Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO: All API Management tiers
In Azure API Management, API publishers can change API behavior through configuration by using policies. This article describes how to use policies.
Policies are a collection of statements that are run sequentially on the request or response of an API. API Management provides more than 75 policies out of the box that you can configure to address common API scenarios like authentication, rate limiting, caching, and transformation of requests or responses. For a complete list, see API Management policy reference.
Popular policies include:
- Format conversion from XML to JSON.
- Call rate limiting to restrict the number of incoming calls from a developer.
- Filtering of requests that come from certain IP addresses.
Policies are applied inside the gateway between the API consumer and the managed API. Although the gateway receives requests and forwards them, unaltered, to the underlying API, a policy can apply changes to both the inbound request and the outbound response.
Understanding policy configuration
Policy definitions are simple XML documents that describe a sequence of statements to apply to requests and responses. To help you configure policy definitions, the portal provides these options:
- A guided, form-based editor to simplify configuring popular policies without coding XML
- A code editor where you can insert XML snippets or edit XML directly
For more information about configuring policies, see Set or edit policies.
The policy XML configuration is divided into inbound, backend, outbound, and on-error sections. This series of specified policy statements runs in order for a request and a response. Here's what it looks like:
<policies>
<inbound>
<!-- statements to be applied to the request go here -->
</inbound>
<backend>
<!-- statements to be applied before the request is forwarded to
the backend service go here -->
</backend>
<outbound>
<!-- statements to be applied to the response go here -->
</outbound>
<on-error>
<!-- statements to be applied if there's an error condition go here -->
</on-error>
</policies>
For policy XML examples, see API Management policy snippets repo.
Error handling
If an error occurs during the processing of a request:
- Any remaining steps in the
inbound,backend, oroutboundsections are skipped. - Execution jumps to the statements in the
on-errorsection.
By placing policy statements in the on-error section, you can:
- Review the error by using the
context.LastErrorproperty. - Inspect and customize the error response by using the
set-bodypolicy. - Configure what happens if an error occurs.
For more information, see Error handling in API Management policies.
Policy expressions
Unless the policy specifies otherwise, policy expressions can be used as attribute values or text values in any of the API Management policies. A policy expression is one of the following:
- A single C# statement enclosed in
@(expression) - A multi-statement C# code block, enclosed in
@{expression}, that returns a value
Each expression has access to the implicitly provided context variable and an allowed subset of .NET Framework types.
Policy expressions provide a sophisticated means to control traffic and modify API behavior without requiring you to write specialized code or modify backend services. Some policies are based on policy expressions, such as Control flow and Set variable.
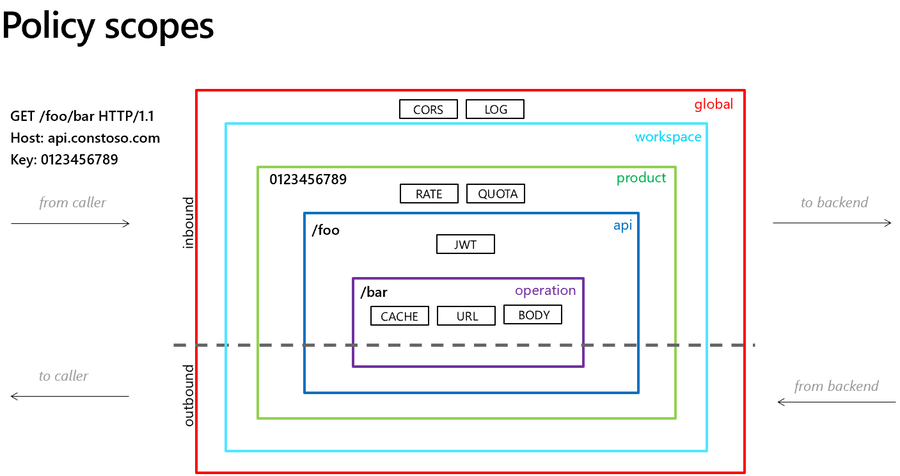
Scopes
API Management enables you to define policies at the following scopes, presented here from broadest to narrowest:
- Global (all APIs)
- Workspace (all APIs associated with a selected workspace)
- Product (all APIs associated with a selected product)
- API (all operations in an API)
- Operation (a single operation in an API)
When configuring a policy, you must first select the scope at which the policy applies.
