Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Important
SQL Data Sync will be retired on 30 September 2027. Consider migrating to alternative data replication/synchronization solutions.
In this tutorial, you learn how to set up SQL Data Sync by creating a sync group that contains both Azure SQL Database and SQL Server instances. The sync group is custom configured and synchronizes on the schedule you set.
The tutorial assumes you have at least some prior experience with SQL Database and SQL Server.
For an overview of SQL Data Sync, see What is SQL Data Sync for Azure?
For PowerShell examples on how to configure SQL Data Sync, see Use PowerShell to sync data between multiple databases in Azure SQL Database or between databases in Azure SQL Database and SQL Server.
The hub database is a sync topology's central endpoint, in which a sync group has multiple database endpoints. All other member databases with endpoints in the sync group, sync with the hub database. SQL Data Sync is only supported on Azure SQL Database. The hub database must be an Azure SQL Database.
Azure SQL Database Hyperscale is only supported as a member database, not as a hub database.
Create sync group
Go to the Azure portal. Search for and select SQL databases to find an existing Azure SQL Database.
Select the existing database you want to use as the hub database for Data Sync.
On the SQL database resource menu for the selected database, under Data management, select Sync to other databases.
On the Sync to other databases page, select New Sync Group. The Create Data Sync group page opens.
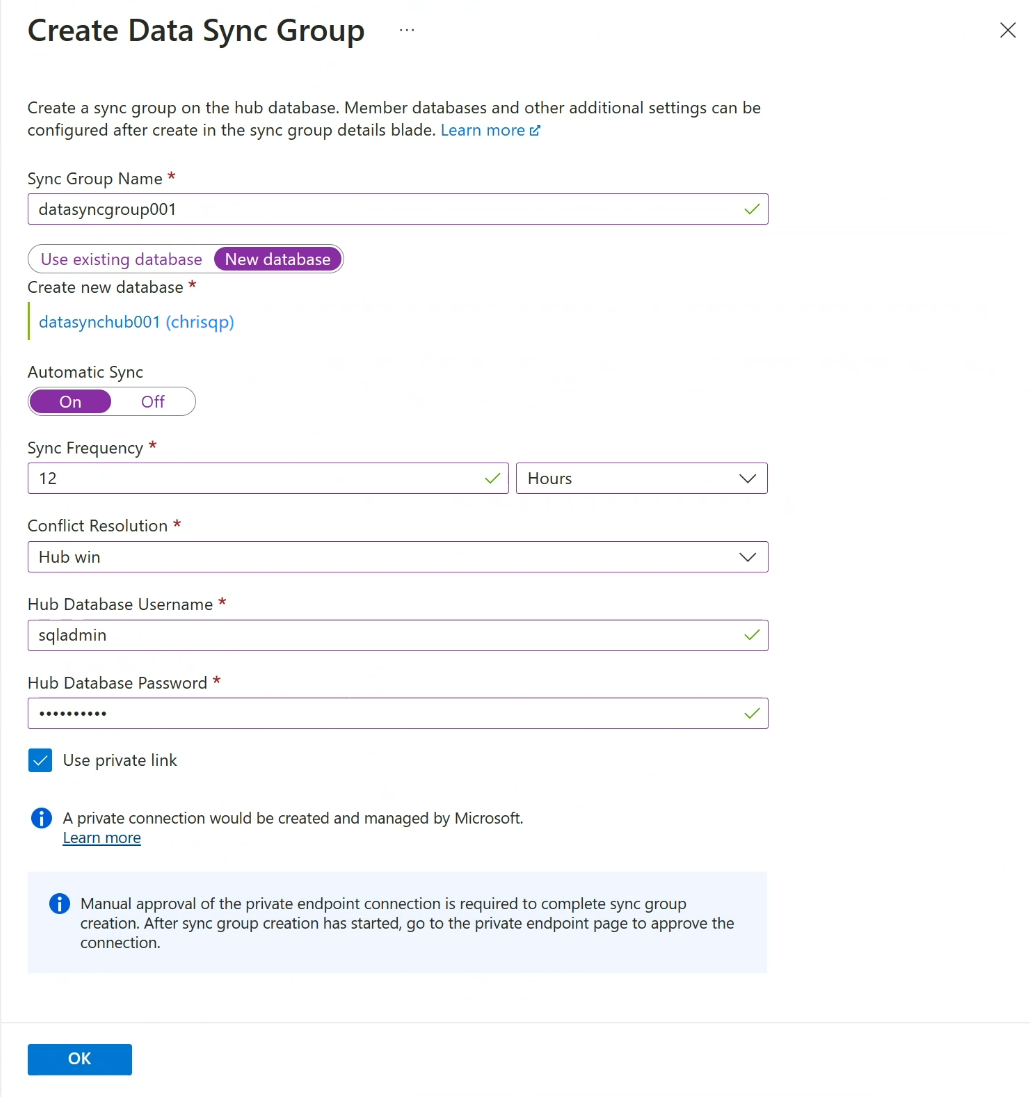
On the Create Data Sync Group page, configure the following settings:
Setting Description Sync Group Name Enter a name for the new sync group. This name is distinct from the name of the database itself. Sync Metadata Database Choose to create a database (recommended) or to use an existing database to serve as the Sync Metadata Database.
