Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Power BI Desktop projects is currently in preview.
Tip
For guidance about how to plan a Power BI development, see Power BI implementation planning.
Power BI Desktop introduces a new way to author, collaborate, and save your projects. When you save your work as a Power BI Project (PBIP), report and semantic model item definitions are saved as individual plain text files in a simple, intuitive folder structure.
Saving your work as a project has the following benefits:
Text editor support - PBIP files are formatted text files containing semantic model and report metadata. These files are publicly documented and human readable. While project files support simple text editing tools like Notepad, it's better to use a code editor like Visual Studio Code (VS Code), which provides a rich editing experience including intellisense, validation, and Git integration.
Folder structure transparency - Separate folders for the semantic model and report, enabling powerful yet simple tasks like copying semantic model tables between projects or reusing report pages. A great choice for creating and reusing development templates.
Source control ready - Open text files, designed for seamless integration with Git, enabling version history and team collaboration. To learn more, see Version control in Git.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) support - Apply CI/CD practices on top of your existing source control systems using PBIP files, incorporating quality gates and automating deployment to production environments. To learn more about CI/CD in Fabric, see Fabric CI/CD workflows.
Programmatic generation and editing item definitions - You can programmatically generate and modify item definition text files, enabling batch operations such as updating all report pages visuals or adding a set of measures to each table. For semantic models, you can use the Tabular Object Model (TOM) client library to deserialize the semantic model metadata, make programmatic modifications, and serialize it back to the files.
Enable preview features
Saving as a Power BI Project in Power BI Desktop is currently in preview, and you must enable it in Preview features.
Go to File > Options and settings > Options > Preview features and check the box next to Power BI Project (.pbip) save option.
Save as a project
If you're working on a new project or you opened an existing Power BI Desktop file (pbix), you can save your work as a Power BI project file (pbip):
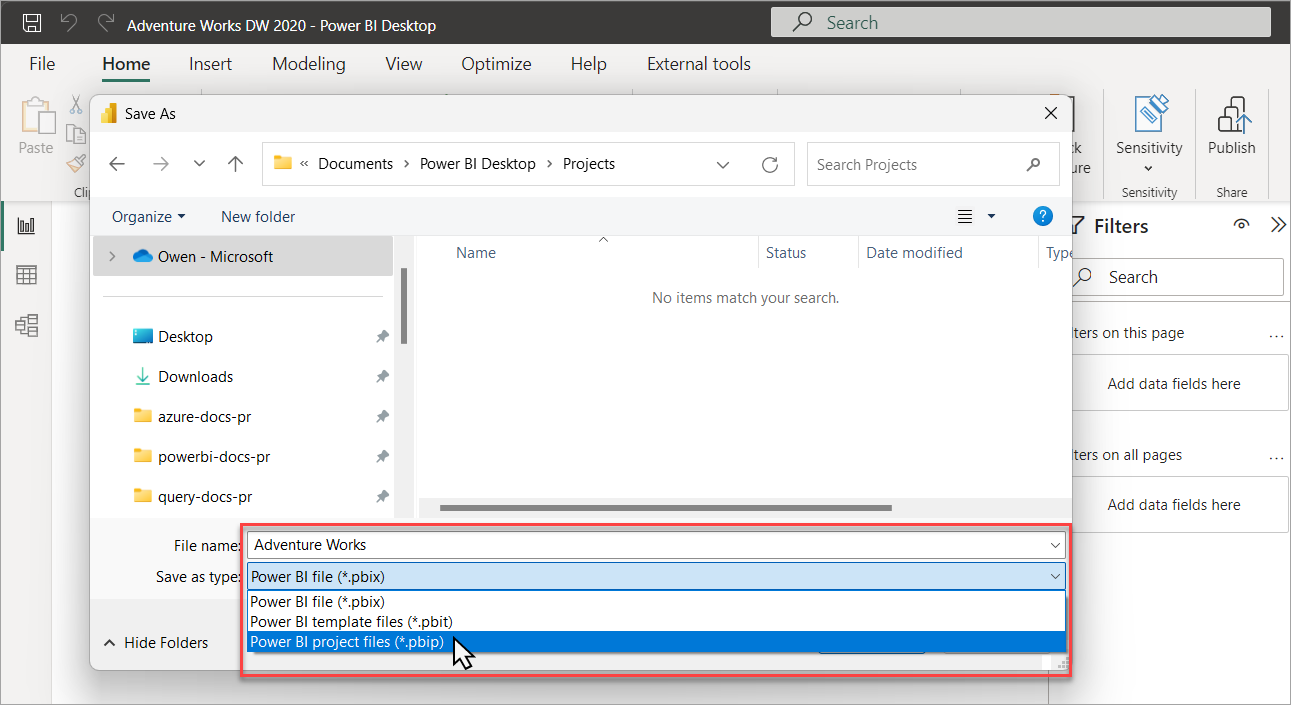
When you save as a project, Power BI Desktop saves report and semantic model items as folders, each containing text files that define the item:
Project/
├── AdventureWorks.Report/
├── AdventureWorks.SemanticModel/
├── .gitignore
└── AdventureWorks.pbip
Let's take a closer look at what you see in your project's root folder:
<project name>.SemanticModel
A collection of files and folders that represent a Power BI semantic model. To learn more about the files and subfolders and files in here, see Project Semantic Model folder.