Things to know
For fine-grained control for different API consumers, you can configure policy definitions at more than one scope.
Not all policies are supported at each scope and policy section.
When configuring policy definitions at more than one scope, you control policy inheritance and the policy evaluation order in each policy section by placement of the
baseelement.Important
As a best practice, include a
baseelement at the beginning of each policy section to inherit policies from the parent scope. This ensures that any policies defined at a higher level are not inadvertently overridden or ignored. A built-in Azure Policy definition (API Management policies should inherit parent scope policies using <base/>) is available to audit or enforce this best practice.Policies applied to API requests are also affected by the request context, including the presence or absence of a subscription key used in the request, the API or product scope of the subscription key, and whether the API or product requires a subscription.
Note
If you're using an API-scoped subscription, an all-APIs subscription, or the built-in all-access subscription, policies configured at the product scope aren't applied to requests from that subscription.
For more information, see:
GraphQL resolver policies
In API Management, a GraphQL resolver is configured with policies scoped to a specific operation type and field in a GraphQL schema.
- Currently, API Management supports GraphQL resolvers that specify either HTTP API, Azure Cosmos DB, or Azure SQL data sources. For example, you can configure a single
http-data-sourcepolicy with elements to specify a request to (and optionally response from) an HTTP data source. - You can't include a resolver policy in policy definitions at other scopes, such as API, product, or all APIs. The policy also doesn't inherit policies configured at other scopes.
- The gateway evaluates a resolver-scoped policy after any configured
inboundandbackendpolicies in the policy execution pipeline.
For more information, see Configure a GraphQL resolver.
Get Copilot assistance
You can get AI assistance from Copilot to create and edit your API Management policy definitions. You can use Copilot to create and update policies that match your specific requirements without needing to know the XML syntax. You can also get explanations of existing policies. And Copilot can help you translate policies that you might have configured in other API management solutions.
- Azure Copilot provides policy authoring assistance with natural language prompts in the Azure portal. You can author policies in the API Management policy editor and ask Copilot to explain policy sections.
- GitHub Copilot for Azure in Visual Studio Code provides policy authoring assistance in Visual Studio Code, and you can use the Azure API Management Extension for Visual Studio Code to speed up policy configuration. You can prompt Copilot Chat or Copilot Edits with natural language to create and refine policy definitions in place.
Example prompt:
Generate a policy that adds an Authorization header to the request with a Bearer token.
Copilot is powered by AI, so surprises and mistakes are possible. For more information, see Copilot general use FAQs.
Examples
Apply policies specified at different scopes
If you have a policy at the global level and a policy configured for an API, both policies can be applied whenever that particular API is used. API Management allows for deterministic ordering of combined policy statements via the base element.
Example policy definition at API scope:
<policies>
<inbound>
<cross-domain />
<base />
<find-and-replace from="xyz" to="abc" />
</inbound>
</policies>
In the preceding example policy definition:
- The
cross-domainstatement runs first. - The
find-and-replacepolicy runs after any policies at a broader scope.
Note
If you remove the base element at the API scope, only policies configured at the API scope will be applied. Policies configured at product and broader scopes won't be applied.
Use policy expressions to modify requests
The following example uses policy expressions and the set-header policy to add user data to incoming requests. The added header includes the user ID that's associated with the subscription key in the request, and the region where the gateway processing the request is hosted.
<policies>
<inbound>
<base />
<set-header name="x-request-context-data" exists-action="override">
<value>@(context.User.Id)</value>
<value>@(context.Deployment.Region)</value>
</set-header>
</inbound>
</policies>
Related content
For more information about working with policies, see:
- Tutorial: Transform and protect your API
- Policy reference for a full list of policy statements and their settings
- Policy expressions
- Set or edit policies
- Reuse policy configurations
- Policy snippets repo
- Policy playground repo
- Azure API Management policy toolkit
- Get Copilot assistance to create, explain, and troubleshoot policies