Migrate Azure HDInsight 3.6 Hive workloads to HDInsight 4.0
HDInsight 4.0 has several advantages over HDInsight 3.6. Here's an overview of what's new in HDInsight 4.0.
This article covers steps to migrate Hive workloads from HDInsight 3.6 to 4.0, including
- Hive metastore copy and schema upgrade
- Safe migration for ACID compatibility
- Preservation of Hive security policies
The new and old HDInsight clusters must have access to the same Storage Accounts.
Migration of Hive tables to a new Storage Account needs to be done as a separate step. See Hive Migration across Storage Accounts.
Changes in Hive 3 and what's new:
Hive client changes
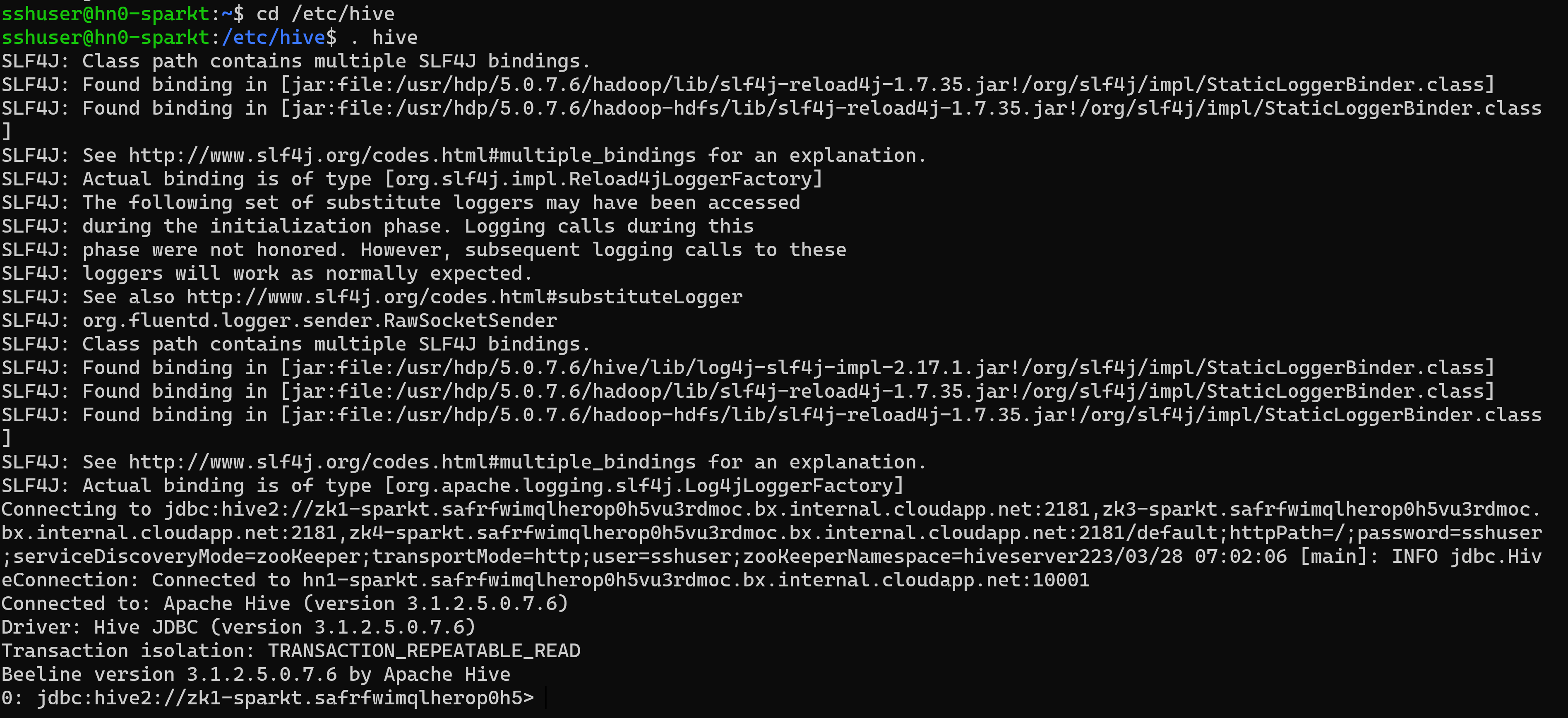
Hive 3 supports only the thin client, Beeline for running queries and Hive administrative commands from the command line. Beeline uses a JDBC connection to HiveServer to execute all commands. Parsing, compiling, and executing operations occur in HiveServer.