<project name>.Report
A collection of files and folders that represent a Power BI report. To learn more about the files and subfolders and files in here, see Project report folder.
.gitIgnore
Specifies intentionally untracked files Git should ignore for Power BI Project files, such as the cache.abf and localSettings.json.
Power BI Desktop creates the .gitignore file only if one doesn't already exist in the chosen save folder or parent Git repository.
Default content of .gitignore when saving as PBIP:
**/.pbi/localSettings.json
**/.pbi/cache.abf
<project name>.pbip
The PBIP file contains a pointer to a report folder, opening a PBIP opens the targeted report and model for authoring.
For more information, see the pbip schema document.
Open a Power BI Project
You can open Power BI Desktop from the Power BI Project folder either by opening the pbip file or the pbir file in the report folder. Both options open the report for editing, and the semantic model, if there's a relative reference to a semantic model.
You can save multiple reports and semantic models to the same folder. Having a separate pbip file for each report isn't required because you can open each report directly from the .pbir within the report folder.
project/
├── AdventureWorks-Sales.Report/
│ └── definition.pbir
├── AdventureWorks-Stocks.Report/
│ └── definition.pbir
├── AdventureWorks.SemanticModel/
│ └── definition.pbism
├── .gitignore
└── AdventureWorks.pbip
Navigate to files
After saving as a project, you can see when you're working on a project by looking at the title bar:
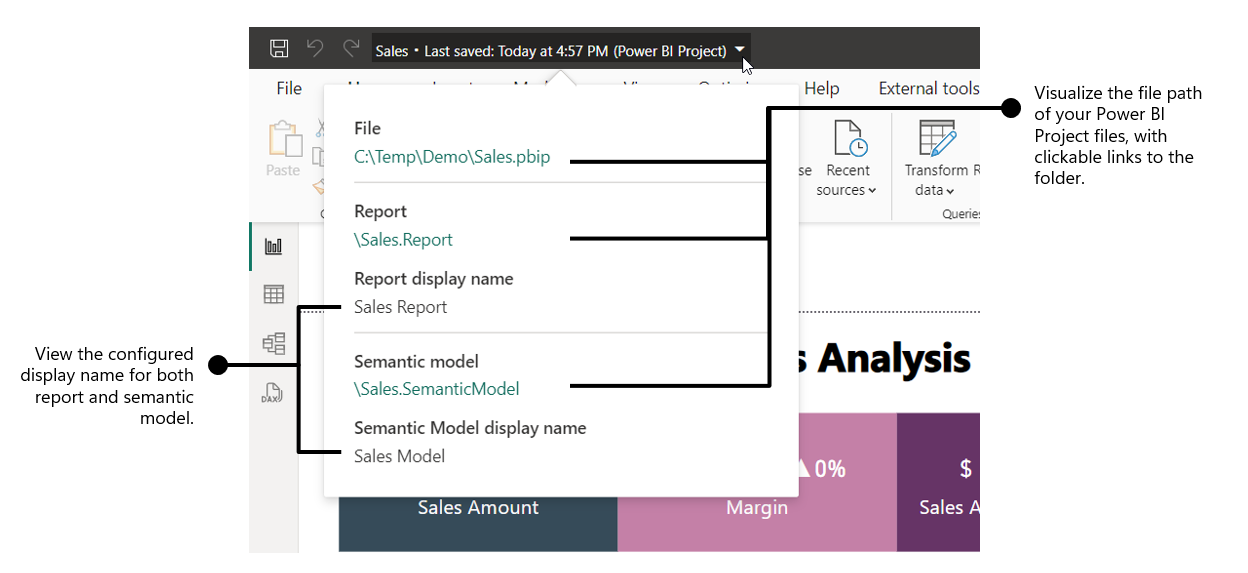
If you select on the title bar, a flyout appears that's specific for Power BI Project. This flyout lets you locate the project files and the display name settings for the report and the semantic model. You can also open the folder in file explorer by clicking on the paths.
Changes outside Power BI Desktop
When saved as a project, you're not forced into making changes to your semantic model and report definitions only in Power BI Desktop. You can use other tools such as VS Code, open-source community tools like Tabular Editor, or even Notepad. However, not every file or change supports editing by external, open-source tools.
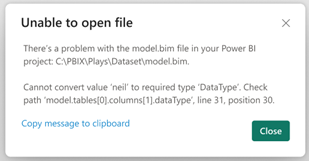
Changes to files or properties outside of Power BI Desktop can cause unexpected errors, or even prevent Power BI Desktop from opening. In those cases, you must resolve the issues in the files before trying to open the project again in Power BI Desktop.
If possible, Power BI Desktop indicates the file and location of error:
Schema details for the following files aren't documented. During preview, changes to these files outside of Power BI Desktop aren't supported:
- Report\
- SemanticModel\
Deploy to Fabric workspace
When working with Power BI project files, you can deploy your content to a Fabric workspace using the following publishing mechanisms:
- Use Fabric Git Integration.