Microsoft recommends creating a new, empty database for use as the Sync Metadata Database. Data Sync creates tables in this database and runs a frequent workload. This database is shared as the Sync Metadata Database for all sync groups in a selected region and subscription. You can't change the database or its name without removing all sync groups and sync agents in the region.
If you choose to create a new database, select New database. Select Configure database settings. On the SQL Database page, name and configure a new Azure SQL Database and select OK.
If you choose Use existing database, select the database from the Sync Metadata Database dropdown list.Automatic Sync Select On or Off.
If you choose On, enter a number and select Seconds, Minutes, Hours, or Days in the Sync Frequency section.
The first sync begins after the selected interval period elapses from the time the configuration is saved.Conflict Resolution Select Hub win or Member win.
Hub win means when conflicts occur, data in the hub database overwrites conflicting data in the member database.
Member win means when conflicts occur, data in the member database overwrites conflicting data in the hub database.Hub Database Username and Hub Database Password Provide the username and password to the server admin SQL authenticated login for the Hub database. This is the server admin username and password for the same Azure SQL logical server that you started on. Microsoft Entra (formerly Azure Active Directory) authentication is not supported. Use private link Choose a service managed private endpoint to establish a secure connection between the sync service and the hub database. Select OK and wait for the sync group to be created and deployed.
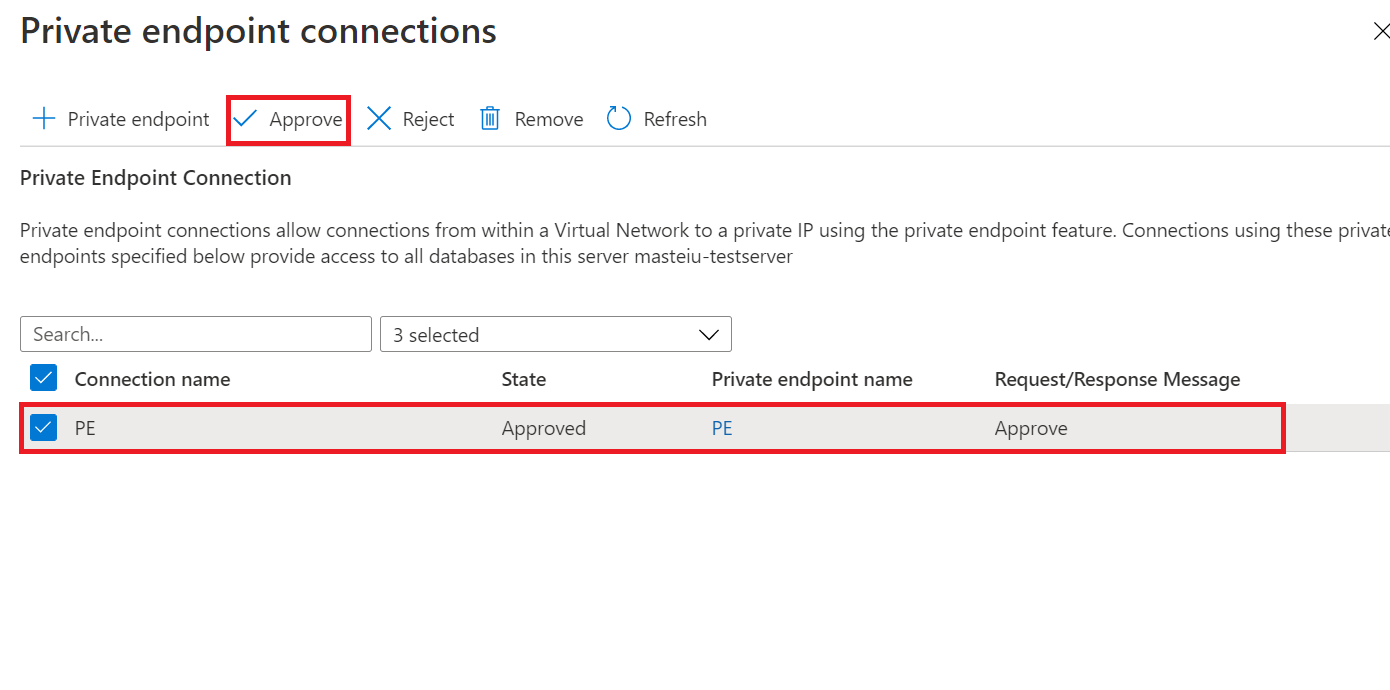
On the New Sync Group page, if you selected Use private link, you will need to approve the private endpoint connection. The link in the info message will take you to the private endpoint connections experience where you can approve the connection.
Note
The private links for the sync group and the sync members need to be created, approved, and disabled separately.
Add sync members
After the new sync group is created and deployed, open the sync group and access the Databases page, where you will select sync members.
Note
To update or insert the username and password to your hub database, go to the Hub Database section in the Select sync members page.
Add a database in Azure SQL Database as a member to a sync group
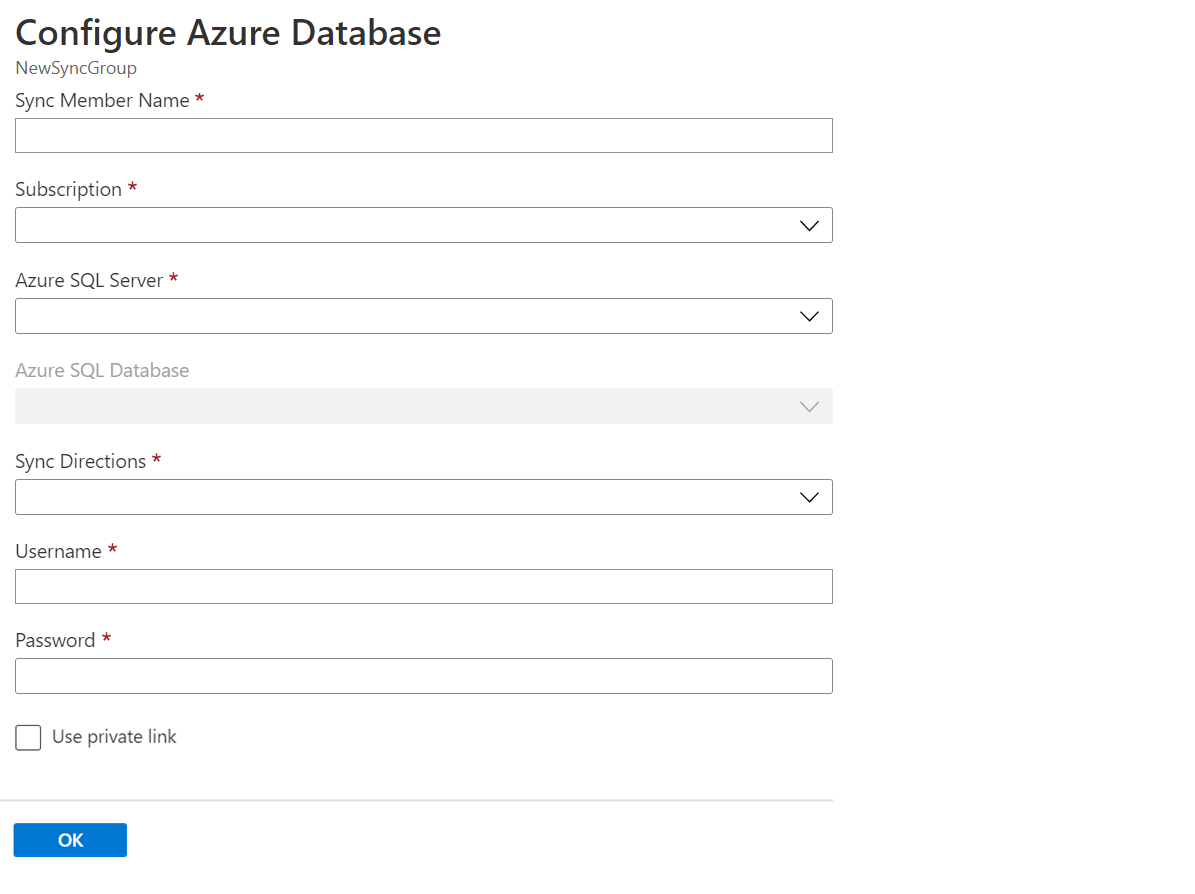
In the Select sync members section, optionally add a database in Azure SQL Database to the sync group by selecting Add an Azure Database. The Configure Azure Database page opens.
