Understanding role-based access to your Azure Quantum workspace
Learn about the different security principals and roles you can use to manage access to your Azure Quantum workspace.
Azure role-based access control (RBAC)
Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) is the authorization system you use to manage access to Azure resources, such as a workspace. To grant access, you assign roles to a security principal.
Security principal
A security principal is an object that represents a user, group, service principal, or managed identity.
| Security principal | Definition |
|---|---|
| User | A user account that signs in to Azure to create, manage, and use resources. |
| Group | A group of users. Used to manage users that need the same access and permissions to resources. |
| Service principal | A user identity for an application, service, or platform that needs to access resources. |
| Managed identity | An automatically managed identity in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for applications to use when connecting to resources that support Azure AD authentication. |
Role
When you grant access to a security principal, you assign a built-in role or create a custom role. The most commonly used built-in roles are Owner, Contributor, and Reader.
| Role | Access level |
|---|---|
| Owner | Grants full access to manage all resources, including the ability to assign roles in Azure RBAC. |
| Contributor | Grants full access to manage all resources, but doesn't allow you to assign roles in Azure RBAC. |
| Reader | View all resources, but doesn't allow you to make any changes. |
Scope
Roles are assigned at a particular scope. Scope is the set of resources that the access applies to. Scopes are structured in a parent-child relationship. Each level of hierarchy makes the scope more specific. The level you select determines how widely the role is applied. Lower levels inherit role permissions from higher levels. You can assign roles at four levels of scope: management group, subscription, resource group, or resource.
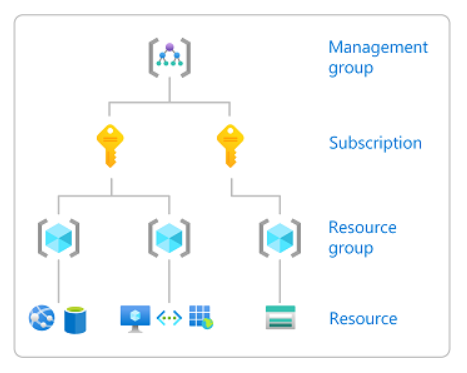
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
| Management group | Helps you manage access, policy, and compliance for multiple subscriptions. All subscriptions in a management group automatically inherit the conditions that are applied to the management group. You may need a management group if your organization has multiple subscriptions. |
| Subscription | Logically associates user accounts with the resources that they create. A user account is a user identity and one or more subscriptions. A subscription represents a grouping of Azure resources. An invoice is generated at the subscription scope. You must have an account with an active subscription to create Azure resources. For subscription options, see Create an Azure Quantum workspace. |
| Resource group | A container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. The resource group includes those resources that you want to manage as a group. For example, the following resources are required to run applications in Azure Quantum:
|
| Resource | An instance of a service that you can create, such as a workspace or storage account. |
Note
Because access can be scoped to multiple levels in Azure, a user may have different roles at each level. For example, someone with owner access to a workspace may not have owner access to the resource group that contains the workspace.
Role requirements for creating a workspace
When you create a new workspace, you first select a subscription, resource group, and storage account to associate with the workspace. Your ability to create a workspace depends on the levels of access you have, starting at the subscription scope. To view your authorization for various resources, see Check your role assignments.
Subscription Owner
Subscription owners can create workspaces using either the Quick create or Advanced create options. You can either choose a resource group and storage account that already exist under the subscription or create new ones. You also have the ability to assign roles to other users.
Subscription Contributor
Subscription contributors can create workspaces using the Advanced create option.
To create a new storage account, you must select an existing resource group that you're an owner of.
To select an existing storage account, you must be an owner of the storage account. You must also select the existing resource group that the storage account belongs to.
Subscription contributors can't assign roles to others.
Subscription Reader
Subscription readers can't create workspaces. You can view all resources created under the subscription, but can't make any changes or assign roles.
Check your role assignments
Check your subscriptions
To see a list of your subscriptions and associated roles:
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- Under the Azure services heading, select Subscriptions. If you don't see Subscriptions here, use the search box to find it.
- The Subscriptions filter beside the search box may default to Subscriptions == global filter. To see a list of all your subscriptions, select the Subscriptions filter and deselect the "Select only subscriptions selected in the..." box. Then select Apply. The filter should then show Subscriptions == all.

Check your resources
To check the role assignment you or another user has for a particular resource, see Check access for a user to Azure resources.
Assign roles
To add new users to a workspace, you must be an owner of the workspace. To grant access to 10 or less users to your workspace, see Share access to your Azure Quantum workspace. To grant access to more than 10 users, see Add a group to your Azure Quantum workspace.
To assign roles for any resource at any scope, including the subscription level, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal.
Troubleshooting
For solutions to common issues, see Troubleshoot Azure Quantum: Creating an Azure Quantum workspace.
When you create a resource in Azure, such as a workspace, you're not directly the owner of the resource. Your role is inherited from the highest scope role that you're authorized against in that subscription.
When you create new role assignments, they can sometimes take up to one hour to take effect over cached permissions across the stack.