Path selection with Azure Route Server
Azure Route Server simplifies dynamic routing between Azure virtual network and your network virtual appliance (NVA) that you're using to control traffic between the virtual network and your on-premises network over the internet. In this article, you learn how Azure Route Server enables path selection to allow you to configure your SDWAN NVA to have a routing preference when communicating with your on-premises network.
How does it work?
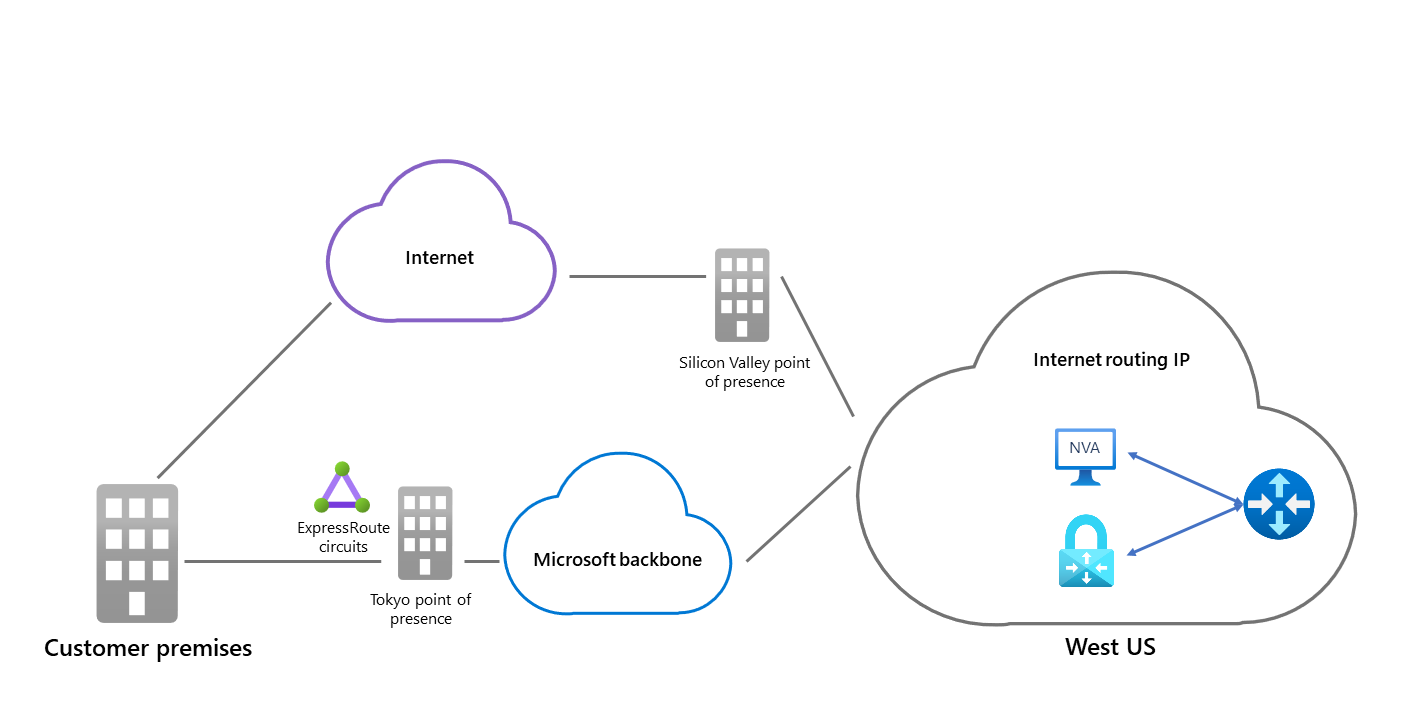
Cold potato routing
When you deploy an SDWAN NVA in the same virtual network as the Azure Route Server, it's configured with Microsoft network routing preference. Traffic from Azure travels over the Microsoft global network and exits it closest to your on-premises. Traffic from your on-premises enters the Microsoft network closest to it on the return path. This method of routing is performance optimized, therefore providing the best possible experience.
Hot potato routing
As a way to optimize for cost, you can use the Internet routing preference to minimize the travel on the Microsoft global network. Traffic exits the Microsoft network in the same Azure region that hosts the service, then it travels through the internet using the ISPs network. Traffic from your on-premises enters the Microsoft network that's closest to the Azure region of the hosted service. This method of routing provides the best overall price when completing a task like transferring large amount of data.
How to enable internet routing preference?
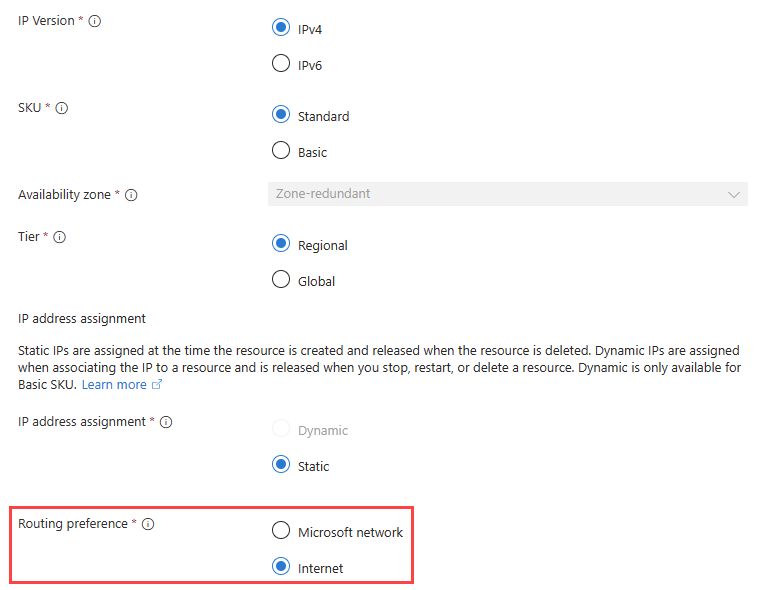
To enable internet routing preference for your NVA, create a new standard SKU Public IP address and select Internet as the Routing preference. Then, assign the public IP address to the NVA.
Microsoft recommends implementing a connectivity solution using both the Microsoft network and the internet to provide your environment with an extra layer of resiliency.
Related content
- Learn more about Azure Route Server.
- Learn how to configure Azure Route Server.