Firewall requirements for Azure Stack HCI
Applies to: Azure Stack HCI, versions 23H2 and 22H2
This article provides guidance on how to configure firewalls for the Azure Stack HCI operating system. It includes firewall requirements for outbound endpoints and internal rules and ports. The article also provides information on how to use Azure service tags with Microsoft Defender firewall.
This article also describes how to optionally use a highly locked-down firewall configuration to block all traffic to all destinations except those included in your allowlist.
If your network uses a proxy server for internet access, see Configure proxy settings for Azure Stack HCI.
Important
Azure Express Route and Azure Private Link are not supported for Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2 or any of its components as it is not possible to access the public endpoints required for Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2.
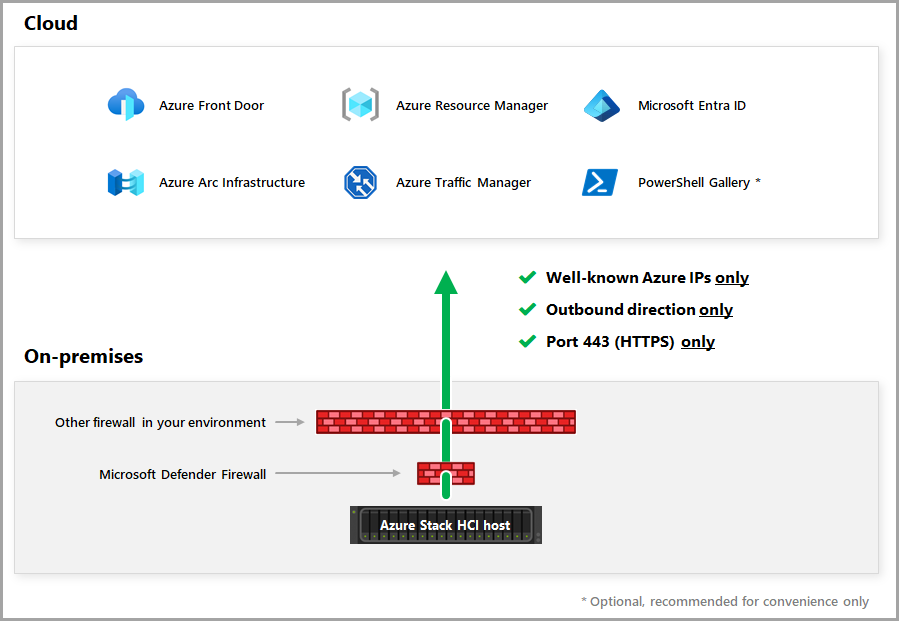
Firewall requirements for outbound endpoints
Opening ports 80 and 443 for outbound network traffic on your organization's firewall meets the connectivity requirements for the Azure Stack HCI operating system to connect with Azure and Microsoft Update.
Azure Stack HCI needs to periodically connect to Azure for:
- Well-known Azure IPs
- Outbound direction
- Ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS)
Important
Azure Stack HCI doesn't support HTTPS inspection. Make sure that HTTPS inspection is disabled along your networking path for Azure Stack HCI to prevent any connectivity errors.
As shown in the following diagram, Azure Stack HCI can access Azure using more than one firewall potentially.
Required firewall URLs for Azure Stack HCI 23H2 deployments
Starting with Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2, all the clusters automatically enables Azure Resource Bridge and AKS infrastructure and uses the Arc for Servers agent to connect to Azure control plane. Along with the list of HCI specific endpoints on the following table, the Azure Resource Bridge on Azure Stack HCI endpoints, the AKS on Azure Stack HCI endpoints and the Azure Arc-enabled servers endpoints must be included in the allow list of your firewall.
For East US consolidated list of endpoints, including HCI, Arc-enabled servers, ARB, and AKS use:
For West Europe consolidated list of endpoints, including HCI, Arc-enabled servers, ARB, and AKS use:
For Australia East consolidated list of endpoints, including HCI, Arc-enabled servers, ARB, and AKS use:
For Canada Central consolidated list of endpoints, including HCI, Arc-enabled servers, ARB, and AKS use:
For Central India consolidated list of endpoints, including HCI, Arc-enabled servers, ARB, and AKS use:
Firewall requirements for additional Azure services
Depending on additional Azure services you enable for Azure Stack HCI, you may need to make additional firewall configuration changes. Refer to the following links for information on firewall requirements for each Azure service:
- Azure Monitor Agent
- Azure portal
- Azure Site Recovery
- Azure Virtual Desktop
- Microsoft Defender
- Microsoft Monitoring Agent (MMA) and Log Analytics Agent
- Qualys
- Remote support
- Windows Admin Center
- Windows Admin Center in Azure portal
Firewall requirements for internal rules and ports
Ensure that the proper network ports are open between all server nodes, both within a site and between sites for stretched clusters (stretched cluster functionality is only available in Azure Stack HCI, version 22H2.). You'll need appropriate firewall rules to allow ICMP, SMB (port 445, plus port 5445 for SMB Direct if using iWARP RDMA), and WS-MAN (port 5985) bi-directional traffic between all servers in the cluster.
