Events
17 Mar, 23 - 21 Mar, 23
Join the meetup series to build scalable AI solutions based on real-world use cases with fellow developers and experts.
Register nowThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
Requirements traceability is the ability to relate and document two or more phases of a development process, which can then be traced both forward or backward from its origin. Requirements traceability helps teams to get insights into indicators such as quality of requirements or readiness to ship the requirement. A fundamental aspect of requirements traceability is association of the requirements to test cases, bugs, and code changes.
Read the glossary to understand test report terminology.
Agile teams have characteristics including, but not limited to the following
The following sections explore traceability from Quality, Bug, and Source standpoints for Agile teams.
Link project requirements to test results for end-to-end traceability with a simple way to monitor test results. To link automated tests with requirements, see Test report.
In the results section under Tests tab of a build or release summary, select the test to be linked to requirements and choose Link.
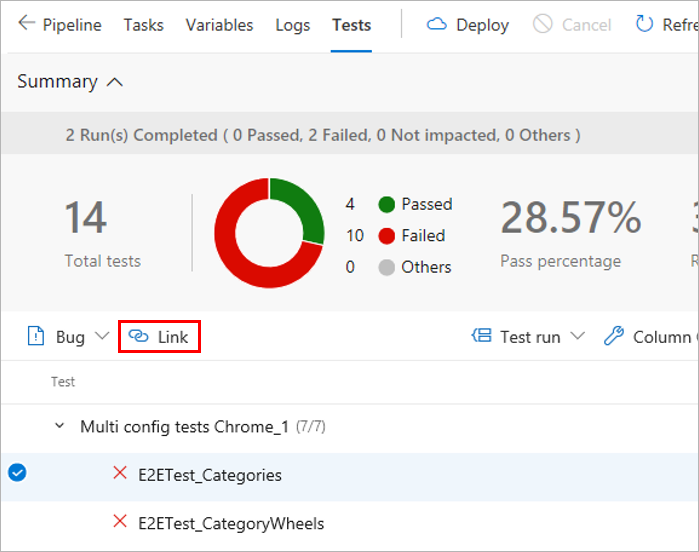
Choose a work item to be linked to the selected test in one of the following ways:

The list shows only work items belonging to the Requirements category.
Once the requirements are linked to the test results, you can view the test results grouped by requirement. Requirement is one of the many "Group by" options provided to make it easy to navigate the test results.
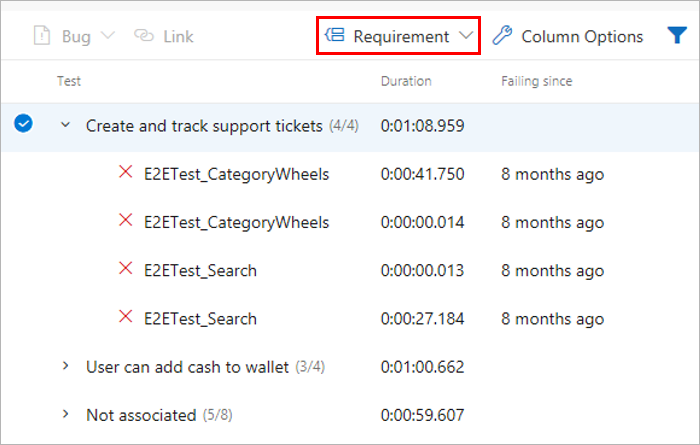
Teams often want to pin the summarized view of requirements traceability to a dashboard. Use the Requirements quality widget to do so.
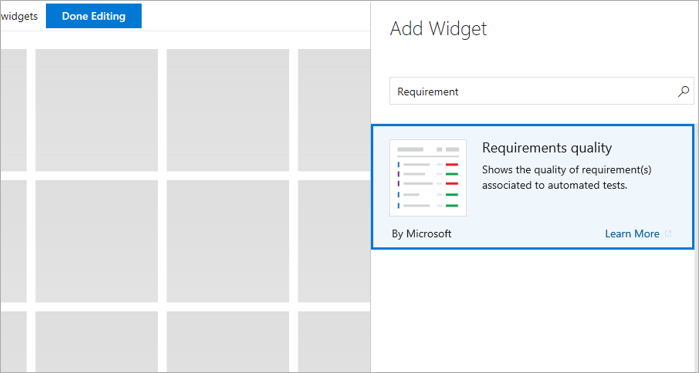
Configure the Requirements quality widget with the required options and save it.
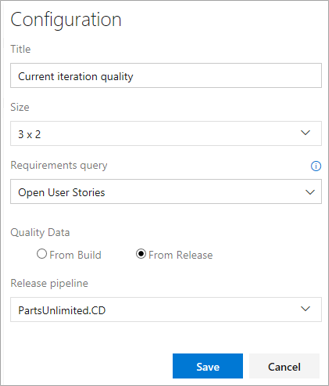
View the widget in the team's dashboard. It lists all the Requirements in scope, along with the Pass Rate for the tests and count of Failed tests. Selecting a Failed test count opens the Tests tab for the selected build or release. The widget also helps to track the requirements without any associated test.