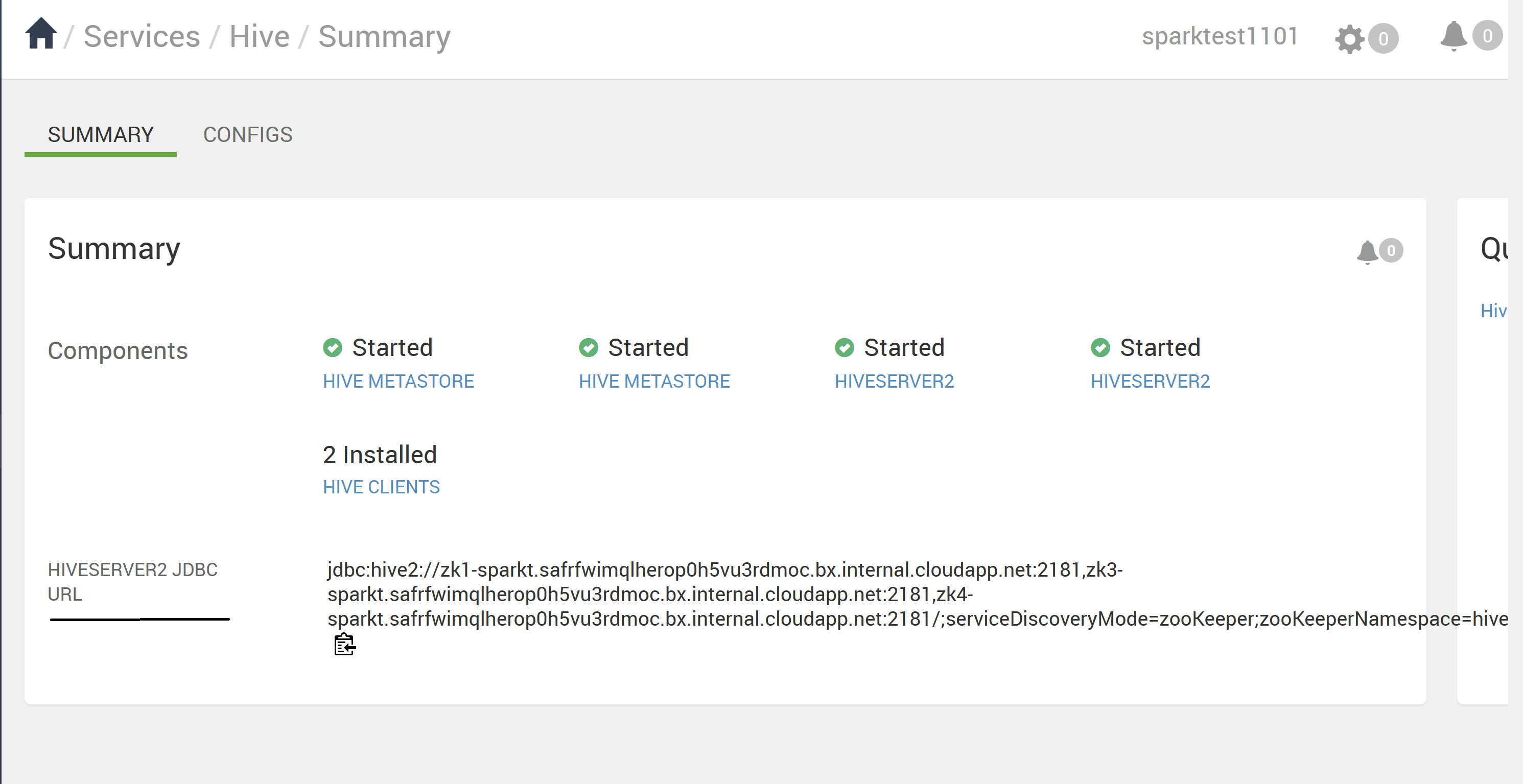
You enter supported Hive CLI commands by invoking Beeline using the Hive keyword as a Hive user or invoke a beeline using beeline -u <JDBC URL>. You can get the JDBC URL from Ambari Hive page.
Use Beeline (instead of the thick client Hive CLI, which is no longer supported) has several advantages, includes:
- Instead of maintaining the entire Hive code base, you can maintain only the JDBC client.
- Startup overhead is lower by using Beeline because the entire Hive code base isn't involved.
You can also execute the Hive script, which is under the directory “/usr/bin”, which invokes a beeline connection using JDBC URL.
A thin client architecture facilitates securing data in
- Session state, internal data structures, passwords, and so on, reside on the client instead of the server.
- The small number of daemons required to execute queries simplifies monitoring and debugging.
HiveServer enforces allowlist and blocklist settings that you can change using SET commands. Using the blocklists, you can restrict memory configuration to prevent Hive Server instability. You can configure multiple HiveServer instances with different allowlist and blocklist to establish different levels of stability.
Hive Metastore changes
Hive now supports only a remote metastore instead of an embedded metastore (within HS2 JVM). The Hive metastore resides on a node in a cluster managed by Ambari as part of the HDInsight stack. A standalone server outside the cluster isn't supported. You no longer set key=value commands on the command line to configure Hive Metastore. Based on the value configured in "hive.metastore.uris=' ' " HMS service used and connection established.
Execution engine change
Apache Tez replaces MapReduce as the default Hive execution engine. MapReduce is deprecated starting Hive 2.0 Refer HIVE-12300. With expressions of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) and data transfer primitives, execution of Hive queries under Tez improves performance. SQL queries you submit to Hive are executed as follows
- Hive compiles the query.
- Tez executes the query.
- YARN allocates resources for applications across the cluster and enables authorization for Hive jobs in YARN queues.
- Hive updates the data in ABFS or WASB.