On the Configure Azure SQL Database page, change the following settings:
Setting Description Sync Member Name Provide a name for the new sync member. This name is distinct from the database name itself. Subscription Select the associated Azure subscription for billing purposes. Azure SQL Server Select the existing server. Azure SQL Database Select the existing database in SQL Database. Sync Directions The Sync Direction can be Hub to Member, or Member to Hub, or both. Select From the Hub, To the Hub, or Bi-directional Sync. For more information, see How it works. Username and Password Enter the existing credentials for the server on which the member database is located. Don't enter new credentials in this section. Use private link Choose a service managed private endpoint to establish a secure connection between the sync service and the member database. Select OK and wait for the new sync member to be created and deployed.
Add a database on a SQL Server instance as a member to a sync group
In the Member Database section, optionally add a database in a SQL Server instance to the sync group by selecting Add an On-Premises Database.
The Configure On-Premises page opens where you can do the following things:
Select Choose the Sync Agent Gateway. The Select Sync Agent page opens.
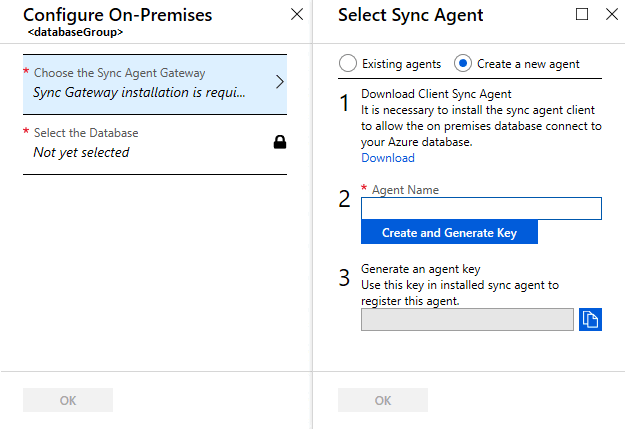
On the Choose the Sync Agent page, choose whether to use an existing agent or create an agent.
If you choose Existing agents, select the existing agent from the list.
If you choose Create a new agent, do the following things:
Download the data sync agent from the link provided and install it on a server that is different than where the SQL Server instance is located. You can also download the agent directly from Azure SQL Data Sync Agent. For best practices on sync client agent, refer to Best practices for Azure SQL Data Sync.
Important
You have to open outbound TCP port 1433 in the firewall to let the client agent communicate with the server.
Enter an Agent Name.
Select Create and Generate Key and copy the agent key to the clipboard.
Select OK to close the Select Sync Agent page.
On the server where sync client agent is installed, locate and run the Client Sync Agent app.
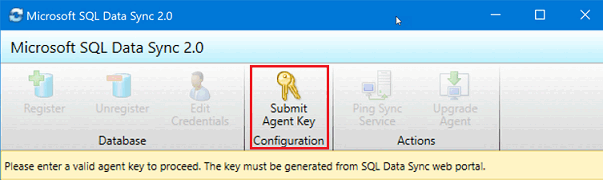
In the sync agent app, select Submit Agent Key. The Sync Metadata Database Configuration dialog box opens.