Link project requirements to test results for end-to-end traceability with a simple way to monitor test results. To link automated tests with requirements, see Test report.
In the results section under Tests tab of a build or release summary, select the test to be linked to requirements and choose Link.

Choose a work item to be linked to the selected test in one of the following ways:

The list shows only work items belonging to the Requirements category.
Teams often want to pin the summarized view of requirements traceability to a dashboard. Use the Requirements quality widget to do so.

Configure the Requirements quality widget with the required options and save it.

View the widget in the team's dashboard. It lists all the Requirements in scope, along with the Pass Rate for the tests and count of Failed tests. Selecting a Failed test count opens the Tests tab for the selected build or release. The widget also helps to track the requirements without any associated test.

Testing gives a measure of the confidence to ship a change to users. A test failure signals an issue with the change. Failures can occur due to errors in the source under test, bad test code, environmental issues, flaky tests, and more. Bugs provide a robust way to track test failures and drive accountability in the team to take the required remedial actions. To associate bugs with test results, see Test report.
In the results section of the Tests tab, select the tests against which the bug should be created and choose Bug. Multiple test results can be mapped to a single bug, which is typically done when the reason for the failures attributes to a single cause, such as an unavailable dependent service, a database connection failure, or similar issues.

Open the work item. The bug captures the complete context of the test results including key information, such as the error message, stack trace, comments, and more.

View the bug with the test result, directly in context, within the Tests tab. The Work Items tab also lists any linked requirements for the test result.
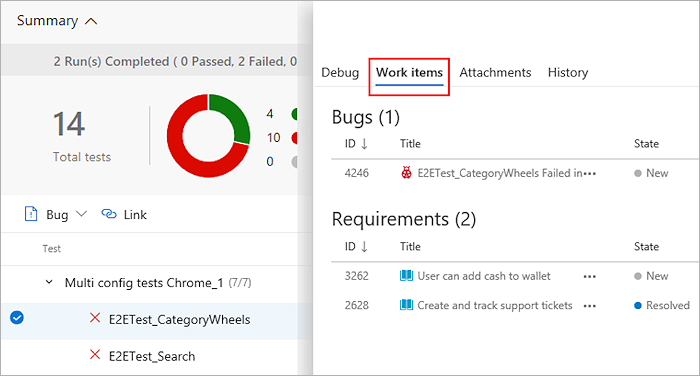
From a work item, navigate directly to the associated test results. Both the test case and the specific test result are linked to the bug.