- Hive returns query results over a JDBC connection.
If a legacy script or application specifies MapReduce for execution, an exception occurs as follows
Note
Most user-defined functions (UDFs) require no change to execute on Tez instead of MapReduce.
Changes with respect to ACID transaction and CBO:
ACID tables are the default table type in HDInsight 4.x with no performance or operational overload.
Simplified application development, operations with stronger transactional guarantees, and simpler semantics for SQL commands
Hive internal takes care of bucketing for ACID tables in HDInsight 4.1, thus removing maintenance overhead.
Advanced optimizations – Upgrade in CBO
Automatic Query cache. The Property used to enable query caching is
hive.query.results.cache.enabled. You need to set this property to true. Hive stores the query result cache in/tmp/hive/__resultcache__/.By default, Hive allocates 2 GB for the query result cache. You can change this setting by configuring the following parameter in byteshive.query.results.cache.max.size.For more information, Benefits of migrating to Azure HDInsight 4.0.
Materialized view rewrites
For more information, on Hive - Materialized Views
Changes after upgrading to Apache Hive 3
To locate and use your Apache Hive 3 tables after an upgrade, you need to understand the changes that occur during the upgrade process. Changes to the management and location of tables, permissions to table directories, table types, and ACID-compliance concerns.
Hive Management of Tables
Hive 3 takes more control of tables than Hive 2, and requires managed tables adhere to a strict definition. The level of control Hive takes over tables is homogeneous to the traditional databases. Hive is self-aware of the delta changes to the data; this control framework enhances the performance.
For example, if Hive knows that resolving a query doesn't require scanning tables for new data, Hive returns results from the hive query result cache. When the underlying data in a materialized view change, Hive needs to rebuild the materialized view. ACID properties reveal exactly which rows changed, and needs to be processed and added to the materialized view.
Hive changes to ACID properties
Hive 2.x and 3.x have both transactional(managed) and nontransactional (external) tables. Transactional tables have atomic, consistent, isolation and durable (ACID) properties. In Hive 2.x, the initial version of ACID transaction processing is ACID v1. In Hive 3.x, the default tables would be with ACID v2.
Native and non-native storage formats
Storage formats are a factor in upgrade changes to table types. Hive 2.x and 3.x supports the following Hadoop native and non-native storage formats
Native: Tables with built-in support in Hive, in the following file formats
- Text
- Sequence File
- RC File
- AVRO File
- ORC File
- Parquet File
Non-native: Tables that use a storage handler, such as the DruidStorageHandler or HBaseStorageHandler
HDInsight 4.x upgrade changes to table types
The following table compares Hive table types and ACID operations before an upgrade from HDInsight 3.x and after an upgrade to HDInsight 4.x. The ownership of the Hive table file is a factor in determining table types and ACID operations after the upgrade
HDInsight 3.x and HDInsight 4.x Table type comparison
| HDInsight 3.x | - | - | - | HDInsight 4.x | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table Type | ACID v1 | Format | Owner (user) of Hive Table File | Table Type | ACID v2 |
| External | No | Native or non-native | Hive or non-Hive | External | No |
| Managed | Yes | ORC | Hive or non-Hive | Managed, updatable | Yes |
| Managed | No | ORC | Hive | Managed, updatable | Yes |
| Managed | No | ORC | non-Hive | External, with data delete | NO |
| Managed | No | Native (but non-ORC) | Hive | Managed, insert only | Yes |
| Managed | No | Native (but non-ORC) | non-Hive | External, with data delete | No |
| Managed | No | Non-native | Hive or non-Hive | External, with data delete | No |
Hive Impersonation
Hive impersonation was enabled by default in Hive 2 (doAs=true), and disabled by default in Hive 3. Hive impersonation runs Hive as end user, or not.
Other HDInsight 4.x upgrade changes
- Managed, ACID tables not owned by the Hive user remain managed tables after the upgrade, but Hive becomes the owner.
- After the upgrade, the format of a Hive table is the same as before the upgrade. For example, native or non-native tables remain native or non-native, respectively.
Location Changes
After the upgrade, the location of managed tables or partitions doesn't change under any one of the following conditions:
- The old table or partition directory wasn't in its default location /apps/hive/warehouse before the upgrade.
- The old table or partition is in a different file system than the new warehouse directory.
- The old table or partition directory is in a different encryption zone than the new warehouse directory.
Otherwise, the location of managed tables or partitions does change. The upgrade process moves managed files to /hive/warehouse/managed. By default, Hive places any new external tables you create in HDInsight 4.x in /hive/warehouse/external
The /apps/hive directory, which is the former location of the Hive 2.x warehouse, might or might not exist in HDInsight 4.x
Following Scenario's are present for location changes
Scenario 1
If the table is a managed table in HDInsight-3.x and if it's present in the location /apps/hive/warehouse and converted as external table in HDInsight-4.x, then the location is the same /apps/hive/warehouse in HDInsight 4.x as well. It doesn't change any location. After this step, if you're performing alter table command to convert it as managed (acid) table at that time present in the same location /apps/hive/warehouse.