In the Sync Metadata Database Configuration dialog box, paste in the agent key copied from the Azure portal. Also provide the existing credentials for the server on which the Sync Metadata Database database is located. Select OK and wait for the configuration to finish.
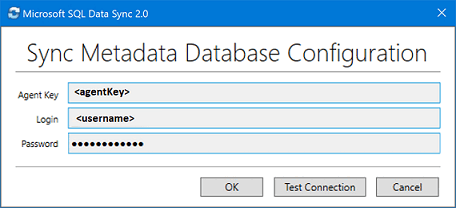
Note
If you get a firewall error, create a firewall rule on Azure to allow incoming traffic from the SQL Server computer. You can create the rule manually in the portal or in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). In SSMS, connect to the hub database on Azure by entering its name as
<hub_database_name>.database.windows.net.Select Register to register a SQL Server database with the agent. The SQL Server Configuration dialog box opens.
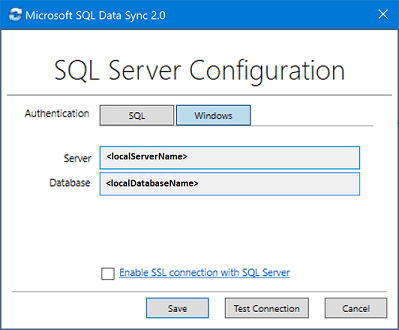
In the SQL Server Configuration dialog box, choose to connect using SQL Server authentication or Windows authentication. If you choose SQL Server authentication, enter the existing credentials. Provide the SQL Server name and the name of the database that you want to sync and select Test connection to test your settings. Then select Save and the registered database appears in the list.
Close the Client Sync Agent app.
In the Azure portal, on the Configure On-Premises page, select Select the Database.
On the Select Database page, in the Sync Member Name field, provide a name for the new sync member. This name is distinct from the name of the database itself. Select the database from the list. In the Sync Directions field, select Bi-directional Sync, To the Hub, or From the Hub.
Select OK to close the Select Database page. Then select OK to close the Configure On-Premises page and wait for the new sync member to be created and deployed. Finally, select OK to close the Select sync members page.
Note
To connect to SQL Data Sync and the local agent, add your user name to the role DataSync_Executor. Data Sync creates this role on the SQL Server instance.
Configure sync group
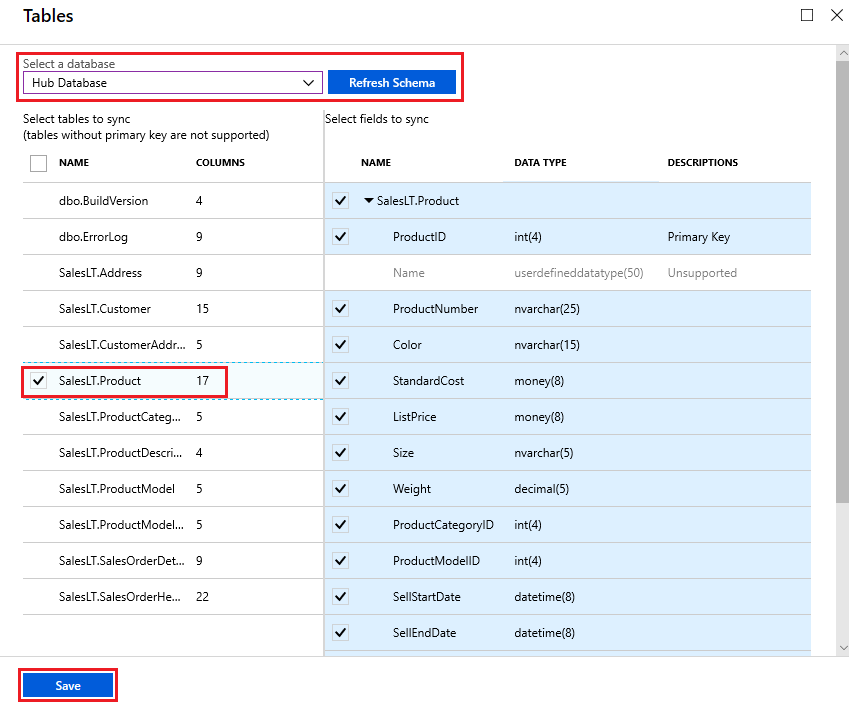
After the new sync group members are created and deployed, go to the Tables section in the Database Sync Group page.