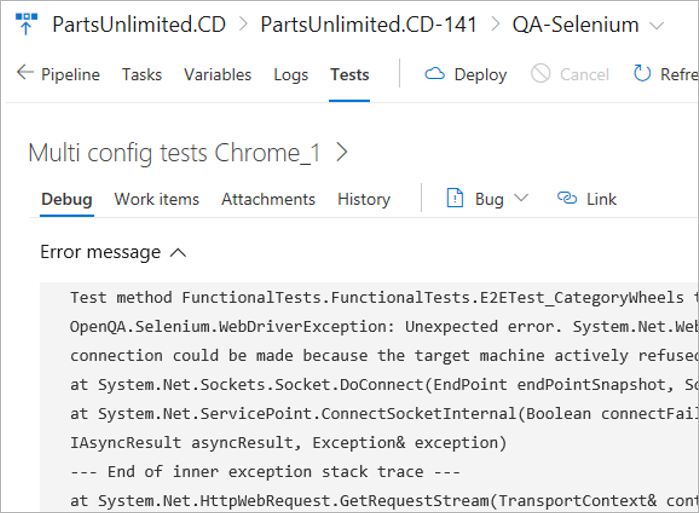
In the work item, select Test case or Test result to go directly to the Tests page for the selected build or release. You can troubleshoot the failure, update your analysis in the bug, and make the changes required to fix the issue as applicable. While both the links take you to the Tests tab, the default sections include History and Debug.
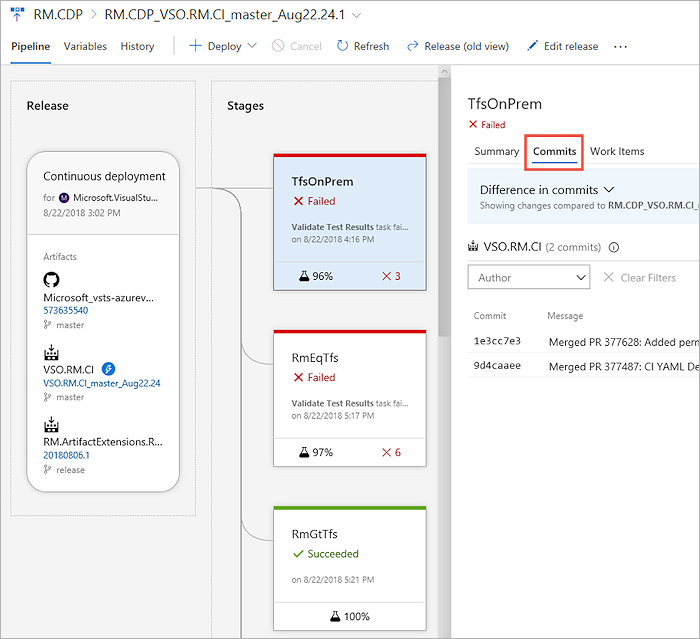
When troubleshooting test failures that occur consistently over a period of time, it's important to trace back to the initial set of changes - where the failure originated. This step can help significantly to narrow down the scope for identifying the problematic test or source under test. To discover the first instance of test failures and trace it back to the associated code changes, visit Tests tab in build or release.
In the Tests tab, select a test failure to be analyzed. Based on whether it's a build or release, choose the Failing build or Failing release column for the test.
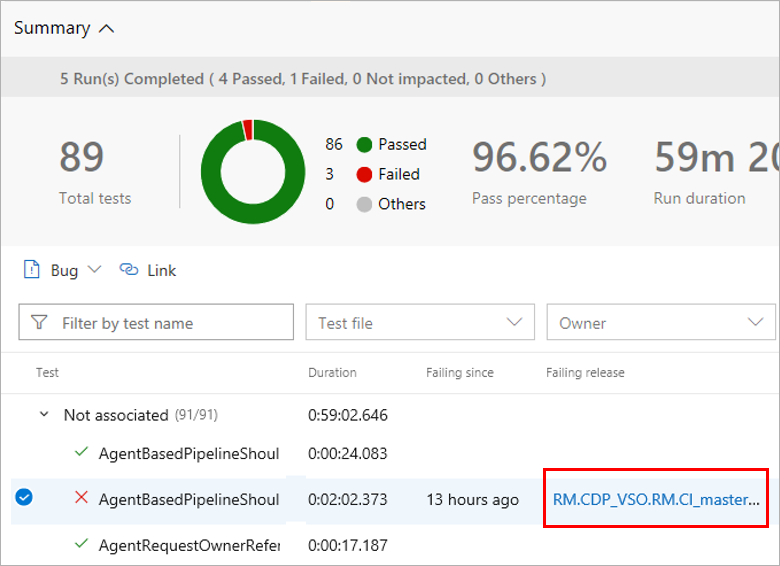
Another instance of the Tests tab opens in a new window, showing the first instance of consecutive failures for the test.
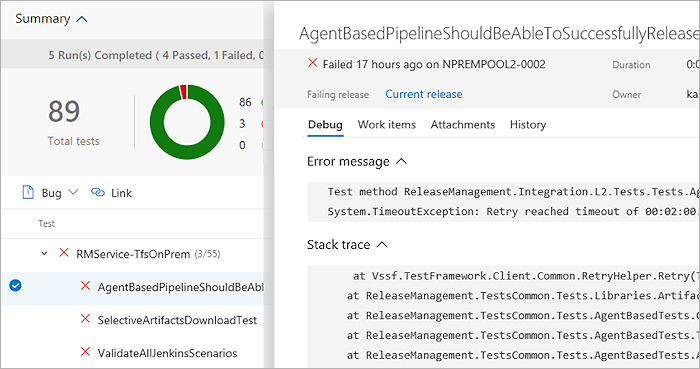
Based on the build or release pipeline, you can choose the timeline or pipeline view to see what code changes were committed. You can analyze the code changes to identify the potential root cause of the test failure.
Teams moving from manual testing to continuous, automated testing, and have a subset of tests that are already automated, can execute them as part of the pipeline or on demand. Planned testing, or "automated tests" can be associated to the test cases in a test plan and executed from Azure Test Plans. Once associated, these tests contribute towards the quality metrics of the corresponding requirements.
Events
17 Mar, 23 - 21 Mar, 23
Join the meetup series to build scalable AI solutions based on real-world use cases with fellow developers and experts.
Register nowTraining
Module
Run quality tests in your build pipeline by using Azure Pipelines - Training
Find out about automated testing that proves your code to be maintainable, understandable, and functioning without repetitive manual testing.
Certification
Microsoft Certified: Power Automate RPA Developer Associate - Certifications
Demonstrate how to improve and automate workflows with Microsoft Power Automate RPA developer.