When using the Cluster Creation wizard in Windows Admin Center to create the cluster, the wizard automatically opens the appropriate firewall ports on each server in the cluster for Failover Clustering, Hyper-V, and Storage Replica. If you're using a different firewall on each server, open the ports as described in the following sections:
Azure Stack HCI OS management
Ensure that the following firewall rules are configured in your on-premises firewall for Azure Stack HCI OS management, including licensing and billing.
| Rule | Action | Source | Destination | Service | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allow inbound/outbound traffic to and from the Azure Stack HCI service on cluster servers | Allow | Cluster servers | Cluster servers | TCP | 30301 |
Windows Admin Center
Ensure that the following firewall rules are configured in your on-premises firewall for Windows Admin Center.
| Rule | Action | Source | Destination | Service | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provide access to Azure and Microsoft Update | Allow | Windows Admin Center | Azure Stack HCI | TCP | 445 |
| Use Windows Remote Management (WinRM) 2.0 for HTTP connections to run commands on remote Windows servers |
Allow | Windows Admin Center | Azure Stack HCI | TCP | 5985 |
| Use WinRM 2.0 for HTTPS connections to run commands on remote Windows servers |
Allow | Windows Admin Center | Azure Stack HCI | TCP | 5986 |
Note
While installing Windows Admin Center, if you select the Use WinRM over HTTPS only setting, then port 5986 is required.
Active Directory
Ensure that the following firewall rules are configured in your on-premises firewall for Active Directory (local security authority).
| Rule | Action | Source | Destination | Service | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allow inbound/outbound connectivity to the Active Directory Web services (ADWS) and Active Directory Management Gateway Service | Allow | Active Directory Services | Azure Stack HCI | TCP | 9389 |
Failover Clustering
Ensure that the following firewall rules are configured in your on-premises firewall for Failover Clustering.
| Rule | Action | Source | Destination | Service | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allow Failover Cluster validation | Allow | Management system | Cluster servers | TCP | 445 |
| Allow RPC dynamic port allocation | Allow | Management system | Cluster servers | TCP | Minimum of 100 ports above port 5000 |
| Allow Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | Allow | Management system | Cluster servers | TCP | 135 |
| Allow Cluster Administrator | Allow | Management system | Cluster servers | UDP | 137 |
| Allow Cluster Service | Allow | Management system | Cluster servers | UDP | 3343 |
| Allow Cluster Service (Required during a server join operation.) |
Allow | Management system | Cluster servers | TCP | 3343 |
| Allow ICMPv4 and ICMPv6 for Failover Cluster validation |
Allow | Management system | Cluster servers | n/a | n/a |
Note
The management system includes any computer from which you plan to administer the cluster, using tools such as Windows Admin Center, Windows PowerShell, or System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
Hyper-V
Ensure that the following firewall rules are configured in your on-premises firewall for Hyper-V.
| Rule | Action | Source | Destination | Service | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allow cluster communication | Allow | Management system | Hyper-V server | TCP | 445 |
| Allow RPC Endpoint Mapper and WMI | Allow | Management system | Hyper-V server | TCP | 135 |
| Allow HTTP connectivity | Allow | Management system | Hyper-V server | TCP | 80 |
| Allow HTTPS connectivity | Allow | Management system | Hyper-V server | TCP | 443 |
| Allow Live Migration | Allow | Management system | Hyper-V server | TCP | 6600 |
| Allow VM Management Service | Allow | Management system | Hyper-V server | TCP | 2179 |
| Allow RPC dynamic port allocation | Allow | Management system | Hyper-V server | TCP | Minimum of 100 ports above port 5000 |
Note
Open up a range of ports above port 5000 to allow RPC dynamic port allocation. Ports below 5000 may already be in use by other applications and could cause conflicts with DCOM applications. Previous experience shows that a minimum of 100 ports should be opened, because several system services rely on these RPC ports to communicate with each other. For more information, see How to configure RPC dynamic port allocation to work with firewalls.
Storage Replica (stretched cluster)
Ensure that the following firewall rules are configured in your on-premises firewall for Storage Replica (stretched cluster).
| Rule | Action | Source | Destination | Service | Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allow Server Message Block (SMB) protocol |
Allow | Stretched cluster servers | Stretched cluster servers | TCP | 445 |
| Allow Web Services-Management (WS-MAN) |
Allow | Stretched cluster servers | Stretched cluster servers | TCP | 5985 |
| Allow ICMPv4 and ICMPv6 (if using the Test-SRTopologyPowerShell cmdlet) |
Allow | Stretched cluster servers | Stretched cluster servers | n/a | n/a |
Update Microsoft Defender firewall
This section shows how to configure Microsoft Defender firewall to allow IP addresses associated with a service tag to connect with the operating system. A service tag represents a group of IP addresses from a given Azure service. Microsoft manages the IP addresses included in the service tag, and automatically updates the service tag as IP addresses change to keep updates to a minimum. To learn more, see Virtual network service tags.
Download the JSON file from the following resource to the target computer running the operating system: Azure IP Ranges and Service Tags – Public Cloud.
Use the following PowerShell command to open the JSON file:
$json = Get-Content -Path .\ServiceTags_Public_20201012.json | ConvertFrom-JsonGet the list of IP address ranges for a given service tag, such as the
AzureResourceManagerservice tag:$IpList = ($json.values | where Name -Eq "AzureResourceManager").properties.addressPrefixesImport the list of IP addresses to your external corporate firewall, if you're using an allowlist with it.
Create a firewall rule for each server in the cluster to allow outbound 443 (HTTPS) traffic to the list of IP address ranges:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow Azure Resource Manager" -RemoteAddress $IpList -Direction Outbound -LocalPort 443 -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -Profile Any -Enabled True
Next steps
For more information, see also:
- The Windows Firewall and WinRM 2.0 ports section of Installation and configuration for Windows Remote Management