On the Tables page, select a database from the list of sync group members and select Refresh schema. Expect a few minutes delay in refresh schema, the delay might be a few minutes longer if using private link.
From the list, select the tables you want to sync. By default, all columns are selected, so disable the checkbox for the columns you don't want to sync. Be sure to leave the primary key column selected.
Select Save.
By default, databases are not synced until scheduled or manually run. To run a manual sync, navigate to your database in SQL Database in the Azure portal, select Sync to other databases, and select the sync group. The Data Sync page opens. Select Sync.

FAQ
This section answers frequently asked questions about the Azure SQL Data Sync service.
Does SQL Data Sync fully create tables?
If sync schema tables are missing in the destination database, SQL Data Sync creates them with the columns you selected. However, this doesn't result in a full-fidelity schema for the following reasons:
- Only columns you select are created in the destination table. Columns not selected are ignored.
- Only selected column indexes are created in the destination table. For columns not selected, those indexes are ignored.
- Indexes on XML type columns aren't created.
- CHECK constraints aren't created.
- Triggers on the source tables aren't created.
- Views and stored procedures aren't created.
Because of these limitations, we recommend the following things:
- For production environments, create the full-fidelity schema yourself.
- When experimenting with the service, use the auto-provisioning feature.
Why do I see tables I didn't create?
Data Sync creates additional tables in the database for change tracking. Don't delete these or Data Sync stops working.
Is my data convergent after a sync?
Not necessarily. Take a sync group with a hub and three spokes (A, B, and C) where synchronizations are Hub to A, Hub to B, and Hub to C. If a change is made to database A after the Hub to A sync, that change isn't written to database B or database C until the next sync task.
How do I get schema changes into a sync group?
Make and propagate all schema changes manually.
- Replicate the schema changes manually to the hub and to all sync members.
- Update the sync schema.
For adding new tables and columns:
New tables and columns don't impact the current sync and Data Sync ignores them until they're added to the sync schema. When adding new database objects, follow the sequence:
- Add new tables or columns to the hub and to all sync members.
- Add new tables or columns to the sync schema.
- Begin inserting values into the new tables and columns.
To change the data type of a column:
When you change the data type of an existing column, Data Sync continues to work as long as the new values fit the original data type defined in the sync schema. For example, if you change the type in the source database from int to bigint, Data Sync continues to work until you insert a value too large for the int data type. To complete the change, replicate the schema change manually to the hub and to all sync members, then update the sync schema.
How can I export and import a database with Data Sync?
After you export a database as a .bacpac file and import the file to create a database, do the following to use Data Sync in the new database:
- Clean up the Data Sync objects and additional tables on the new database by using Data Sync complete cleanup.sql. The script deletes all the required Data Sync objects from the database.
- Recreate the sync group with the new database. If you no longer need the old sync group, delete it.
Where can I find information on the client agent?
For frequently asked questions about the client agent, see Agent FAQ.
Is it necessary to manually approve the link before I can start using it?
Yes. You must manually approve the service managed private endpoint, in the Private endpoint connections page of the Azure portal during the sync group deployment or by using PowerShell.
Why do I get a firewall error when the Sync job is provisioning my Azure database?
This can happen because Azure resources are not allowed to access your server. There are two solutions:
Ensure that the firewall on the Azure database has set Allow Azure services and resources to access this server to Yes. For more information, see Azure SQL Database and network access controls.
Configure a private link for Data Sync, which is different from an Azure Private Link. Private Link is the way to create Sync groups using secure connection with databases sitting behind a firewall. SQL Data Sync Private Link is Microsoft-managed endpoint and internally creates a subnet within the existing virtual network, so there is no need to create another virtual network or subnet.
What versions of SQL Server on-premises can be part of a Sync group?
Only the following versions of SQL Server on-premises can be part of a sync group:
- SQL Server 2008
- SQL Server 2008 R2
- SQL Server 2012
- SQL Server 2016
- SQL Server 2017 on Windows
- SQL Server 2019 on Windows
- SQL Server 2022 on Windows