Scenario 2
If the table is a managed table in HDInsight-3.x and if it's present in the location /apps/hive/warehouse and converted to managed (ACID) table in HDInsight 4.x, then the location is /hive/warehouse/managed.
Scenario 3
If you're creating an external table, in HDInsight-4.x without specifying any location then it presents in the location /hive/warehouse/external.
Table conversion
After upgrading, to convert a nontransactional table to an ACID v2 transactional table, you use the ALTER TABLE command and set table properties to
transaction'='true' and 'EXTERNAL'='false
- The managed table, non-ACID, ORC format and owned by non-Hive user in HDInsight-3.x will be converted to external, non-ACID table in HDInsight-4.x.
- If the user wishes to change the external table (non-ACID) to ACID, then they should change the external table to managed and ACID as well. Because in HDInsight-4.x all the managed tables are strictly ACID by default. You can't convert the external tables(non-ACID) to ACID table.
Note
The table must be a ORC table.
To convert external table (non-ACID) to Managed (ACID) table,
- Convert external table to managed and acid equals to true using the following command:
alter table <table name> set TBLPROPERTIES ('EXTERNAL'='false', 'transactional'='true'); - If you try to execute the following command for external table, you get the below error.
Scenario 1
Consider table rt is external table (non-ACID). If the table is non-ORC table,
alter table rt set TBLPROPERTIES ('transactional'='true');
ERROR : FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. Unable to alter table. The table must be stored using an ACID compliant format (such as ORC): work.rt
The table must be ORC format
Scenario 2
>>>> alter table rt set TBLPROPERTIES ('transactional'='true'); If the table is ORC table.
ERROR:
Error: Error while processing statement: FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. Unable to alter table. work.rt can't be declared transactional because it's an external table (state=08S01,code=1)
This error is occurring because the table rt is external table and you can't convert external table to ACID.
Scenario 3
>>>> alter table rt set TBLPROPERTIES ('EXTERNAL'='false');
ERROR:
Error: Error while processing statement: FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. Unable to alter table. Table work.rt failed strict managed table checks due to the following reason: Table is marked as a managed table but isn't transactional. (state=08S01,code=1)
Here we're trying to change the external table first to managed table. In HDInsight 4.x, it should be Strictly managed table (which means it should be ACID). So, here you get a deadlock. The only way to convert the external table(NON_ACID) to managed (ACID) you have to follow the command:
alter table rt set TBLPROPERTIES ('EXTERNAL'='false', 'transactional'='true');
Syntax and semantics
Creating a table To improve useability and functionality, Hive 3 changed table creation. Hive has changed table creation in the following ways
- Creates ACID-compliant table, which is the default in HDP
- Supports simple writes and inserts
- Writes to multiple partitions
- Inserts multiple data updates in a single SELECT statement
- Eliminates the need for bucketing.
If you have an ETL pipeline that creates tables in Hive, the tables create as ACID. Hive now tightly controls access and performs compaction periodically on the tables
Before Upgrade In HDInsight 3.x, by default CREATE TABLE created a non-ACID table.
After Upgrade By default CREATE TABLE creates a full, ACID transactional table in ORC format.
Action Required To access Hive ACID tables from Spark, you connect to Hive using the Hive Warehouse Connector (HWC). To write ACID tables to Hive from Spark, you use the HWC and HWC API
Escaping
db.tableReferencesYou need to change queries that use db.table references to prevent Hive from interpreting the entire db.table string as the table name. Hive 3.x rejects
db.tablein SQL queries. A dot (.) isn't allowed in table names. You enclose the database name and the table name in backticks. Find a table having the problematic table reference.math.studentsthat appears in a CREATE TABLE statement. Enclose the database name and the table name in backticks.TABLE `math`.`students` (name VARCHAR(64), age INT, gpa DECIMAL(3,2));CASTING TIMESTAMPS Results of applications that cast numerics to timestamps differ from Hive 2 to Hive 3. Apache Hive changed the behavior of CAST to comply with the SQL Standard, which doesn't associate a time zone with the TIMESTAMP type.
Before Upgrade Casting a numeric type value into a timestamp could be used to produce a result that reflected the time zone of the cluster. For example, 1597217764557 is 2020-08-12 00:36:04 PDT. Running the following query casts the numeric to a timestamp in PDT:
SELECT CAST(1597217764557 AS TIMESTAMP);| 2020-08-12 00:36:04 |After Upgrade Casting a numeric type value into a timestamp produces a result that reflects the UTC instead of the time zone of the cluster. Running the query casts the numeric to a timestamp in UTC.
SELECT CAST(1597217764557 AS TIMESTAMP);| 2020-08-12 07:36:04.557 |Action Required Change applications. Don't cast from a numeral to obtain a local time zone. Built-in functions from_utc_timestamp and to_utc_timestamp can be used to mimic behavior before the upgrade.
CHECKING COMPATIBILITY OF COLUMN CHANGES A default configuration change can cause applications that change column types to fail.
Before Upgrade In HDInsight 3.x Hive.metastore.disallow.incompatible.col.type.changes is false by default to allow changes to incompatible column types. For example, you can change a STRING column to a column of an incompatible type, such as MAP<STRING, STRING>. No error occurs.
