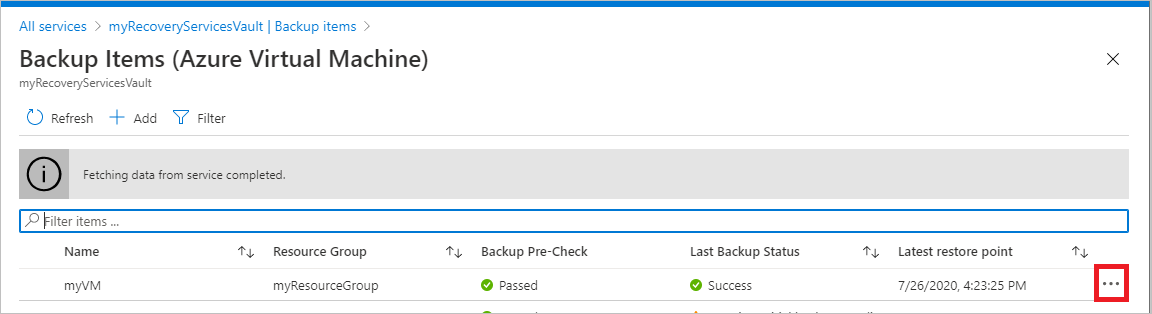
On the context menu, select Stop backup to open Stop Backup menu.
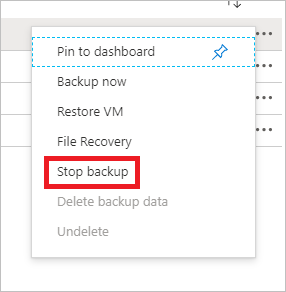
In the Stop Backup menu, select the upper drop-down menu and choose Delete Backup Data.
In the Type the name of the Backup item dialog, type myVM.
Once the backup item is verified (a check mark appears), Stop backup button is enabled. Select Stop Backup to stop the policy and delete the restore points.
Note
Deleted items are retained in the soft delete state for 14 days. Only after that period can the vault be deleted. For more information, see Delete an Azure Backup Recovery Services vault.
When there are no more items in the vault, select Delete.
Once the vault is deleted, you'll return to the list of Recovery Services vaults.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you used the Azure portal to:
- Create a Recovery Services vault
- Set the vault to protect virtual machines
- Create a custom backup and retention policy
- Assign the policy to protect multiple virtual machines
- Trigger an on-demand back up for virtual machines
Continue to the next tutorial to restore an Azure virtual machine from disk.

