Enable Federal Information Process Standard (FIPS) for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) node pools
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-2 is a US government standard that defines minimum security requirements for cryptographic modules in information technology products and systems. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) allows you to create Linux and Windows node pools with FIPS 140-2 enabled. Deployments running on FIPS-enabled node pools can use those cryptographic modules to provide increased security and help meet security controls as part of FedRAMP compliance. For more information on FIPS 140-2, see Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140.
Prerequisites
- Azure CLI version 2.32.0 or later installed and configured. Run
az --versionto find the version. For more information about installing or upgrading the Azure CLI, see Install Azure CLI.
Note
AKS Monitoring Addon supports FIPS enabled node pools with Ubuntu, Azure Linux, and Windows starting with Agent version 3.1.17 (Linux) and Win-3.1.17 (Windows).
Limitations
- FIPS-enabled node pools have the following limitations:
- FIPS-enabled node pools require Kubernetes version 1.19 and greater.
- To update the underlying packages or modules used for FIPS, you must use Node Image Upgrade.
- Container images on the FIPS nodes haven't been assessed for FIPS compliance.
- Mounting of a CIFS share fails because FIPS disables some authentication modules. To work around this issue, see Errors when mounting a file share on a FIPS-enabled node pool.
Important
The FIPS-enabled Linux image is a different image than the default Linux image used for Linux-based node pools. To enable FIPS on a node pool, you must create a new Linux-based node pool. You can't enable FIPS on existing node pools.
FIPS-enabled node images may have different version numbers, such as kernel version, than images that aren't FIPS-enabled. The update cycle for FIPS-enabled node pools and node images may differ from node pools and images that aren't FIPS-enabled.
Create a FIPS-enabled Linux node pool
Create a FIPS-enabled Linux node pool using the
az aks nodepool addcommand with the--enable-fips-imageparameter.az aks nodepool add \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --cluster-name myAKSCluster \ --name fipsnp \ --enable-fips-imageNote
You can also use the
--enable-fips-imageparameter with theaz aks createcommand when creating a cluster to enable FIPS on the default node pool. When adding node pools to a cluster created in this way, you still must use the--enable-fips-imageparameter when adding node pools to create a FIPS-enabled node pool.Verify your node pool is FIPS-enabled using the
az aks showcommand and query for the enableFIPS value in agentPoolProfiles.az aks show \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --query="agentPoolProfiles[].{Name:name enableFips:enableFips}" \ -o tableThe following example output shows the fipsnp node pool is FIPS-enabled:
Name enableFips --------- ------------ fipsnp True nodepool1 FalseList the nodes using the
kubectl get nodescommand.kubectl get nodesThe following example output shows a list of the nodes in the cluster. The nodes starting with
aks-fipsnpare part of the FIPS-enabled node pool.NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION aks-fipsnp-12345678-vmss000000 Ready agent 6m4s v1.19.9 aks-fipsnp-12345678-vmss000001 Ready agent 5m21s v1.19.9 aks-fipsnp-12345678-vmss000002 Ready agent 6m8s v1.19.9 aks-nodepool1-12345678-vmss000000 Ready agent 34m v1.19.9Run a deployment with an interactive session on one of the nodes in the FIPS-enabled node pool using the
kubectl debugcommand.kubectl debug node/aks-fipsnp-12345678-vmss000000 -it --image=mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/runtime-deps:6.0From the interactive session output, verify the FIPS cryptographic libraries are enabled. Your output should look similar to the following example output:
root@aks-fipsnp-12345678-vmss000000:/# cat /proc/sys/crypto/fips_enabled 1
FIPS-enabled node pools also have a kubernetes.azure.com/fips_enabled=true label, which deployments can use to target those node pools.
Create a FIPS-enabled Windows node pool
Create a FIPS-enabled Windows node pool using the
az aks nodepool addcommand with the--enable-fips-imageparameter. Unlike Linux-based node pools, Windows node pools share the same image set.az aks nodepool add \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --cluster-name myAKSCluster \ --name fipsnp \ --enable-fips-image \ --os-type WindowsVerify your node pool is FIPS-enabled using the
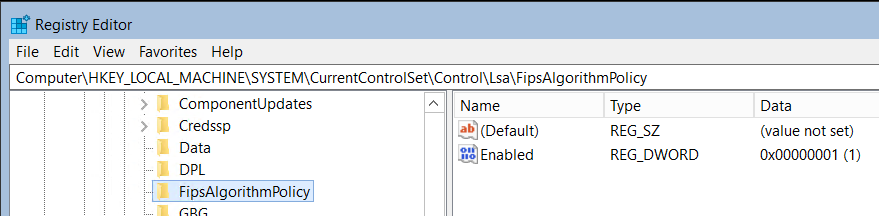
az aks showcommand and query for the enableFIPS value in agentPoolProfiles.az aks show \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --query="agentPoolProfiles[].{Name:name enableFips:enableFips}" \ -o tableVerify Windows node pools have access to the FIPS cryptographic libraries by creating an RDP connection to a Windows node in a FIPS-enabled node pool and check the registry. From the Run application, enter
regedit.Look for
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\FIPSAlgorithmPolicyin the registry.If
Enabledis set to 1, then FIPS is enabled.
FIPS-enabled node pools also have a kubernetes.azure.com/fips_enabled=true label, which deployments can use to target those node pools.
Next steps
To learn more about AKS security, see Best practices for cluster security and upgrades in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for