After Upgrade The hive.metastore.disallow.incompatible.col.type.changes is true by default. Hive prevents changes to incompatible column types. Compatible column type changes, such as INT, STRING, BIGINT, aren't blocked.
Action Required Change applications to disallow incompatible column type changes to prevent possible data corruption.
DROPPING PARTITIONS
The OFFLINE and NO_DROP keywords in the CASCADE clause for dropping partitions causes performance problems and is no longer supported.
Before Upgrade You could use OFFLINE and NO_DROP keywords in the CASCADE clause to prevent partitions from being read or dropped.
After Upgrade OFFLINE and NO_DROP aren't supported in the CASCADE clause.
Action Required Change applications to remove OFFLINE and NO_DROP from the CASCADE clause. Use an authorization scheme, such as Ranger, to prevent partitions from being dropped or read.
RENAMING A TABLE After the upgrade Renaming a managed table moves its location only if the table is created without a
LOCATIONclause and is under its database directory.
Limitations with respect to CBO
We see that the select output gives trailing zero's in few columns. For example, if we have a table column with datatype as decimal(38,4) and if we insert data as 38 then it adds the trailing zero's and provide result as 38.0000 As per https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/HIVE-12063 and https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/HIVE-24389, the idea is retained the scale and precision instead of running a wrapper in decimal columns. This is the default behavior from Hive 2. To fix this issue, you can follow the below option.
- Modify the datatype at source level to adjust the precision as col1(decimal(38,0)). This value provides the result as 38 without trailing zero's. But if you insert the data as 35.0005 then it's .0005 and provides only the value as 38
1.Remove the trailing zeros for the columns with issue and then cast to string,
- Use select TRIM(cast(<column_name> AS STRING))+0 FROM <table_name>;
- Use regex.
- Modify the datatype at source level to adjust the precision as col1(decimal(38,0)). This value provides the result as 38 without trailing zero's. But if you insert the data as 35.0005 then it's .0005 and provides only the value as 38
1.Remove the trailing zeros for the columns with issue and then cast to string,
Hive query fails with "Unsupported SubQuery Expression" when we use UNIX_TIMESTAMP in the query. For example, If we run a query, then it throws an error "Unsupported SubQuery Expression"
select * from (SELECT col_1 from table1 where col_2 >= unix_timestamp('2020-03-07','yyyy-MM-dd'));The root case of this issue is that the current Hive codebase is throwing an exception which parsing the UNIX_TIMESTAMP because there's no precision mapping in
HiveTypeSystemImpl.java codefor the precision ofUNIX_TIMESTAMPwhich Calcite recognizes asBIGINT. But the below query works fineselect * from (SELECT col_1 from table1 where col_2 >= 1);This command executes successfully since col_2 is an integer. The above issue was fixed in hdi-3.1.2-4.1.12(4.1 stack) and hdi-3.1.2-5.0.8(5.0 stack)
Steps to upgrade
1. Prepare the data
HDInsight 3.6 by default doesn't support ACID tables. If ACID tables are present, however, run 'MAJOR' compaction on them. See the Hive Language Manual for details on compaction.
If using Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1, Hive table locations are likely dependent on the cluster's HDFS configurations. Run the following script action to make these locations portable to other clusters. See Script action to a running cluster.
Property Value Bash script URI https://hdiconfigactions.blob.core.windows.net/linuxhivemigrationv01/hive-adl-expand-location-v01.shNode type(s) Head Parameters
2. Copy the SQL database
If the cluster uses a default Hive metastore, follow this guide to export metadata to an external metastore. Then, create a copy of the external metastore for upgrade.
If the cluster uses an external Hive metastore, create a copy of it. Options include export/import and point-in-time restore.
3. Upgrade the metastore schema
This step uses the Hive Schema Tool from HDInsight 4.0 to upgrade the metastore schema.
Warning
This step isn't reversible. Run this only on a copy of the metastore.
Create a temporary HDInsight 4.0 cluster to access the 4.0 Hive
schematool. You can use the default Hive metastore for this step.From the HDInsight 4.0 cluster, execute
schematoolto upgrade the target HDInsight 3.6 metastore. Edit the following shell script to add your SQL server name, database name, username, and password. Open an SSH Session on the headnode and run it.SERVER='servername.database.windows.net' # replace with your SQL Server DATABASE='database' # replace with your 3.6 metastore SQL Database USERNAME='username' # replace with your 3.6 metastore username PASSWORD='password' # replace with your 3.6 metastore password STACK_VERSION=$(hdp-select status hive-server2 | awk '{ print $3; }') /usr/hdp/$STACK_VERSION/hive/bin/schematool -upgradeSchema -url "jdbc:sqlserver://$SERVER;databaseName=$DATABASE;trustServerCertificate=false;encrypt=true;hostNameInCertificate=*.database.windows.net;" -userName "$USERNAME" -passWord "$PASSWORD" -dbType "mssql" --verboseNote
This utility uses client
beelineto execute SQL scripts in/usr/hdp/$STACK_VERSION/hive/scripts/metastore/upgrade/mssql/upgrade-*.mssql.sql.SQL Syntax in these scripts isn't necessarily compatible to other client tools. For example, SSMS and Query Editor on Azure Portal require keyword
GOafter each command.If any script fails due to resource capacity or transaction timeouts, scale up the SQL Database.