- Use Fabric APIs.
- Use Power BI Desktop publish option.
Note
Publishing through Power BI Desktop publish uses a temporary PBIX file that is published to the service, similar to saving and publishing a PBIX file. Unlike other PBIP deployment options that only deploy metadata, this publishing method deploys both the metadata and the local data cache of the semantic model being edited.
Model authoring
You can make changes to the semantic model definition by using external tools in two ways:
- By connecting to Power BI Desktop's Analysis Service (AS) instance with external tools.
- By editing TMDL metadata in the
/definitionfolder using VS Code or another external tool.
All semantic model metadata is accessible to read. Write operations are fully supported, however, be aware that modifying the metadata outside of Power BI Desktop may result in unexpected behavior or, in rare cases, lead to inconsistencies within the model. Use caution when making changes through external tools.
Keep in mind:
Any changes to open files made outside Power BI Desktop requires a restart for those changes to be shown in Power BI Desktop. Power BI Desktop isn't aware of changes to project files made by other tools.
Automatic date tables created by Power BI Desktop shouldn't be changed by using external tools.
If the semantic model has the Auto date/time feature enabled, and you create a new datetime column outside of Power BI Desktop, the local date table isn't automatically generated.
Semantic models - such as composite models or Direct Lake - can include objects and properties sourced from other models or data sources. When customizing these properties or removing synced objects, Power BI requires the
changedPropertiesproperty and thePBI_RemovedChildrenannotation to be set. These indicators mark the changes as user customizations, ensuring they are preserved during the next schema synchronization with the data source. To learn more, see Lineage tags for Power BI semantic models.Any expression edits outside of Power BI Desktop in a project with unappliedChanges.json are lost when those changes are applied.
JSON file schemas
Most project files contain metadata in JSON format. Corresponding JSON schemas can be used for validation and documentation.
With JSON schemas, you can:
- Learn about configurable properties.
- Use inline JSON validation provided by the code editor.
- Improve authoring with syntax highlighting, tooltips, and autocomplete.
- Use external tools with knowledge of supported properties within project metadata.
Use VS Code to map JSON schemas to the files being authored. JSON schemas for project files are provided in the json-schemas Git repo.
Considerations and limitations
- Power BI Desktop isn't aware of changes made with other tools or applications. Changes made by using external tools require you to restart Power BI Desktop before those changes are shown.
- Sensitivity labels aren't supported with Power BI projects.
- Diagram view is ignored when editing models in the Service.
- When saving a PBIP, be aware that the maximum path length for project files is limited to 260 characters by default on Windows. Since PBIP files are stored as sub-folders and files, long object names such as table names can cause the total path length to exceed this limit, resulting in errors during save operations. To mitigate this risk, use a short folder path as the root location for your PBIP.
- In Power BI Desktop, you can't save as a PBIP directly to OneDrive and SharePoint. You can use Save As to save files to a locally synced OneDrive folder; however, this may cause file syncing issues, potentially leading to failed save operations in Power BI Desktop.
- When editing PBIP files outside of Power BI Desktop, they should be saved using UTF-8 without BOM encoding.
- Report Linguistic Schema (report page synonyms) isn't supported with Power BI projects.
- Power BI Desktop uses CRLF as end-of-line. To avoid problems in your diffs, configure Git to handle line endings by enabling autocrlf.
- Power BI Projects is currently not supported in Microsoft Power BI Desktop version optimized for Power BI Report Server.
- It's not possible to get and set Row-level security role members using Fabric REST API
- It's not possible to get and set incremental refresh partitions using Fabric REST API. However, it does export a single partition using the query defined in the refresh policy.
Frequently asked questions
Question: Looking at semantic model and report item folder definitions only a few files are marked as required, what happens if I delete them?
Answer: Power BI Desktop automatically creates them when you save as a project (PBIP).
Question: Is Power BI Desktop aware of changes I make to the Power BI Project files from an external tool or application?
Answer: No. Any change made to the files requires Power BI Desktop to be restarted to reflect those changes.
Question: If I convert a PBIX to a PBIP, can I convert it back to PBIX?
Answer: Yes. You can save a PBIX as a PBIP, or save a PBIP as a PBIX.
Question: Can I convert PBIX into PBIP and vice-versa programmatically?
Answer: No. You can only convert a PBIX into a PBIP and vice-versa using Power BI Desktop's File > Save as.
Question: Can I deploy a Power BI Desktop project to Azure Analysis Services (AAS) or SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS)?
Answer: No. Power BI Desktop project report definitions aren't supported in AAS and SSAS. And model definitions use an enhanced metadata unique to Power BI. For AAS and SSAS projects, use Microsoft Visual Studio for model authoring, Git, and Azure DevOps integration.
Question: Why isn't there a *.pbip file when I connect my Fabric workspace to Git? How can I edit my report and semantic model in Power BI Desktop?
Answer: The PBIP file is optional and simply serves as a shortcut to the report folder. You can open both the report and the semantic model for editing in Power BI Desktop by opening the definition.pbir file located in the report folder.