Verify the final version with query
select schema_version from dbo.version.The output should match that of the following bash command from the HDInsight 4.0 cluster.
grep . /usr/hdp/$(hdp-select --version)/hive/scripts/metastore/upgrade/mssql/upgrade.order.mssql | tail -n1 | rev | cut -d'-' -f1 | revDelete the temporary HDInsight 4.0 cluster.
4. Deploy a new HDInsight 4.0 cluster
Create a new HDInsight 4.0 cluster, selecting the upgraded Hive metastore and the same Storage Accounts.
The new cluster doesn't require having the same default filesystem.
If the metastore contains tables residing in multiple Storage Accounts, you need to add those Storage Accounts to the new cluster to access those tables. See add extra Storage Accounts to HDInsight.
If Hive jobs fail due to storage inaccessibility, verify that the table location is in a Storage Account added to the cluster.
Use the following Hive command to identify table location:
SHOW CREATE TABLE ([db_name.]table_name|view_name);
5. Convert Tables for ACID Compliance
Managed tables must be ACID-compliant on HDInsight 4.0. Run strictmanagedmigration on HDInsight 4.0 to convert all non-ACID managed tables to external tables with property 'external.table.purge'='true'. Execute from the headnode:
sudo su - hive
STACK_VERSION=$(hdp-select status hive-server2 | awk '{ print $3; }')
/usr/hdp/$STACK_VERSION/hive/bin/hive --config /etc/hive/conf --service strictmanagedmigration --hiveconf hive.strict.managed.tables=true -m automatic --modifyManagedTables
6. Class not found error with MultiDelimitSerDe
Problem
In certain situations when running a Hive query, you might receive java.lang.ClassNotFoundException stating org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe class isn't found. This error occurs when customer migrates from HDInsight 3.6 to HDInsight 4.0. The SerDe class org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe, which is a part of hive-contrib-1.2.1000.2.6.5.3033-1.jar in HDInsight 3.6 is removed and we're using org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe class, which is a part of hive-exec jar in HDI-4.0. hive-exec jar will load to HS2 by default when we start the service.
STEPS TO TROUBLESHOOT
- Check if any JAR under a folder (likely that it supposed to be under Hive libraries folder, which is
/usr/hdp/current/hive/libin HDInsight) contains this class or not. - Check for the class
org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDeandorg.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDeas mentioned in the solution.
Solution
Although a JAR file is a binary file, you can still use
grepcommand with-Hrniswitches as below to search for a particular class namegrep -Hrni "org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe" /usr/hdp/current/hive/libIf it couldn't find the class, it will return no output. If it finds the class in a JAR file, it will return the output
Below is the example took from HDInsight 4.x cluster
sshuser@hn0-alters:~$ grep -Hrni "org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe" /usr/hdp/4.1.9.7/hive/lib/ Binary file /usr/hdp/4.1.9.7/hive/lib/hive-exec-3.1.0.4.1-SNAPSHOT.jar matchesFrom the above output, we can confirm that no jar contains the class
org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDeand hive-exec jar containsorg.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe.Try to create the table with row format DerDe as
ROW FORMAT SERDE org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDeThis command will fix the issue. If you've already created the table, you can rename it using the below commands
Hive => ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME SET SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe' Backend DB => UPDATE SERDES SET SLIB='org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe' where SLIB='org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.serde2.MultiDelimitSerDe';
The update command is to update the details manually in the backend DB and the alter command is used to alter the table with the new SerDe class from beeline or Hive.
Hive Backend DB schema compare Script
You can run the following script after completing the migration.
There's a chance of missing few columns in the backend DB, which causes the query failures. If the schema upgrade wasn't happened properly, then there's chance that we may hit the invalid column name issue. The below script fetches the column name and datatype from customer backend DB and provides the output if there's any missing column or incorrect datatype.
The following path contains the schemacompare_final.py and test.csv file. The script is present in "schemacompare_final.py" file and the file "test.csv" contains all the column name and the datatype for all the tables, which should be present in the hive backend DB.
https://hdiconfigactions2.blob.core.windows.net/hiveschemacompare/schemacompare_final.py
https://hdiconfigactions2.blob.core.windows.net/hiveschemacompare/test.csv
Download these two files from the link. And copy these files to one of the head nodes where hive service is running.
Steps to execute the script:
Create a directory called "schemacompare" under "/tmp" directory.
Put the "schemacompare_final.py" and "test.csv" into the folder "/tmp/schemacompare". Do "ls -ltrh /tmp/schemacompare/" and verify whether the files are present.
To execute the Python script, use the command "python schemacompare_final.py". This script starts executing the script and it takes less than five minutes to complete. The above script automatically connects to your backend DB and fetches the details from each and every table, which Hive uses and update the details in the new csv file called "return.csv". After creating the file return.csv, it compares the data with the file "test.csv" and prints the column name or datatype if there's anything missing under the tablename.
Once after executing the script you can see the following lines, which indicate that the details are fetched for the tables and the script is in progressing
KEY_CONSTRAINTS
Details Fetched
DELEGATION_TOKENS
Details Fetched
WRITE_SET
Details Fetched
SERDES
Details Fetched
And you can see the difference details under "DIFFERENCE DETAILS:" line. If there's any difference, it prints
PART_COL_STATS;
('difference', ['BIT_VECTOR', 'varbinary'])
The line with semicolon PART_COL_STATS; is the table name. And under the table name you can find the differences as ('difference', ['BIT_VECTOR', 'varbinary']) if there are any difference in column or datatype.
If there are no differences in the table, then the output is
BUCKETING_COLS;
('difference', [])
PARTITIONS;
('difference', [])
From this output, you can find the column names that are missing or incorrect. You can run the following query in your backend DB to verify once if the column is missing or not.
SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.columns WHERE TABLE_NAME = 'PART_COL_STATS';
In case any of the columns is missed in the table, for example, if we run the queries like insert or insert overwrite then the stats will be calculated automatically and it tries to update the stats table like PART_COL_STATS and TAB_COL_STATS. And if the column like "BIT_VECTOR" is missing in the tables then it will fail with "Invalid column name" error. You can add the column as mentioned in the following commands. As a workaround you can disable the stats by setting the following properties, which can't update the stats in the backend Database.
hive.stats.autogather=false;
hive.stats.column.autogather=false;
To Fix this issue, run the following two queries on backend SQL server (Hive metastore DB):
ALTER TABLE PART_COL_STATS ADD BIT_VECTOR VARBINARY(MAX);
ALTER TABLE TAB_COL_STATS ADD BIT_VECTOR VARBINARY(MAX);
This step avoids the query failures, which fail with "Invalid column name" once after the migration.
Secure Hive across HDInsight versions
HDInsight optionally integrates with Microsoft Entra ID using HDInsight Enterprise Security Package (ESP). ESP uses Kerberos and Apache Ranger to manage the permissions of specific resources within the cluster. Ranger policies deployed against Hive in HDInsight 3.6 can be migrated to HDInsight 4.0 with the following steps:
- Navigate to the Ranger Service Manager panel in your HDInsight 3.6 cluster.
- Navigate to the policy named HIVE and export the policy to a json file.
- Make sure that all users referred to in the exported policy json exist in the new cluster. If a user is referred to in the policy json but doesn't exist in the new cluster, either add the user to the new cluster or remove the reference from the policy.
- Navigate to the Ranger Service Manager panel in your HDInsight 4.0 cluster.
- Navigate to the policy named HIVE and import the ranger policy json from step 2.
Hive changes in HDInsight 4.0 that may require application changes
See Extra configuration using Hive Warehouse Connector for sharing the metastore between Spark and Hive for ACID tables.
HDInsight 4.0 uses Storage Based Authorization. If you modify file permissions or create folders as a different user than Hive, you'll likely hit Hive errors based on storage permissions. To fix, grant
rw-access to the user. See HDFS Permissions Guide.HiveCLIis replaced withBeeline.
Refer to HDInsight 4.0 Announcement for other changes.
Post the migration
Make sure to follow these steps after completing the migration.
Table Sanity
- Recreate tables in Hive 3.1 using CTAS or IOW to change table type instead of changing table properties.
- Keep doAs as false.
- Ensure managed table/data ownership is with “hive” user.
- Use managed ACID tables if table format is ORC and managed non-ACID for non-ORC types.
- Regenerate stats on recreated tables as migration would have caused incorrect stats.
Cluster Health
If multiple clusters share the same storage and HMS DB, then we should enable auto-compaction/compaction threads only in one cluster and disable everywhere else.
Tune Metastore to reduce their CPU usage.
Disable transactional event listeners.
Note
Perform the following steps, only if the hive replication feature not used.
- From Ambari UI, remove the value for hive.metastore.transactional.event.listeners.
- Default Value:
org.apache.hive.hcatalog.listener.DbNotificationListener - New value:
<Empty>
Disable Hive PrivilegeSynchronizer
- From Ambari UI, set hive.privilege.synchronizer = false.
- Default Value:
true - New value:
false
Optimize the partition repair feature
Disable partition repair - This feature is used to synchronize the partitions of Hive tables in storage location with Hive metastore. You may disable this feature if “msck repair” is used after the data ingestion.
To disable the feature add "discover.partitions=false" under table properties using ALTER TABLE. OR (if the feature can't be disabled)
Increase the partition repair frequency.
From Ambari UI, increase the value of “metastore.partition.management.task.frequency” (in seconds).
Note
This change can delay the visibility of some of the partitions ingested into storage.
- Default Value:
60 - Proposed value:
3600
- Default Value:
Advanced Optimizations The following options need to be tested in a lower(non-prod) environment before applying to production.
- Remove the Materialized view related listener if Materialized view isn't used.
- From Ambari UI, add a custom property (in custom hive-site.xml) and remove the unwanted background metastore threads.
- Property name: metastore.task.threads.remote
- Default Value:
N/A (it uses few class names internally) - New value:
org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.txn.AcidHouseKeeperService,org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.txn.AcidOpenTxnsCounterService,org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.txn.AcidCompactionHistoryService,org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.txn.AcidWriteSetService,org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.PartitionManagementTask
Disable the background threads if replication is disabled.
- From Ambari UI, add a custom property (in custom hive-site.xml) and remove the unwanted threads.
- Property name: metastore.task.threads.always
- Default Value:
N/A (it uses few class names internally) - New value:
org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.RuntimeStatsCleanerTask
Query Tuning
- Keep default configs of Hive to run the queries as they're tuned for TPC-DS workloads. Need query level tuning only if it fails or running slow.
- Ensure stats are up to date to avoid bad plan or wrong results.
- Avoid mixing external and managed ACID tables in join type of queries. In such case, try to convert external to managed non-ACID table through recreation.
- In Hive-3, lot of work happened on vectorization, CBO, timestamp with zone etc., which may have product bugs. So, if any query gives wrong results, try disabling vectorization, CBO, map-join etc., to see if that helps.
Other steps to be followed to fix the incorrect results and poor performance after the migration
Issue Hive query gives the incorrect result. Even the select count(*) query gives the incorrect result.
Cause The property “hive.compute.query.using.stats” is set to true, by default. If we set it to true, then it uses the stats, which is stored in metastore to execute the query. If the stats aren't up to date, then it results in incorrect results.
Resolution collect the stats for the managed tables using
alter table <table_name> compute statics;command at the table level and column level. Reference link - https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/hive/statsdev#StatsDev-TableandPartitionStatisticsIssue Hive queries are taking long time to execute.
Cause If the query has a join condition then hive creates a plan whether to use map join or merge join based on the table size and join condition. If one of the tables contains a small size, then it loads that table in the memory and performs the join operation. This way the query execution is faster when compared to the merge join.
Resolution Make sure to set the property "hive.auto.convert.join=true" which is the default value. Setting it to false uses the merge join and may result in poor performance. Hive decides whether to use map join or not based on following properties, which is set in the cluster
set hive.auto.convert.join=true; set hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask=true; set hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask.size=<value>; set hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize = <value>;Common join can convert to map join automatically, when
hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask=true, if estimated size of small table(s) is smaller than hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask.size(default value is 10000000 MB).If you face any issue related to OOM by setting the property
hive.auto.convert.jointo true, then it's advisable to set it to false only for that particular query at the session level and not at the cluster level. This issue might occur if the stats are wrong and Hive decides to use map join based on the stats.
Issue Hive query gives the incorrect result if the query has a join condition and the tables involved has null or empty values.
Cause Sometimes we may get an issue related to null values if the tables involved in the query have lot of null values. Hive performs the query optimization wrongly with the null values involved which results in incorrect results.
Resolution We recommend try setting the property
set hive.cbo.returnpath.hiveop=trueat the session level if you get any incorrect results. This config introduces not null filtering on join keys. If the tables had many null values, for optimizing the join operation between multiple tables, we can enable this config so that it considers only the not null values.Issue Hive query gives the incorrect result if the query has a multiple join conditions.
Cause Sometime Tez produce bad runtime plans whenever there are same joins multiple time with map-joins.
Resolution There's a chance of getting incorrect results when we set
hive.merge.nway.joinsto false. Try setting it to true only for the query, which got affected. This helps query with multiple joins on the same condition, merge joins together into a single join operator. This method is useful if large shuffle joins to avoid a reshuffle phase.Issue' There's an increase in time of the query execution day by day when compared to the earlier runs.
Cause This issue might occur if there's an increase in more numbers of small files. So hive takes time in reading all the files to process the data, which results in increase in execution time.
Resolution Make sure to run the compaction frequently for the tables, which are managed. This step avoids the small files and improves the performance.
Reference link: Hive Transactions - Apache Hive - Apache Software Foundation.
Issue Hive query gives incorrect result when customer is using a join condition on managed acid orc table and managed non-ACID orc table.
Cause From HIVE 3 onwards, it's strictly requested to keep all the managed tables as an acid table. And if we want to keep it as an acid table then the table format must be orc and this is the main criteria. But if we disable the strict managed table property “hive.strict.managed.tables” to false then we can create a managed non-ACID table. Some case customer creates an external ORC table or after the migration the table converted to an external table and they disable the strict managed table property and convert it to managed table. At this point, the table converted to non-ACID managed orc format.
Resolution Hive optimization goes wrong if you join table with non-ACID managed ORC table with acid managed orc table.
If you're converting an external table to managed table,
- Don’t set the property “hive.strict.managed.tables” to false. If you set then you can create a non-ACID managed table but it's not requested in HIVE-3
- Convert the external table to managed table using the following alter command instead of
alter table <table_name> set TBLPROPERTIES ('EXTERNAL'='false');
alter table rt set TBLPROPERTIES ('EXTERNAL'='false', 'transactional'='true');
Troubleshooting guide
HDInsight 3.6 to 4.0 troubleshooting guide for Hive workloads provides answers to common issues faced when migrating Hive workloads from HDInsight 3.6 to HDInsight 4.0.
Further reading
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for